Summary
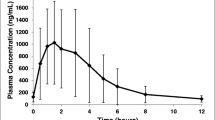
Following the oral administration of either chlorambucil/prednisolone or prednimustine to patients, the plasma levels of free chlorambucil and phenylacetic acid mustard, the β-oxidation product of chlorambucil, were measured using a new high-performance liquid chromatographic (HPLC) assay. This assay permitted the simultaneous detection of the analyzed compounds with a lower limit of detection of 30 ng/ml. The pharmacokinetics of chlorambucil and phenylacetic acid mustard were found to be entirely different when prednimustine was administered as opposed to its components chlorambucil and prednisolone together. After the ingestion of the conjugate, the plasma concentration-time curves of chlorambucil and phenylacetic acid mustard showed a “delayed” pattern compared with those obtained after the administration of the components. The mean area under the concentration-time curves (AUCs) of prednimustine-derived chlorambucil and phenylacetic acid mustard were 25% and 40%, respectively, of the areas obtained after a stoichiometrically equivalent dose of chlorambucil. Free plasma prednimustine could not be detected at any time. This different pharmacokinetic behavior might offer an explanation for the superior therapeutic effects of prednimustine demonstrated by clinical studies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ehrsson H, Wallin I, Nilsson SO, Johannson B (1983) Pharmacokinetics of chlorambucil in man after administration of the free drug and its prednisolone ester (Prednimustine, Leo 1031). Eur J Pharmacol 24: 251–253
Gaver RC, Deeb G, Pittman KA, Issell BF, Mittelman A, Smyth RD (1983) Disposition of orally administered C14-prednimustine in cancer patients. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 11: 139–143
Gunnarson PO, Johansson SA, Svensson L (1984) Cholesterol ester formation by transesterification of chlorambucil: a novel pathway in drug metabolism. Xenobiotica 14: 569–574
Harrap KR, Riches PG, Sellwood SM, Wilkinson R, Koenyves I (1977) Studies on the toxicity and antitumour activity of prednimustine, a prednisolone ester of chlorambucil. Eur J Cancer 13: 873–881
Hartley-Asp B, Gunnarson PO, Liljequist J (1986) Cytotoxicity and metabolism of prednimustine, chlorambucil and prednisolone in a Chinese hamster cell line. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 16: 85–91
Ideström K, Kimby E, Bjoerkholm M, Mellstedt H, Engstedt L, Gahrton G, Johansson B, Killander D, Roberts KH, Stalfelt AM, Uden AM, Wadman B, Waehlby S (1982) Treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia and well-differentiated lymphocytic lymphoma with continuous low- or intermittent high-dose prednimustine versus chlorambucil/prednisolone. Eur J Cancer 18: 1117–1123
Kirdani RY, Murphy GP, Sandberg AA (1978) Some metabolic aspects of a nitrogen mustard of prednisolone. Oncology 35: 47–53
Knospe WH, Loeb V, Huguley CM (1974) Bi-weekly chlorambucil treatment with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Cancer 33: 555–562
Koenyves I, Liljequist J (1976) The steroid group as a carrier of cytotoxic groups. In: Davis W (ed) biological characterisation of human tumours. Elsevier, Amsterdam, p 98
Koenyves I, Nordenskjoeld B, Plym Forshell G, de Schryver A, Westerberg-Larson W (1975) Preliminary clinical and absorption studies with prednimustine in patients with mammary carcinoma. Eur J Cancer 11: 841–844
Loeber J, Mouridsen HT, Christiansen IE, Dobernowsky P, Mattson W, Roerth HT (1983) A phase III trial comparing prednimustine (Leo 1031) to chlorambucil plus prednisolone in advanced breast cancer. Cancer 52: 1570–1576
Musch E, Loos U, Bojar H, Hügl E, Wellens W (1987) Pharmacokinetics of prednimustine and cellular metabolism of prednimustine versus chlorambucil/prednisolone. In: Seeber S, Kaufmann M (eds) Sterecyt/prednimustine: proceedings of a satellite symposoum. AB Leo, Halsingborg, Sweden, pp 19–27
Newell DR, Hart LI, Harrap KR (1979) Estimation of chlorambucil, phenyl acetic mustard and prednimustine in human plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr 164: 114–119
Newell DR, Shepherd CR, Harrap KR (1981) The pharmacokinetics of prednimustine and chlorambucil in the rat. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 6: 85–91
Newell DR, Calvert AH, Harrap KR, McElwain TJ (1983) Studies on the pharmacokinetics of chlorambucil and prednimustine in man. Br J Clin Pharmacol 15: 253–258
Sayed A, van Howe W, Vermeulen A (1981) Prednisolone plasma levels after oral administration of prednimustine. Oncology 38: 351–355
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by the Ministry of Science and Research, Land Nordrhein-Westfalen
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oppitz, M.M., Musch, E., Malek, M. et al. Studies on the pharmacokinetics of chlorambucl and prednimustine in patients using a new high-performance liquid chromatographic assay. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 23, 208–212 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00451643
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00451643