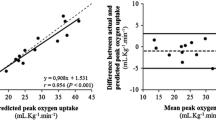
Abstract
The present study was designed to investigate the interrelationships of pulmonary diffusing capacity for CO (\(D_{L_{{\text{CO}}} } \)), pulmonary capillary blood flow (\(\dot Q_c \)), oxygen uptake (\(\dot V_{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}} } \)), and related functions in exercise. Six young adult men were tested on a bicycle ergometer on 9–20 occasions at various intensities of exercise up to the maximal level that could be sustained for 5 min. Measurements at each exercise level included work load (kgm/min), heart rate (HR), minute ventilation (V I ), \(\dot Q_c \), \(D_{L_{{\text{CO}}} } \), and \(\dot V_{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}} } \). Using regression analysis, it was established that \(\dot Q_c \) and D L CO increased linearly with \(\dot V_{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}} } \) throughout the work range in each subject and no tendency toward a plateau was observed. While the maximal value varied from subject to subject, there was no difference between individuals in the coefffcient describing the relationship of D L and \(\dot Q_c \) to \(\dot V_{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}} } \). Combining all subjects, D L was found to increase linearly with \(\dot Q_c \) the regression equation being:
These results suggest that high-intensity short-duration exercise (5 min) is probably not limited by either of these functions in normals.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrew, G. M., Guzman, C. A., Becklake, M. R.: Effect of athletic training on exercise output. J. appl. Physiol. 21, 603–608 (1966)
Asmussen, E., Nielsen, M.: Physiological deadspace and alveolar gas pressures at rest and during muscular exercise. Acta physiol. scand. 38, 1–21 (1956)
Åstrand, P.-O., Cuddy, T. E., Saltin, B., Stenberg, J.: Cardiac output during sub-maximal and maximal work. J. appl. Physiol. 19, 268–274 (1964)
Bartlett, R. G., Jr., Brubach, H. F., Specht, H.: Oxygen cost of breathing. J. appl. Physiol. 12, 413–424 (1958)
Bates, D. V., Boucot, N. G., Dormer, A. E.: The pulmonary diffusing capacity in normal subjects. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 129, 237–252 (1955)
Cohn, J. E., Carroll, D. G., Armstrong, B. W., Shepard, R. H., Riley, R. L.: Maximal diffusing capacity of the lung in normal male subjects of different ages. J. appl. Physiol. 6, 588–597 (1954)
Donevan, R. E., Palmer, W. H., Varvis, C. J., Bates, D. V.: Influence of age on pulmonary diffusing capacity. J. appl. Physiol. 14, 483–492 (1959)
Douglas, F. G. V., Becklake, M. R.: Effect of seasonal training on maximal cardiac output. J. appl. Physiol. 25, 600–605 (1968)
Ekblom, B., Åstrand, P.-O., Saltin, B., Stenberg, J., Wallström, B.: Effect of training on circulatory response to exercise. J. appl. Physiol. 24, 518–528 (1968)
Ekelund, L. G., Holmgren, A.: Central hemodynamics during exercise. Circulat. Res. Supp. 1, 20/21, 33–43 (1967)
Eriksson, B. O., Grimby, G., Saltin, B.: Cardiac output and arterial blood gases during exercise in pubertal boys. J. appl. Physiol. 31, 348–362 (1971)
Faulkner, J. A., Roberts, D. E., Elk, R. L., Conway, J.: Cardiovascular responses to submaximum and maximum effort cycling and running. J. appl. Physiol. 30, 457–461 (1971)
Ferguson, R. J., Faulkner, J. A., Julius, S., Conway, J.: Comparison of cardiac output determined by CO2 rebreathing and dye-dilution methods. J. appl. Physiol. 25, 450–454 (1968)
Filley, G. F., MacIntosh, D. J., Wright, G. W.: Carbon monoxide uptake and pulmonary diffusing capacity in normal subjects at rest and during exercise. J. clin. Invest. 33, 530–539 (1954)
Freyschuss, U., Holmgren, A.: On the variation of D L CO with increasing oxygen uptake during exercise in healthy ordinary untrained young men and women. Acta physiol. scand. 65, 193–206 (1965)
Grimby, G., Nilsson, N. J., Saltin, B.: Cardiac output during submaximal and maximal exercise in active middle-aged athletes. J. appl. Physiol. 21, 1150–1156 (1966)
Hartley, L. H., Grimby, G., Kilbom, A., Nilsson, N. J., Åstrand, I., Bjure, J., Ekblom, B., Saltin, B.: Physical training in sedentary middle-aged and older men. III. Cardiac output and gas exchange at submaximal and maximal exercise. Scand. J. clin. Lab. Invest. 24, 335–344 (1969)
Holmgren, A., Åstrand, P.-O.: D L and the dimensions and functional capacities of the O2 transport system in humans. J. appl. Physiol. 21, 1463–1470 (1966)
Jebavý, P., Widimský, J.: Lung-transfer factor at maximal effort in healthy men. Respiration 30, 297–310 (1973)
Johnson, R. L., Jr., Taylor, H. F., Lawson, W. H., Jr.: Maximal diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide. J. clin. Invest. 44, 349–355 (1965)
Magel, J. R., Andersen, K. L.: Pulmonary diffusing capacity and cardiac output in young trained Norwegian swimmers and untrained subjects. Med. Sci. Sports 1, 131–139 (1969)
Mitchell, J. H., Sproule, B. J., Chapman, C. B.: The physiological meaning of the maximal oxygen intake test. J. clin. Invest. 37, 538–547 (1958)
Newman, F., Smalley, B. F., Thomson, M. L.: Effect of exercise, body and lung size on CO diffusion in athletes and nonathletes. J. appl. Physiol. 17, 649–655 (1962)
Quellet, Y., Poh, S. C., Becklake, M. R.: Circulatory factors limiting maximal aerobic exercise capacity. J. appl. Physiol. 27, 874–880 (1969)
Reuschlein, P. S., Reddan, W. G., Burpee, J., Gee, J. B. L., Rankin, J.: Effect of physical training on the pulmonary diffusing capacity during submaximal work. J. appl. Physiol. 24, 152–158 (1968)
Riley, E. L., Shepard, R. H., Cohn, J. E., Carroll, D. G., Armstrong, B. W.: Maximal diffusing capacity of the lungs. J. appl. Physiol. 6, 573–587 (1954)
Shepard, R. H., Varnauskas, E., Martin, H. B., White, H. A., Permutt, S., Cotes, J. E., Riley, R. L.: Relationship between cardiac output and apparent diffusing capacity of the lung in normal men during treadmill exercise. J. appl. Physiol. 13, 205–210 (1958)
Simmons, R., Shepard, R. J.: Measurements of cardiac output in maximum exercise. Application of an acetylene rebreathing method to arm and leg exercise. Int. Z. angew. Physiol. 29, 159–172 (1971)
Turino, G. M., Bergofsky, E. H., Goldring, R. M., Fishman, A. P.: Effect of exercise on pulmonary diffusing capacity. J. appl. Physiol. 18, 447–456 (1963)
Williams, C. G., Bredell, G. A. G., Wyndham, C. H., Stryd9om, N. B., Morrison, J. F., Peter, J., Fleming, P. W., Ward, J. S.: Circulatory and metabolic reactions to work in heat. J. appl. Physiol. 17, 625–638 (1962)
Zedda, S.: Steady-state diffusing capacity for CO during exercise in normal subjects. Respiration 30, 127–131 (1973)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Andrew, G.M., Baines, L. Relationship of pulmonary diffusing capacity (D L ) and cardiac output (\(\dot Q_c \)) in exercise. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 33, 127–137 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00449514
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00449514