Abstract
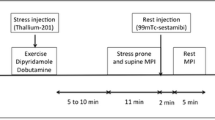
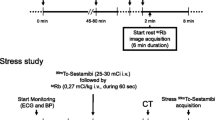
99mTc-hexamibi (methoxy isobutyl isonitrile) is a new 99mTc-hexakis analog that can be used as a myocardial perfusion imaging agent. The purposes of this study were to compare 99mTc-hexamibi to 201Tl-thallous chloride myocardial stress scintigraphy in patients referred for investigation of chest pain and to evaluate the sensitivity of 99mTc-hexamibi in detection of coronary artery disease. One hundred patients were prospectively studied with both 201Tl and 99mTc-hexamibi planar imaging. Sixty five patients had a current coronary angiography. There was a total of 97 significantly (≤70%) stenosed major coronary arteries. 99mTc-hexamibi (25 mCi) study was done within a week of the 201Tl scan with similar double products upon standard treadmil stress testing. Rest studies with 99mTc-hexamibi were obtained 24–48 h after the stress test using the same acquisition parameters and dose. Analysis was performed blind by three observers. The left ventricle was divided into five segments in each image. Analysis of 201Tl and 99mTc-hexamibi results in 1500 left ventricle segments showed an overall agreement in 1326/1500 (88.4%) segments. Correlation between the patient diagnosis on the 201Tl and 99mTc-hexamibi studies showed an agreement in 89 patients (89%). 201Tl revealed myocardial uptake defects in 526 segments, detecting 72 out of 97 (74.2%) significantly stenosed coronary arteries and 99mTc-hexamibi detected 513 segments corresponding to 68 (70.1%) stenosed arteries (no significant statistical difference). In conclusion, these results show a good correlation between 201Tl and 99mTc-hexamibi myocardial imaging in the detection of significant coronary artery disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Campbell S, Holman BL, Kirshenbaum JM (1986) The scintigraphic evaluation of myocardial infarction and regional ventricular performance using technetium-99m-hexakis (t-butylisonitrile) Technetium (I) (TBI): a new myocardial imaging agent. Eur J Nucl Med 12:219–225
Deutsh E, Glavan KA, Sodd VJ, Nishiyama H, Ferguson DL, Lukes SJ (1981) Cationic Tc-99m complexes as potential myocardial imaging agents. J Nucl Med 22:897–907
Dudczak R, Angelberger P, Homan R (1983) Evaluation of 99m-Tc-dichlorobis (1,2-dimethylphosphino) ethane (99mTc-DMPE) for myocardial scintigraphy in man. Eur J Nucl Med 8:513–515
Holman BL, Jones AG, Lister JJ (1984) A new Tc-99m labeled myocardial imaging agent, hexakis (t-butylisonitrile) technetium (I): initial experience in the human. J Nucl Med 25:1350–1355
Holman BL, Sporn V, Jones AG (1987) Myocardial imaging with Technetium-99m CPI: initial experience in the human. J Nucl Med 28:13–18
Jones AG, Abrams MJ, Davison A, Brodack JW, Toothaker AK (1984) Biological studies of a new class of technetium complexes: the hexakis (alkylisonitrile) technetium (I) cations. Int J Nucl Med Biol 11:225–234
Maddahi J, Merz R, Van Train KF, Roy L, Wang C, Berman DS (1987) Tc-99m-MIBI (RP-30) and Tl-201 myocardial perfusion scintigraphy in patients with coronary artery disease: quantitative comparison of planar and tomographic techniques for perfusion defect intensity and defect reversibility. J Nucl Med 28:654 (abstr.)
McKusick KA, Holman BL, Jones AG, Rigo P, Sporn BV, Vosberg AH, Moretti JL (1986) Comparison of 3 Tc-99m isonitriles for detection of ischemic heart disease in humans. J Nucl Med 27:878 (abstr.)
Mousa SA, Cooney JM, Williams SJ (1987) Regional myocardial distribution of RP-30 in animal models of myocardial ischemia and reperfusion. J Nucl Med 28:620 (abstr.)
Nishiyama H, Deutsh E, Adolph RJ (1982) Basal kinetic studies of Tc-99m DMPE as a myocardial imaging agent in the dog. J Nucl Med 23:1093–1101
Okada RD, Boucher CA, Strauss HW, Pohost GM (1980) Exercise radionuclide imaging approaches to coronary artery disease. Am J Cardiol 46:1188–1204
Perez-Balino N, Sporn V, Kuschnir E, Masoli D, Castro R, Troilo A, Mitta A, Camin L (1987) Simultaneous test of ventricular function and myocardial perfusion with Tc-99m RP-30. J Nucl Med 28:662 (abstr.)
Picard M, Dupras G, Taillefer R, Arsenault A, Boucher P (1987) Myocardial perfusion agents: compared biodistribution of 201-Thallium, Tc-99m Tertiary Butyl Isonitrile (TBI) and Tc-99m-Methoxy isobutyl isonitrile (MIBI). J Nucl Med 28:654–655 (abstr.)
Rothendler JA, Okada RD, Wilson RA (1985) Effect of a delay in commencing imaging on the ability to detect transient thallium defects. J Nucl Med 26:880–883
Sands H, Delano ML, Gallagher BM (1986) Uptake of hexakis (t-butylisonitrile) Technetium (I) and hexakis (isopropylisonitrile) Technetium (I) by neonatal rat myocytes and human erythrocytes. J Nucl Med 27:404–408
Sia STB, Holman BL, McKusick KA (1986) The utilization of Tc-99m-TBI as a myocardial perfusion agent in exercise studies: Comparison with Tl-201 thallous chloride and examination of its biodistribution in humans. Eur J Nucl Med 12:333–336
Sia STB, Holman BL, Campbell S, Lister-James J, English RJ, Kronauge JF, Davison A, Jones AG (1987) The utilization of technetium-99m CPI as a myocardial perfusion imaging agent in exercise studies. Clin Nucl Med 12:681–687
Taillefer R, Laflamme L, Dupras G, Picard M, Phaneuf DC, Leveille J (1988) Myocardial perfusion imaging with Tc-99m-methoxy-isobutyl-isonitrile (MIBI): Comparison of short and long time intervals between rest and stress injections. Eur J Nucl Med 13:515–522
Taillefer R, Dupras G, Sporn V, Rigo P, Léveillé J, Boucher P, Perez-Balino N, Camin L, McKusick KA (1989) Myocardial perfusion imaging with a new radiotracer, Tc-99m-Hexamibi (methoxy isobutyl isonitrile): Comparison with Tl-201 imaging. Clin Nucl Med
Williams SL, Mousa SA, Morgan RA, Carroll TR, Maheu LJ (1986) Pharmacology of Tc-99m isonitrile agents with favorable characteristics for heart imaging. J Nucl Med 27:877–878 (abstr.)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taillefer, R., Lambert, R., Dupras, G. et al. Clinical comparison between thallium-201 and Tc-99m-methoxy isobutyl isonitrile (hexamibi) myocardial perfusion imaging for detection of coronary artery disease. Eur J Nucl Med 15, 280–286 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00435466
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00435466