Abstract
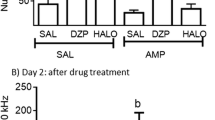
The hypothesis that yawning and suppression of exploration, induced by low doses of dopamine agonists, are mediated by stimulation of dopamine autoreceptors was tested by studying the influence of amphetamine on these behavioural models and on extracellular levels of dopamine sampled by microdialysis. Behaviour was measured in a holeboard apparatus. A low dose of amphetamine (0.2 mg/kg) caused slight activation of habituated rats. The same dose of amphetamine completely counteracted the decrease in extracellular dopamine levels caused by pergolide (0.02 mg/kg) and, instead, elevated the dopamine levels to 300% above baseline. The same or higher doses of amphetamine (0.5–1.0 mg/kg) did not completely antagonise suppression of exploration or yawning induced by apomorphine (0.05 mg/kg) or pergolide (0.02 mg/kg). The results suggest that both yawning and suppression of exploration induced by low doses of dopamine agonists are not mediated by dopamine autoreceptors, since these behaviours could be elicited when the extracellular levels of dopamine were elevated above baseline. The alternative hypothesis that these behaviours are mediated by sensitive post-synaptic receptors is suggested. It was also found that combined treatment with SCH 23390 (0.05 mg/kg) and amphetamine (2 mg/kg) induced yawning, which further supports the new hypothesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aghajanian GK, Bunney BS (1973) Central dopaminergic neurons: neurophysiological identification and responses to drugs. In: Snyder S, Usdin E (eds) Frontiers in catecholamine research. Pergamon Press, New York, pp 643–648.
Brown F, Campbell W, Mitchell PJ, Randall K (1985) Dopamine autoreceptors and the effects of drugs on locomotion and dopamine synthesis. Br J Pharmacol 84:853–860.
Carlsson A (1975) Receptor-mediated control of dopamine metabolism. In: Usdin E, Snyder S (eds) Pre- and postsynaptic receptors. Dekker, New York, pp 49–63.
Carroll JB, Curtis GC, Kokman E (1977) Paradoxical response to dopamine agonists in tardive dyskinesia. Am J Psychiatry 134:785–789.
Corsini GU, DelZompo M, Manconi S, Piccardi MP, Onali PL, Mangoni A, Gessa GL (1977) Evidence for dopamine receptors in the human brain mediating sedation and sleep. Life Sci 20:1613–1618.
Cutler NR, Jeste DV, Kaufman CA, Karoum F, Schran HF, Wyatt RJ (1984) Low dose bromocriptine: a study of acute effects in chronic medicated schizophrenics. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 8:277–283.
DiChiara G, Porceddu ML, Vargiu L, Argiolas A, Gessa GL (1976) Evidence for dopamine receptors mediating sedation in the mouse brain. Nature 264:564–565.
Dourish CT, Cooper SJ (1985) Behavioural evidence for the existence of dopamine autoreceptors. TINS 7:18.
Franebo L-O, Hamberger B (1971) Drug induced changes in the release of 3H-monoamines from field-stimulated rat brain slices. Acta Physiol Scand [Suppl] 371:35–44.
Gower AJ, Berendsen HHG, Princen MM, Broekkamp CLE (1984) The yawning-penile erection syndrome as a model for putative dopamine autoreceptor activity. Eur J Pharmacol 103:81–89.
Kehr W, Carlsson A, Lindqvist M, Magnusson T, Atack C (1972) Evidence for receptor mediated feedback control of striatal tyrosine hydroxylase activity. J Pharm Pharmacol 24:744–747.
Lehman J, Briely M, Langer SZ (1981) Characterization of dopamine autorcceptors and 3H spiperone binding sites in vitro with classical and novel dopamine agonists. Eur J Pharmacol 88:11–26.
Lindefors N (1987) Brain tachykinins and their interaction with dopamineric transmission. Thesis, Department of Pharmacology, Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, Sweden
Ljungberg T, Ungerstedt U (1976) Automatic registration of behaviour related to dopamine and noradrenaline transmission. Eur J Pharmacol 36:181–188.
Ljunberg T, Ungerstedt U (1978) A method for simultaneous recording of eight behavioural parameters related to monoamine neurotransmission. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 8:483–489.
Lognoni R, Spina L, DiChiara G (1987) Permissive role of D-1 receptor stimulation by endogenous dopamine for the expression of postsynaptic D-2 mediated behavioural responses. Yawning in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 134:163–173.
Mailman RB, Schultz DW, Lewis MH, Staples L, Rollema H, Deharen DL (1984) SCH 23390: a selective D1 dopamine antagonist with potent D2 behavioural actions. Eur J Pharmacol 101:159–160.
Meller E, Helmer-Matyjek R, Bohmaker K, Adler CH, Friedhoff AJ, Goldstein M (1986) Receptor reserve at striatal dopamine autoreceptors: implications for selectivity of dopamine agonists. Eur J Pharmacol 123:311–314.
Meltzer HY, Kolakowska T, Robertson A, Tricou BJ (1983) Effect of low-dose bromocriptine in treatment of psychosis: the dopamine autoreceptor stimulation strategy. Psychopharmacology 81:37–41.
Mogilnicka E, Klimek V (1977) Drugs affecting dopamine neurons and yawning behaviour. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 7:303–305.
Morelli M, Langoni R, Spina L, DiChiara G (1986) Antagonism of apomorphine-induced yawning by SCH 23390: evidence against the dopamine autoreceptor hypothesis. Psychopharmacology 89:259–260.
Protais P, Dubuc I, Costentin J (1983) Pharmacological characteristics of dopamine receptors involved in the dual effect of dopamine agonists on yawning behaviour in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 94:271–280.
Puech AJ, Simon P, Chermat R, Boissier JR (1974) Profil neuropsychopharmacologique de l'apomorphine. J Pharmacol (Paris) 5:241–254.
Pugh MT, O'Boyle KM, Molloy AG, Waddington JL (1985) Effects of the putative D-1 antagonist SCH 23390 on stereotyped behaviour induced by the D-2 agonist RU 24213. Psychopharmacology 87:308–312.
Scheel-Krüger J (1986) The syndrome of sedation and yawning behaviour in the rat is dependent on postsynaptic dopamine D-2 receptors. Psychopharmacology 89:S32.
Serra G, Collu M, Gessa GL (1986) Dopamine receptors mediating yawning: are they autoreceptors. Eur J Pharmacol 120:187–192.
Sharp T, Zetterström T, Ungerstedt U (1986) An in vivo study of dopamine release and metabolism in rat brain regions using intracerebral dialysis. J Neurochem 47:113–122.
Sharp T, Zetterström T, Ljungberg T, Ungerstedt U (1987) A direct comparison of amphetamine induced behaviours and regional brain dopamine release in the rat using intracerebral dialysis. Brain Res 401:322–330.
Skirboll LR, Grace AA, Bunney BS (1979) Dopamine auto- and postsynaptic receptors: Electrophysiologic evidence for differential sensitivity to dopamine receptors. Science 206:80–82.
Smith RC, Tamminga C, Davies JM (1977) Effect of apomorphine on schizophrenic symptoms. J Neural Transm 40:171–176.
Ståhle L (1987) Pharmacological studies on behavioural changes induced by dopamine agonists in the rat: a multivariate approach. Thesis, Department of Pharmacology, Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, Sweden
Ståhle L, Ungerstedt U (1984) Assessment of dopamine autoreceptor agonist properties of apomorphine (+)-3-PPP and (-)-3-PPP by recording of yawning behaviour in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 98:307–310.
Ståhle L, Ungerstedt U (1986a) Different behavioural patterns induced by the dopamine agonist apomorphine analysied by multivariate statistics. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 24:291–298.
Ståhle L, Ungerstedt U (1986b) Effects of neuroleptic drugs on the inhibition of exploratory behaviour induced by a low dose of apomorphine: implications for the identity of dopamine receptors. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 25:473–480.
Ståhle L, Ungerstedt U (1987) Reduction of extracellular dopamine levels can be dissociated from suppression of exploratory behaviour in rats. Acta Physiol Scand 130:533–534.
Ståhle L, Ungerstedt U (1988) Discrepancy in the time-course of EMD 23448 induced yawning and reduction of extracellular dopamine. Psychopharmacology (in press)
Ståhle L, Wold S (1986) On the use of some multivariate statistical methods in pharmacological research. J Pharmacol Methods 16:91–110.
Ståhle L, Wold S (1987) Partial least squares analysis with crossvalidation for the two-class problem: a Monte Carlo study. J Chemometrics 1:185–196.
Ståhle L, Wold S (1988) Multivariate data analysis and experimental design in biomedical research. Prog Med Chem 26:300–349.
Ståhle L, Zetterström T, Ungerstedt U (1982) Apomorphine effects on dopamine release and exploratory behaviour. Acta Physiol Scand [Suppl] 508:33.
Starke K, Reimann A, Zumstein A, Hertting G (1978) Effects of dopamine receptor agonists and antagonists on release of dopamine in rabbit caudate nucleus in vitro. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 305:27–36.
Stephenson RP (1956) A modification of receptor theory. Br J Pharmacol 11:379–393.
Strömbom U (1976) Catecholamine receptor agonists: effects on motor activity and tyrosine hydroxylation in mouse brain. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 292:167–176.
Tolosa ES, Sparber SB (1974) Apomorphine in Huntington's chorea: clinical observations and theoretical consideration. Life Sci 15:1371–1380.
Tossman U (1986) Neurochemical studies of amino acids in the rat central nervous system. Thesis, Department of Pharmacology, Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, Sweden
Ungerstedt U (1984) Measurement of neurotransmitter release by intracerebral dialysis. In: Marsden CA (ed) Measurement of neurotransmitter release in vivo. Wiley, London, pp 81–105.
Urba-Holmgren R, Holmgren B, Anias J (1982) Pre- and postsynaptic receptors involved in apomorphine-induced yawning. Acta Neurobiol Exp 42:115–125.
Walter J, Roth R (1976) Dopaminergic neurons: an in vivo system for measuring drug interactions with presynaptic receptors. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 296:5–14.
Westfall TC, Besson MJ, Giorguieff MF, Glowinski J (1976) The role of presynaptic receptors in the release and synthesis of 3H-dopamine in slices of rat striatum. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 292:279–287.
Wold H (1982) Soft moedling, the basic design and some extentions. In: Jöreskog KG, Wold H (eds) Systems under indirect observation vol II. North Holland Publ Co Amsterdam, pp 1–54.
Wold S, Ruhe A, Wold H, Dunn III WJ (1984) The collinearity problem in linear regression, the partial least squares (PLS) approach to generalized inverses. SIAM J Stat Comput 5:735–743.
Yamada K, Furukawa T (1980) Direct evidence for involvement of dopaminergic inhibition and cholinergic activation in yawning. Psychopharmacology 67:39–43.
Zetterström T (1986) Pharmacological analysis of central dopaminergic neurotransmission using a novel in vivo brain perfusion method. Thesis, Department of Pharmacology, Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, Sweden
Zetterström T, Ungerstedt U (1984) Effects of apomorphine on the in vivo release of dopamine and its metabolites studied by brain dialysis. Eur J Pharmacol 97:29–36.
Zetterström T, Sharp T, Marsden CA, Ungerstedt U (1983) In vivo measurement of dopamine and its metabolites by intracerebral dialysis: changes after d-amphetamine. J Neurochem 41:1769–1773.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ståhle, L., Ungerstedt, U. Yawning and suppression of exploration in amphetamine-treated rats, incompatibility with the autoreceptor hypothesis. Psychopharmacology 97, 553–560 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00439563
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00439563