Summary
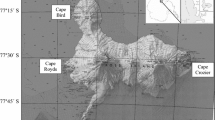
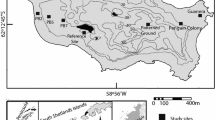
The microbial activity of guano samples from an age sequence of penguin rookery sites and adjacent areas at Cape Bird, Antarctica, was examined. Field moist and artificially moistened samples were buried at the sites (4°C) and duplicate samples incubated in the hut (10°C). Samples were then frozen and transported to New Zealand. Gas from above the frozen samples was analysed for CO2 using gas chromatography. The samples were thawed and further incubated at 25°C. Microbial activity in the guano depended on the degree of penguin influence and was low in the field moist samples from all sites incubated both ‘in situ’, in the hut and at 25°C. In contrast microbial activity was higher in samples with added water, and very high in guano incubated at 25°C. Under favourable moisture and temperature conditions there may be rapid breakdown of penguin guano, but averaged over a year the estimated annual loss of carbon is less than 0.5% of the total carbon present.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baross JA, Morita RY (1978) Life at low temperatures: ecological aspects. In: Kushner DJ (ed) Microbial life in extreme environments. Academic Press, London New York
Blakemore LC, Searle PL, Daly BK (1977) Methods for chemical analysis of soils. N Z Soil Bureau Sci Rep 10A
Boyd WL, Boyd JW (1963) Soil microorganisms of the McMurdo Sound area, Antarctica. Appl Microbiol 11:116–121
Boyd WL, Rothenburg I, Boyd JW (1970) Soil microorganisms at Paradise Harbour, Antarctica. Ecology 51:1040–1045
Cameron RE (1971) Antarctic soil microbial and ecological investigations. In: Quam LO (ed) Research in the Antarctic. Am Assoc Adv Sci No 93, Washington DC, pp 137–169
Cameron RE (1972) Microbial and ecologic investigations in Victoria Valley, Southern Victoria Land, Antarctica. Antarct Res Ser 20:195–260
Cameron RE, Conrow HP (1969) Antarctic Dry Valley soil microbial incubation and gas composition. Antarct J US 4:28–33
Camcron RE, King J, David C (1968) Soil microbial and ecological studies in Southern Victoria Land. Antarct J US 3:121–123
Campbell IB, Claridge GGC (1966) A sequence of soils from a penguin rookery, Inexpressible Island, Antarctica. NZ J Sci 9:361–372
Claridge GGC Campbell IB, Stout JD, Dutch ME (1971) The occurrence of soil organisms in the Scott Glacier region, Queen Maud Range, Antarctica. NZ J Sci 14:306–312
Douglas LA, Tedrow JCF (1959) Organic matter decomposition rates in Arctic soils. Soil Sci 88:305–312
Flint EA, Stout JD (1960) Microbiology of some soils from Antarctica. Nature (London) 188:767–768
Hubbard JS, Cameron RE, Miller AB (1968) Soil studies — Desert Microflora. XV. Analysis of Antarctic Dry Valley soils by cultural and radiorespirometric methods. JPP Space Progr Summary 3:37–52
Ino Y, Oshima Y, Kanda H, Matsuda T (1981) Soil respiration in the vicinity of Syowa Station, Antarctica. I. Relationships between soil respiration rate and water content or nitrogen content. Antarct Rec 70:31–39
MacFadyen A (1973) Inhibitory effects of carbon dioxide on microbial activity in soil. Pedobiologia 13:140–149
Miwa T (1976) Anaerobic bacteria of Antarctica — isolation of Clostridia from the soil around Syowa Station. Mem Natl Inst Polar Res E32:56–63
Orchard VA, Cook FJ (1983) Relationship between soil respiration and soil moisture. Soil Biol Biochem (in press)
Ross DJ (1972) Effects of freezing and thawing of some grassland topsoils on oxygen uptakes and dehydrogenase activities. Soil Biol Biochem 4:115–117
Rudolph ED (1966) Terrestrial vegetation of Antarctica: past and present studies. Antarct Res Ser 8:109–124
Sieburth J McN (1963) Bacterial habitats in the Antarctic environment. In: Oppenheimer CH (ed) Symposium on marine microbiology. CC Thomas, Springfield Ill, pp 533–548
Soulides DA, Allison FE (1961) Effect of dyring and freezing soils on carbon dioxide production, available mineral nutrients, aggregation and bacterial population. Soil Sci 91:291–298
Speir TW, Heine JC (1982) Penguin guano, decomposition and influence of soil development. Soil Bureau Rec 83:1–39
Syroechkovsky, EE (1959) The role of animals in primary soil formation under conditions of pre-polar region of the globe (exemplified by the Antarctic). Zool Zh Ukr 38:1770–1775
Ugolini FC (1972) Ornithogenic soils of Antarctica. Antarct Res Ser 20:181–193
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Orchard, V.A., Corderoy, D.M. Influence of environmental factors on the decomposition of penguin guano in Antarctica. Polar Biol 1, 199–204 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00443188
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00443188