Abstract
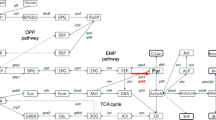
In Rhodopseudomonas capsulata the enzymes of the Entner-Doudoroff pathway and the Embden-Meyerhof pathway have been examined. Fructose-grown cells contained inducible activities of phosphoenolpyruvate-fructosephospho-transferase and 1-phosphofructokinase and only low levels of fructokinase and 6-phosphofructokinase. Although fructose-grown cells contained, in addition, all the enzymes of the Entner-Doudoroff pathway together with fructose-1,6-diphosphatase and phosphoglucose isomerase, the Entner-Doudoroff pathway was not operative in fructose catabolism and served only the degradation of glucose. The functional separation of glucose and fructose catabolism via the Entner-Doudoroff and a modified Embden-Meyerhof pathway, respectively, was confirmed by different approaches:
-
1.
Radiorespirometric experiments with glucose and fructose labelled in positions 1, 2, 3+4 and 6 have been carried out. The pattern of 14CO2-evolution from position-labelled glucose was characteristic for the Entner-Doudoroff pathway, that from position-labelled fructose for the Embden-Meyerhof pathway.
-
2.
In the presence of arsenite up to 50% of glucose-and fructose-carbon was excreted as pyruvate. Using 1-14C-glucose, 86% of the pyruvate was labelled in the carboxyl group, whereas using 1-14C-fructose only 19% of the pyruvate was labelled in the carboxyl group.
-
3.
A glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase-deficient mutant was isolated which lacked a functional Entner-Doudoroff pathway but which was unaltered in its ability to grow on fructose.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EMP:
-
Embden-Meyerhof pathway
- EDP:
-
F.ntner-Doudoroff pathway
- PPP:
-
pentose-phosphate pathway
- PEP-fructose-PTS:
-
phosphoenolpyruvate-fructose-phosphotransferase
- 1-PFK:
-
1-phosphofructokinase
- 6-PFK:
-
6-phosphofructokinase
- PGI:
-
phosphoglucose isomerase
- F-6-P:
-
glucose-6-phosphate
- F-1-P:
-
fructose-1-phosphate
- G-6-P:
-
glucose-6-phosphate
- 6-PG:
-
6-phosphogluconate
- FDP:
-
fructose-1-6-diphosphate
- KDPG:
-
2-keto-3-deoxy-6-phosphogluconate
- DHAP:
-
dihydroxyacetonephosphate
- GAP:
-
glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
- Ru-5-P:
-
ribulose-5-phosphate
- PEP:
-
phosphoenolpyruvate
References
Avigad, G., Englard, S., Pifko, S.: 5-Keto-d-fructose. IV. A specific reduced nicotinamide aldenine dinucleotide phosphate-linked reductase from Gluconobacter cerinus. J. biol. Chem. 241, 373–378 (1966)
Baumann, P., Baumann, L.: Catabolism of d-fructose and d-ribose by Pseudomonas doudoroffii. I. Physiological studies and mutant analysis. Arch. Microbiol. 105, 225–240 (1975)
Bergmeyer, H. U., Gawehn, K., Graßl, M.: Enzyme als biochemische Reagenzien. Phosphogluco-Mutase. In: Methoden der enzymatischen Analyse, Bd. 1 (H. U. Bergmeyer, Hrsg.), S. 532–533. Weinheim: Verlag Chemie 1974
Conrad, R., Schlegel, H. G.: Different pathways for fructose and glucose utilization in Rhodopseudomonas capsulata and demonstration of 1-phosphofructokinase in phototrophic bacteria. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 358, 221–225 (1974)
Dawes, E. A., Holms, W. H.: Metabolism of Sarcina lutea. II. Isotopic evaluation of the routes of glucose utilization. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 29, 82–91 (1958)
Eidels, L., Preiss, J.: Carbohydrate metabolism in Rhodopseudomonas capsulata: Enzyme titers, glucose metabolism, and polyglucose polymer synthesis. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 140, 75–89 (1970)
Ferenci, T., Kornberg, H. L.: Pathway of fructose utilization by Escherichia coli. FEBS-Letters 13, 127–130 (1971)
Ferenci, T., Kornberg, H. L.: The utilization of fructose by Escherichia coli. Properties of a mutant defective in fructose 1-phosphate kinase activity. Biochem. J. 132, 341–347 (1973)
Fraenkel, D. G.: The phosphoenolpyruvate-initiated pathway of fructose metabolism in Escherichia coli. J. biol. Chem. 243, 6458–6463 (1968)
Fromageot, C., Desnuelle, P.: Eine neue Methode zur Bestimmung der Brenztraubensäure. Biochem. Z. 279, 174–183 (1935)
Gay, P., Rapoport, G.: Etude des mutants dépourvus de fructose-1-phosphate kinase chez Bacillus subtilis. C. R. Acad. Sci. (Paris) 271D, 374–377 (1970)
Gee, D. L., Baumann, P., Baumann, L.: Enzymes of d-fructose catabolism in species of Beneckea and Photobacterium. Arch. Microbiol. 103, 205–207 (1975)
Gibson, M. S., Wang, C. H.: Utilization of fructose and glutamate by Rhodospirillum rubrum. Canad. J. Microbiol. 14, 493–498 (1968)
Hanson, T. E., Anderson, R. L.: d-Fructose-1-phosphate kinase, a new enzyme instrumental in the metabolism of d-fructose. J. biol. Chem. 241, 1644–1645 (1966)
Hanson, T. E., Anderson, R. L.: Phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent formation of d-fructose 1-phosphate by a four component phosphotransferase system. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) 61, 269–276 (1968)
Hsu, D. S., Reeves, R. E.: Improved purification of 1-phosphofructokinase from Bacteroides symbiosus and some properties of the enzyme. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 137, 59–64 (1970)
von Hugo, H., Gottschalk, G.: Distribution of 1-phosphofructokinase and PEP: fructose phosphotransferase activity in Clostridia. FEBS-Letters 46, 106–108 (1974)
Kahana, S. E., Lowry, O. H., Schulz, D. W., Passonneau, J. V., Crawford, E. J.: The kinetics of phosphoglucoisomerase. J. biol. Chem. 235, 2178–2184 (1960)
Katz, J., Wood, H. G.: The use of C14O2 yields from glucose-1-and-6-C14 for the evaluation of the pathways of glucose metabolism. J. biol. Chem. 238, 517–523 (1963)
Kistner, A., Kotzé, J. P.: Enzymes of intermediary metabolism of Butyrivibrio fibrisolvens and Ruminococcus albus grown under glucose limitation. Canad. J. Microbiol. 19, 1119–1127 (1973)
Klemme, J. H.: Untersuchungen zur Photoautotrophie mit molekularem Wasserstoff bei neuisolierten schwefelfreien Purpurbakterien. Arch. Mikrobiol. 64, 29–42 (1968)
Landau, B. R., Katz, J.: A quantitative estimation of the pathway of glucose metabolism in rat adipose tissue in vitro. J. biol. Chem. 239, 697–704 (1964)
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., Randall, R. J.: Protein measurement with the Folin-phenol reagent. J. biol. Chem. 193, 265–275 (1951)
Marrs, B., Stahl, C. L., Lien, S., Gest, H.: Biochemical physiology of a respiration-deficient mutant of the photosynthetic bacterium Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) 69, 916–920 (1972)
Muntz, J. A., Carroll, R. E.: A method for converting glucose to fructose. J. biol. Chem. 235, 1258–1260 (1960)
Newsholme, E. A., Robinson, J., Taylor, K.: A radiochemical enzymatic activity assay for glycerol kinase and hexokinase. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 132, 338–346 (1967)
Patni, N. J., Alexander, J. K.: Catabolism of fructose and mannitol in Clostridium thermocellum: Presence of phosphoenolpyruvate: fructose phosphotransferase, fructose-1-phosphate kinase, phosphoenolpyruvate: mannitol phosphotransferase, and mannitol-1-phosphate dehydrogenase in cell extracts. J. Bact. 105, 226–231 (1971)
Pfennig, N., Lippert, K. D.: Über das Vitamin B12-Bedürfnis phototropher Schwefelbakterien. Arch. Mikrobiol. 55, 245–256 (1966)
Probst, I., Schlegel, H. G.: Studies on a Gram-positive hydrogen bacterium, Nocardia opaca strain 1b. II. Enzyme formation and regulation under the influence of hydrogen or fructose as growth substrates. Arch. Mikrobiol. 88, 319–330 (1973)
Robra, K. H.: Optimierung der Begasung in Submerskulturen von Hydrogenomonas eutropha H16 mit H2 und O2 und enzymatische KDPG-Synthese. Diss., Univ. Göttingen (1971)
Saier, M. H., Jr., Feucht, B. U., Roseman, S.: Phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent fructose phosphorylation in photosynthetic bacteria. J. biol. Chem. 246, 7819–7821 (1971)
Sapico, V., Hanson, T. E., Walter, R. W., Anderson, R. L.: Metabolism of d-fructuse-6-phosphate kinase and d-fructose-1,6-diphosphatase. J. Bact. 96, 51–54 (1968)
Sawyer, M. H., Baumann, P., Baumann, L., Berman, S. M., Cánovas, J. L., Berman, R. H.: Pathways of d-fructose catabolism in species of Pseudomonas. Arch. Microbiol. 112, 49–55 (1977)
Sobel, M. E., Krulwich, T. A.: Metabolism of d-fructose by Arthrobacter pyridinolis. J. Bact. 113, 907–913 (1973)
Szymona, M., Doudoroff, M.: Carbohydrate metabolism in Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. J. gen. Microbiol. 22, 167–183 (1960)
Thauer, R. K., Rupprecht, E., Jungermann, K.: Separation of 14C-formate from CO2-fixation metabolites by isoionic-exchange chromatography. Analyt. Biochem. 38, 461–468 (1970)
du Toit, P. J., Potgieter, D. J. J., de Villiers, V.: A study of the properties of 1-phosphofructokinase isolated from Clostridium pasteurianum. Enzymologia 43, 285–300 (1972)
Vincente, M., Cánovas, J. L.: Glucolysis in Pseudomonas putida: Physiological role of alternative routes from the analysis of defective mutants. J. Bact. 116, 908–914 (1973)
Wang, C. H., Stern, J., Gilmour, C. M., Klungsoyr, s., Reed, D. J., Bialy, J. J., Christensen, B. E., Cheldelin, V. H.: Comparative study of glucose catabolism by the radiorespirometric method. J. Bact. 76, 207–216 (1958)
Wilkerson, L. S., Eagon, R. G.: Transport of citric acid by Aerobacter aerogenes. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 149, 209–221 (1972)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Conrad, R., Schlegel, H.G. Different degradation pathways for glucose and fructose in Rhodopseudomonas capsulata . Arch. Microbiol. 112, 39–48 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00446652
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00446652