Summary
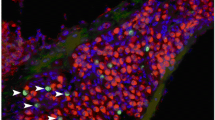
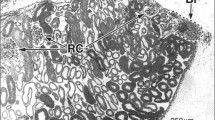
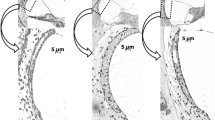
We studied the distribution of wheat germ agglutinin (WGA)-bindable glycoconjugates in the vestibular ampulla of mongolian gerbils. WGA was conjugated with gold particles and applied to Lowicryl K4M sections of the ampulla. WGA-binding sites were found on the cupula and some of the secretory granules and Golgi apparatuses in the supporting cells of the sensory epithelia. The granules were seen to secrete into the endolymphatic space through reticular membrane. It is likely, therefore, that glycoconjugates are glycosylated at the Golgi apparatus in the supporting cells, stored in the granules, and secreted through the reticular membrane into the endolymphatic space to be used as a component of the cupula. The cell membranes of various cells, connective tissue filaments in the perilymphatic space and the cytoplasm of melanocytes were also labeled with WGA-gold.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carlemalm E, Garavito RM, Villinger W (1982) Resin development for electron microscopy and an analysis of embedding at low temperature. J Microbiol 126:123–143
Engstrom H (1972) Macula utriculi and macula sacculi in the squirrel monkey. Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh) [Suppl] 301:75–126
Frens G (1973) Controlled nucleation for the regulation of the particle size in monodisperse gold solution. Nature 241:20–22
Geoghegan WD, Ackerman GA (1977) Adsorption of horseradish peroxidase, ovomucoid and anti-immunoglobulin to colloidal gold for the indirect detection of concanavalin A, wheat germ agglutinin and goat antihuman immunoglobulin G on cell surfaces at the electron microscopic level: a new method, theory and application. J Histochem Cytochem 25:1187–1200
Gil-Loyzaga P, Raymond J, Gabrion J (1985) Carbohydrates detected by lectins in the vestibular organ. Hear Res 18:269–272
Goldstein U, Hayes CE (1983) Carbohydrate-binding proteins of plants and animals. Adv Carbohydr Chem Biochem 35:127–340
Harada Y (1984) The vestibular organs-morphology, physiology and pathology (in Japanese). Nishimura, Niigata
Harada Y, Tagashira N, Takumida M, Suzuki M (1985) Three-dimensional structures of the vestibular sensory epithelia. Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh) 57:517–530
Heinegard D, Paulsson M (1984) Structure and metabolism of proteoglyans. In: Piez KA, Reddi AH (eds) Extracellular matrix biochemistry. Elsevier, New York, pp 277–328
Kimura R (1969) Secretory epithelia linings in the ampullae of the guinea pig labyrinth. Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh) 57:517–530
Lash JW, Vasan NS (1983) Glycosaminoglycans and cartilage. In: Hall BK (ed) Cartilage, vol 1. Structure, function, and biochemistry. Academic Press, New York, pp 215–251
Machino M, Morioka H, Tachibana M (1985) Staining of serous acinar cells of human parotid gland with wheat germ agglutinin-gold complex. Acta Histochem Cytochem 18: 391–394
Peters BP, Ebisu S, Goldstein IJ, Flasher M (1979) Interaction of wheat germ agglutinin with sialic acid. Biochemistry 18:5505–5511
Roth J (1984) Cytochemical localization of terminal N-acetyl-d-galactosamine residue in cellular compartments of intestinal goblet cells: implication for the topology of Oglycosylation. J Cell Biol 98:399–406
Stahle J, Lyttkens L, Larsson B (1981) Some views on medical treatment in Meniere's disease: use of urea and target-seeking drugs. In: Vosteen K-H, Schuknecht H, Pfaltz CR, Wersall J, Kimura RS, Morgenstern C, Juhn SK (eds) Meniere's disease. Thieme, Stuttgart, pp 199–208
Suzuki S, Tsuyama S, Yamamoto N, Murata F (1981) Post-embedding staining of Brunner's gland with lectin-ferritin conjugates. J Histochem Cytochem 29:946–952
Tachibana M, Morioka H, Machino M, Mizukoshi O (1987) Cytochemical localization of specific carbohydrates in the cochlea using wheat germ agglutinin-gold. Hear Res 25:115–119
Tachibana M, Morioka H, Machino M, Yoshimatsu M, Mizukoshi O (1987) Wheat germ agglutinin binding sites in the organ of Corti as revealed by lectin-gold labeling. Hear Res (in press)
Wersäll J (1956) Studies on the structure and innervation of sensory epithelium of the crista ampullaris in the guinea pig. Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh) [Suppl] 126:1–85
Wersäll J, Bagger-Sjöbäck D (1930) Morphologicy of the vestibular sense organ. In: Kornhuber HH (ed) Handbook of sensory physiology, vol VI/1. Springer, Berlin, pp 124–170
Wislocki GB, Ladman AJ (1955) Selective and histochemical staining of the otolithic membranes, cupulae and tectorial membrane of the inner ear. J Anat 78:3–12
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tachibana, M., Morioka, H., Machino, M. et al. Cupulogenesis and glycoconjugates in the labyrinthine ampulla as revealed by WGA-gold labeling. Arch Otorhinolaryngol 244, 112–116 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00458560
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00458560