Abstract
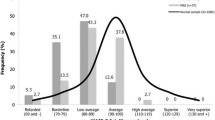
The I.Q. of 129 patients with PMD-D and 27 patients suffering from Werdnig-Hoffmann disease were estimated. Among the patients with PMD-D there was one group without any complicating factors and 3 other groups with additional factors that might influence the intelligence level. Comparing mean values and distribution of I.Q. for all these groups, one can conclude that, besides additional unfavourable pathological and environmental factors in all cases, PMD-D itself causes a small decrease of the I.Q. by about 1 SD. The frequent changes of the EEG record in these patients could reflect involvement of the CNS by the pathological process.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, J. D., Rodgin, D. W.: Mental retardation in association with progressive muscular dystrophy. Amer. J. Dis. Child. 100, 208–211 (1960)
Cohen, H. J., Molnar, F., Taft, L. T.: The genetic relationship of progressive muscular dystrophy (Duchenne type) and mental retardation. Develop. Med. Child. Neurol. 10, 754–765 (1968)
Dubowitz, V.: Intellectual impairment in muscular dystrophy. Arch. Dis. Child. 40, 296–301 (1965)
Hausmanowa-Petrusewicz, I., Askanas, W., Fidziańska, A., Prot, J.: Infantile and juvenile spinal muscular atrophy. J. Neurol. Sci. 6, 269–287 (1968)
Kozicka, A.: Mental development of children with Duchenne type of progressive muscular dystrophy (pol.). Neur. Neurochir. Pol., V (XXI), 4, 523–528 (1971)
Kozicka, A., Prot, J., Wasilewski, R.: Mental retardation in patients with Duchenne progressive muscular dystrophy. J. Neurol. Sci. 14, 209–213 (1971)
Prosser, E. J., Murphy, F. G., Thompson, N. W.: Intelligence and the gene for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Arch. Dis. Child. 44, 221–230 (1969)
Rosman, P. N.: The cerebreal defect and myopathy in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. A comparative clinicopathological study. Neurology (Minneap.) 20, 329–335 (1970)
Wechsler, D.: Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children. Manual. New York: Psychological Corporation 1949
Worden, D., Vignos, P. J.: Intellectual function in childhood progressive muscular dystrophy Pediatrics 29, 968–977 (1962)
Zellweger, H., Hanson, J. W.: Psychometric studies in muscular dystrophy type IIIa (Duchenne). Develop. Med. Child. Neurol. 9, 576–581 (1967)
Zellweger, H., Niedermayer, F.: Central nervous system manifestation in childhood muscular dystrophy. I. Psychometric and electroencephalographic findings. Ann. Pediat. (Basel) 205, 25–33 (1965)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The investigations were carried out as part of an agreement with NIH, Bethesda, USA, No. 05-002-N
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Florek, M., Karolak, S. Intelligence level of patients with the duchenne type of progressive muscular dystrophy (PMD-D). Eur J Pediatr 126, 275–282 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00477054
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00477054