Summary
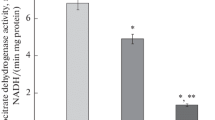
Microquantitative determinations of ADH activity were carried out on the livers of male and female rats. The animals were either starved for 84 h, or starved and then refed with a carbohydrate-rich diet for 6 nights. When the enzyme activity is expressed in μmoles/min/g dry weight, fasting does not appear to alter liver ADH activity, while in starved and subsequently refed rats it is diminished by 20%. Microquantitative measurements of ADH activity in 50–150 ng lyophilized tissue samples, microdissected the whole way along the sinusoidal length, made the computeraided plotting of intra-acinar distribution patterns possible. The results showed that, under the feeding conditions selected, only minor changes in the ADH activity profiles occur in the liver acinus. These are within the range of the standard deviations of the normal mean values. From these results it can be deduced that fasting and refeeding do not lead to specific inhibition or induction of liver ADH activity.—The decrease of ADH activity of total liver (μmol/min) per total body weight in starved rats is obviously the result of a loss of protein which affects the liver cells of all acinar zones almost equally.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bode JC, Thiele D (1975) Hemmung des Äthanolabbaus beim Menschen durch Fasten: Reversibilität durch Fructose-Infusion. Dtsch Med Wochenschr 100:1849–1851
Buehler R, Hess M, von Wartburg JP (1982) Immunohistochemical localization of human liver alcohol dehydrogenase in liver tissue, cultured fibroblasts, and HeLa cells. Am J Pathol 108:89–99
Büttner H (1965) Aldehyd- und Alkoholdehydrogenase-Aktivität in Leber und Niere der Ratte. Biochem Z 341:300–314
Eriksson CJP (1980) Metabolism of acetaldehyde in the liver and gastrointestinal tract. In: Stock C, Sarles H (eds) Alcohol and the gastrointestinal tract. INSERM Colloque, Vol. 95, INSERM, Paris 111–130
Jungermann K, Katz N, Teutsch HF, Sasse D (1977) Possible metabolic zonation of liver parenchyma into glucogenic and glycolytic hepatocytes. In: Thurman R, Williamson J, Drott H, Chance B (eds) Alcohol and aldehyde metabolizing systems. Academic Press, New York, pp 65–77
Jungermann K, Sasse D (1978) Heterogeneity of liver parenchymal cells. Trends Biochem Sci 3:198–202
Jungermann K, Heilbronn R, Katz N, Sasse D (1982) The glucose/glucose-6-phosphate cycle in the periportal and perivenous zone of rat liver. Eur J Biochem 123:383–395
Katz N, Teutsch HF, Jungermann K, Sasse D (1977) Heterogeneous reciprocal localization of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase and of glucokinase in microdissected periportal and perivenous rat liver tissue. FEBS Lett 83:272–276
Leevy CM, Frank O, Leevy CB, Baker H (1985) Nutritional factors in liver disease of the alcoholic. Acta Med Scand (Suppl) 703:67–79
Lowry OH, Passonneau JV (1972) A flexible system of enzymatic analysis. Academic Press, New York London
Lumeng L, Bosron WF, Li TK (1979) Quantitative correlation of ethanol elimination rates in vivo with alcohol dehydrogenase activities in fed, fasted and food-restricted rats. Biochem Pharmacol 28:1547–1551
Maly IP, Sasse D (1983) A technical note on the histochemical demonstration of G6Pase activity. Histochemistry 78:409–411
Maly IP, Sasse D (1985) Microquantitative determination of the distribution patterns of alcohol dehydrogenase activity in the liver of rat, guinea pig and horse. Histochemistry 83:431–436
Morrison GR, Brock FE (1967) Quantitative measurement of alcohol dehydrogenase in the lobule of normal livers. J Lab Clin Med 70:116–120
Nuber R, Teutsch HF, Sasse D (1980) Metabolic zonation in thioacetamide-induced liver cirrhosis. Histochemistry 69:277–288
Rieder H (1981) NADP-dependent dehydrogenases in rat liver parenchyma. III. The description of a liponeogenic area on the basis of histochemically demonstrated enzyme activities and the neutral fat content during fasting and refeeding. Histochemistry 72:579–615
Sasse D (1975) Dynamics of liver glycogen. The topochemistry of glycogen synthesis, glycogen content and glycogenolysis under the experimental conditions of glycogen accumulation and depletion. Histochemistry 45:237–254
Sasse D, Möllinger H, Wimmer M (1983) Antagonistic reaction of the periportal and perivenous zone in the rat liver after castration and estrogen treatment. Histochemistry 79:383–395
Smith ME, Newman HW (1959) The rate of ethanol metabolism in fed and fasting animals. J Biol Chem 234:1544–1551
Teutsch HF (1981) Chemomorphology of liver parenchyma. Prog Histochem Cytochem 14/3. Gustav Fischer, Stuttgart New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This study is part of a dissertation which will be presented to the Phil.-Nat. Faculty of the University of Basel by I.P. Maly
Supported by grants from the “Schweizerische Stiftung für Alkoholforschung”
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maly, I.P., Sasse, D. The effects of starving and refeeding on the intra-acinar distribution pattern of alcohol-dehydrogenase activity in rat liver. Histochemistry 86, 275–279 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00490258
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00490258