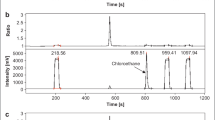
Summary
An analytical procedure was developed which allows the trace determination of Cl−, Br− and I− in different water samples by isotope dilution mass spectrometry within a single reprocessing of the sample. This definitive method has the advantage that the analytical results are relatively accurate. Therefore, this type of analysis is especially suitable as a calibration method. Its application is shown by analysing water samples from a drinking water reservoir, different springs, river and a mineral water. The relative standard deviation for the chloride determination in the lower ppm-range is 0.2–1.6%, for the bromide and iodide analysis in the lower ppb-range it is 0.5–5%. The detection limits of this method — which could be improved by a more precise isotope ratio measurement — are 13 ppb for Cl−, 0.4 ppb for Br− and 0.1 ppb for I−. An analytical comparison for the chloride determination shows good agreement between the mass spectrometric method and ion chromatography. Additionally, an analysis procedure is given which allows the determination of the inorganic iodine species iodide and iodate in water samples by isotope dilution mass spectrometry.
Zusammenfassung
Es wurde ein Verfahren entwickelt, welches es erlaubt, in den verschiedenartigsten Wasserproben Spuren von Cl−, Br− und I− innerhalb einer Probenauf arbeitung durch massenspektrometrische Isotopenverdünnungstechnik zu bestimmen. Dabei hat diese definitive Methode den Vorteil, daß sie vergleichsweise richtige Analysenergebnisse liefert, weshalb sie sich vor allem auch als Eichmethode eignet. Am Beispiel von Talsperren-, Quell-, Flußund Mineralwasser wird die Anwendbarkeit des Verfahrens gezeigt. Dabei werden relative Standardabweichungen für die Chloridbestimmung im unteren ppm-Bereich von 0,2–2 1,6%, für die Analyse von Bromid und Iodid im unteren ppb-Bereich von 0,5–5% erreicht. Die Nachweisgrenze des Verfahrens, die durch genauere Isotopenverhältnismessungen noch verbesserungsfähig ist, liegt momentan bei 13 ppb für Cl−, bei 0,4 ppb für Br− und bei 0,1 ppb für I−. Ein analytischer Vergleich der Chloridbestimmung zeigt gute Übereinstimmung der massenspektrometrischen Ergebnisse mit denjenigen der Ionen-Chromatographie. Zusätzlich wird an einem Beispiel auch ein Verfahren erläutert, welches die Bestimmung der anorganischen Iodspezies Iodid und Iodat in Wässern durch massenspektrometrische Isotopenverdünnungsanalyse erlaubt.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Davis SN, De Wiest RJM (1966) Hydrogeology. Wiley and Sons, New York, p 111
Bunn WW, Haas BB, Deane ER, Kleopfer RD (1975) Environ Lett 10:205
Minear RA, Morrow CM (1983) Report PB 83-256735, Tennessee Water Resources Res Cent, Knoxville, p 290
Jones SD, Spencer CP, Truesdale VW (1982) Analyst 107:1417
Cook JM, Miles DL (1980) Report 80/5, Institute of Geological Sciences, London, p 17
Stoyanov AS, Simeonov VD, Andreev GA (1980) Chim Anal (Sofia) 33:219
Masschelein WJ, Denis M (1981) Water Research 15:857
Stetzenbach KJ, Thompson GM (1983) Ground Water 21:36
Pyen GS, Erdmann DE (1983) Anal Chim Acta 149:355
Heumann KG, Hoffmann R (1978) Adv Mass Spectrom 7:610
Heumann KG, Schindlmeier W (1981) Fresenius Z Anal Chem 306:245
Heumann KG, Schindlmeier W (1982) Fresenius Z Anal Chem 312:595
Persky A, Greene EF, Kuppermann A (1968) J Chem Phys 49:2347
Heumann KG, Baier K, Beer F, Kifmann R, Schindlmeier W (1980) Adv Mass Spectrom 8:318
Schmidt M, Heumann KG, Schindlmeier W, Zeininger H (1985) Fresenius Z Anal Chem 320: 457
Garner EL, Machlan LA, Gramlich JW, Moore LJ, Murphy TJ, Barnes IL (1976) NBS Spec Publ 422:951
Heumann KG, Beer F, Kifmann R (1980) Talanta 27:567
Heumann KG, Beer F, Weiß H (1983) Mikrochim Acta 95
Hoefs J (1973) Stable isotope geochemistry. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, p 43
Holden NE, Martin RL, Barnes IL (1983) Pure Appl Chem 56:675
Heumann KG, Kastenmayer P, Zeininger H (1981) Fresenius Z Anal Chem 306:173
Rössner B, Schwedt G (1983) Fresenius Z Anal Chem 315:197
Rössner B, Schwedt G (1984) Fresenius Z Anal Chem 320: Heft 6
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Vortrag anläßlich des Symposiums Anorganische Anionenanalytik, Regensburg, 19.–21. 9. 1984
Diese Arbeit wurde im Rahmen des DFG-Schwerpunktprogramms „Hydrogeochemische Vorgänge im Wasserkreislauf in der ungesättigten und gesättigten Zone“ finanziell unterstützt.
Herrn Prof. G. Schwedt, Stuttgart, und Herrn Prof. K. H. Wedepohl, Göttingen, danken wir für die gute Zusammenarbeit bei der Bearbeitung dieses Teilthemas im Rahmen des Schwerpunktprogramms.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heumann, K.G., Seewald, H. Gleichzeitige Bestimmung von Cl−, Br− und I− in Wässern durch massenspektrometrische Isotopenverdünnungsanalyse. Z. Anal. Chem. 320, 493–497 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00479819
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00479819