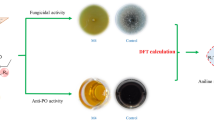
Abstract
Polyamine (PA) biosynthesis inhibitors, difluoromethylornithine (DFMO), difluoromethylarginine (DFMA), methylglyoxal bis-(guanylhydrazone) (MGBG) and bis-(cyclohexylammonium) sulphate (BCHA) have been tested for their effects on colony diameters at different intervals after inoculation of four plant pathogenic fungi (Helminthosporium oryzae, Curvularia lunata, Pythium aphanidermatum and Colletotrichum capsici). All these inhibitors, except DFMA had strongly retarded the growth of four fungi in a dose- and species-dependent fashion, and H. oryzae and C. lunata were found to be most sensitive to the effects of PA inhibitors. P. aphanidermatum and C. capsici were relatively insensitive and required rather high concentrations of inhibitors to get greater inhibition of mycelial growth, except DFMA which had stimulatory effect on the growth of these two fungi. However DFMA had greatly suppressed the growth of H. oryzae and C. lunata. The effect was generally more pronounced with MGBG than with DFMO and BCHA, and 1 mM Put completely prevented the inhibitory effects of 1 and 5 mM DFMO. Analysis of free and conjugated PAs in two sensitive fungi (H. oryzae and C. lunata) revealed that Put was present in highest concentrations followed by Spd and Spm and their levels were greatly reduced by DFMO application, and such inhibitions were totally reversed by exogenously supplied Put; in fact, PA titers were considerably increased by 1 mM Put alone and in combination with 1 mM DFMO. These results suggest that PA inhibitors, particularly DFMO and MGBG may be useful as target-specific fungicides in plants.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barker JHA, Smith TA, Owen WJ. Inhibition of polyamine metabolism in Phytopthora species. Mycol Res 1993; 97: 1358–1362.
Bey P, Danzin C, Jung M. Inhibition of basic amino acid decarboxylases involved in polyamine biosynthesis. In: McCann PP, Pegg AE, Sjoerdsma A (eds), Inhibition of Polyamine Metabolism, Academic Press, San Diego, 1987, pp. 1–31.
Bharti Rajam MV. Effects of the polyamine biosynthesis inhibitor difluoromethylornithine on growth, polyamine levels, chromosome behaviour and polygenic traits in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Ann Bot 1995; 76: 297–301.
Biondi S, Polgrossi I, Bagni N. Effect of polyamine biosynthesis inhibitors on mycelial growth and concentrations of polyamines in Ophiostoma ulmi (Buism) Nannf. New Phytol 1993; 123: 415–419.
Carson CM, McCann PP. Ornithine decarboxylase inhibitors as fungicides for uredinales. Chemical Abstracts (US Patent 4760091), 1988; 109: 185468.
Flores HE, Galston AW. Analysis of polyamines in higher plants by high performance liquid chromatography. Plant Physiol 1982; 69: 701–706.
Galston AW, Weinstein LH. Control of phytopathogens by inhibitors of polyamine biosynthesis. In: Zappia V, Pegg AE (eds), Progress of Polyamine Research: Novel Biochemical, Pharmacological and Clinical Aspects, Plenum Press, New York, 1988, pp. 589–599.
Galston AW, Kaur-Sawhney R. Polyamines in plant physiology. Plant Physiol 1990; 94: 406–410.
Garcia JI, Gomez A, Valle T. Effect of methylglyoxal bis-(guanylhydrazone) on the growth of Ceratocystis ulmi. J Plant Physiol 1991; 138: 625–627.
Garcia JI, Nicolas G, Valle T. Effect of difluoromethylomithine on growth, cell size and germination of Cerotacystis ulmi spores. Plant Sci 1991; 77: 131–136.
Khan AJ, Minocha SC. Biosynthetic arginine decarboxylase in phytopathogenic fungi. Life Sci 1989; 44: 1215–1222.
McCann PP, Pegg AE, Sjoerdsma A. Inhibition of Polyamine Metabolism, Academic Press, San Diego, 1987.
Pfaller MA, Riley J, Gerarden T. Polyamine depletion and growth inhibition of Cryptococcus neoformans by α-difluoromethylomithine and cyclohexylamine. Mycopathol 1990; 112: 27–32.
Rajam MV. Insecticidal activity of inhibitors of polyamine biosynthesis on Spodoptera litura F. larvae. Indian J Exp Biol 1991; 29: 881–882.
Rajam MV. Polyamine biosynthesis inhibitors: New protectants against fungal plant diseases. Curr Sci 1993; 65: 461–469.
Rajam MV, Galston AW. The effects of some polyamine biosynthetic inhibitors on growth and morphology of phytopathogenic fungi. Plant Cell Physiol 1985; 26: 683–692.
Rajam MV, Weinstein LH, Galston AW. Prevention of a plant disease by specific inhibition of fungal polyamine biosynthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1985; 82: 6874–6878.
Rajam MV, Weinstein LH, Galston AW. Kinetic studies on the control of bean rust fungus (Uromyces phaseoli L.) by an inhibitor of polyamine biosynthesis. Plant Physiol 1986; 82: 485–487.
Rajam MV, Weinstein LH, Galston AW. Inhibition of uredospore germination and germ tube growth by inhibitors of polyamine metabolism in Uromyces phaseoli L. Plant Cell Physiol 1989; 30: 37–41.
Rajam MV, Weinstein LH, Galston AW. Effect of polyamine biosynthesis inhibitors on polyamine levels in bean seedlings. Curr Sci 1991; 60: 178–180.
Singhania S, Satyanarayana T, Rajam MV. Polyamines of thermophilic moulds: Distribution and effect of polyamine biosynthesis inhibitors on growth. Mycol Res 1991; 95: 915–917.
Sinha M, Rajam MV. Control of zoopathogenic fungi in vitro by polyamine biosynthesis inhibitors. Indian J Exp Biol 1992; 30: 538–540.
Sjoerdsma A, Schechter PJ. Chemotherapeutic implications of polyamine biosynthesis inhibition. Clin Pharmacol Ther 1984; 35: 287–300.
Slocum RD, Kaur-Sawhney R, Galston AW. The physiology and biochemistry of polyamines in plants. Arch Biochem Biophys 1984; 235: 283–303.
Slocum RD, Bitonti AJ, McCann PP, Feirer RP. DL-α-Difluoromethyl [3,4-3H]arginine metabolism in tobacco and mammalian cells. Inhibition of ornithine decarboxylase activity after arginase-mediated hydrolysis of DL-α-difluoromethylarginine to DL-α-difluoromethylornithine. Biochem J 1988; 255: 197–202.
Smith TA, Barker JHA, Owen WJ. Insensitivity of Septoria tritici and Ustilago maydis to inhibitors of ornithine decarboxylase. Mycol Res 1992; 96: 395–400.
Tabor CW, Tabor H. Polyamines in microorganisms. Microbial Rev 1985; 49: 81–89.
Tiburcio AF, Kaur-Sawhney R, Ingersoli R, Galston AW. Correlation between polyamines and pyrrolidine alkaloids in developing tobacco callus. Plant Physiol 1985; 78: 323–326.
Walters DR, Havis ND, Foster SA, Robins DJ. Control of fungal diseases of arable crops using inhibitors of polyamine biosynthesis. In: Brighton Crop Protection Conference-Pests and Diseases, 1992, pp. 645–657.
Weinstein LH, Galston AW. Prevention of a plant disease by specific inhibition of fungal polyamine biosynthesis using DL-α-difluoromethylornithine. Chemical Abstracts (Int. Publ. No. WO 88 / 02986), 1988; 109: 106548.
West HM, Walters DR. Effects of polyamine biosynthesis inhibitors on growth of Pyrenophora teres, Gaeumannomyces graminis, Fusarium culmorum and Septoria nodurum in vitro. Mycol Res 1989; 92: 453–457.
West HM, Walters DR. Uptake of the polyamine biosynthesis inhibitor α-difluoromethylornithine by the plant pathogenic fungus, Fusarium culmorum. Mycol Res 1991; 95: 621–623.
Zarb J, Walters DR. The effects of polyamine biosynthesis inhibitors on growth, enzyme activities and polyamine concentrations in the mycorrhizal fungus Laccaria proximo. New Phytol 1994; 126: 99–104.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rajam, B., Rajam, M.V. Inhibition of polyamine biosynthesis and growth in plant pathogenic fungi in vitro . Mycopathologia 133, 95–103 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00439120
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00439120