Abstract
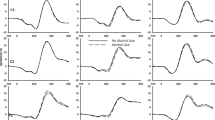
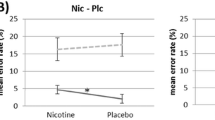
To examine the separate and combined effects of alcohol and tobacco smoking on cortical functioning, the amplitude of the contingent negative variation (CNV) was studied during a simple reaction time task in non-smokers, tobacco-deprived smokers and nondeprived smokers in sessions involving administration of four cigarettes and/or 0.65 g/kg ethyl alcohol. Computer analysis indicated that alcohol and combined alcohol + tobacco significantly reduced the CNV amplitude in non-deprived smokers. Two sub-groups of non-smokers were identified, one showing large pre-drug CNV amplitudes and significant alcohol-induced reductions and the other showing small pre-drug amplitudes and no change in CNV amplitude after alcohol. No significant results were observed with alcohol, tobacco or alcohol + tobacco combined in tobacco-deprived smokers. The results are discussed in relation to previously reported studies which have indicated both synergistic and antagonistic interactions between alcohol and tobacco, and suggestions are forwarded regarding the experimental and clinical significance of tobacco-induced enhancement of CNV amplitude reduction by alcohol.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashton H, Marsh V, Millman J, Rawlins M, Telford R, Thompson J (1978) The use of event-related slow potentials of the brain as a means to analyse the effects of cigarette smoking and nicotine in humans. In: Thornton R (ed) Smoking behaviour: physiological and psychological influences, Churchill Livingstone, Edingburgh, p 54
Beaumanoir A, Ballis T, Nahory A, Genier M (1972) Modification of the contingent negative variation and psycho-galvanic reflex under the effects of alcohol. Rev Electroencephalogr Neurophysiol 2:328–332
Bhagat B, Bayer T, Lind C (1971) Effects of chronic administration of nicotine on drug-induced hypnosis in mice. Psychopharmacologia 21:287–293
Binnie C, Comer A (1978) The effect of cigarette smoking on the contingent negative variation and eye movement. In: Thornton R (ed) Smoking behaviour: Physiological and psychological influences, Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh, p 69
Dreher K, Fraser J (1967) Smoking habits of alcoholic out-patients. Int J Addict 2:259–270
Dreher K, Fraser J (1968) Smoking of alcoholic out-patients. Int J Addict 2:65–80
Drew G, Colquhoun W, Long H (1958) Effects of small doses of alcohol on a skill resembling driving. Br Med J 2:993–999
Eysenck H, O'Connor K (1979) Smoking, arousal and personality. In: Rémond A, Izard C (eds) Electrophysiological effects of nicotine, Elsevier, Amsterdam, p 147
Frankenhaeuser M, Myrsten A, Post B, Johansson G (1971) Behavioral and physiological effects of cigarette smoking in a monotonous situation. Psychopharmacology 22:1–7
Franks H, Hensley V, Hensley W, Starmer G (1976) The relationship between alcohol dosage and performance decrement in humans. J Stud Alcohol 37:284–297
Griffiths R, Bigelow G, Liebson I (1976) Facilitation of human tobacco self-administration by ethanol: A behavioral analysis. J Exp Anal Behav 25:279–292
Joyce D, Steele J, Summerfield A (1972) Chronic ingestion of nicotine modifies the behaviour of mice after ethanol. Br J Pharmacol 45:164–165
Kopell B, Tinklenberg J, Hollister L (1972) Contingent negative variation amplitudes: marihuana and alcohol. Arch Gen Psychiatry 27:809–811
Knott V, Venables P (1977) EEG alpha correlates of non-smokers, smokers, smoking and smoking deprivation. Psychophysiology 14:150–156
Knott V, Venables P (1978) Stimulus intensity control and the cortical-evoked response in smokers and non-smokers. Psychophysiology 15:186–192
Knott V, Venables P (1979) EEG alpha correlates of alcohol consumption in smokers and non-smokers: Effects of smoking and smoking deprivation. J Stud Alcohol 40:247–257
Leigh G, Tong J (1976) Effects of ethanol and tobacco on time judgement. Percept Mot Skills 43:899–903
Leigh G, Tong J, Campbell J (1977) Effects of ethanol and tobacco on divided attention. J Stud Alcohol 38:1233–1239
Ludwig A, Wikler A, Stark L (1974) The first drink: Psychobiological aspects of craving. Arch Gen Psychiatry 30:539–543
Ludwig A, Stark L (1975) Arousal and alcoholism: Psychophysiological response to alcohol. In: Gross M (ed) Alcohol intoxication and withdrawal, Plenum, New York, p 515
Lyon R, Tong J, Leigh G, Clare G (1975) The influence of alcohol and tobacco on the components of choice reaction time. J Stud Alcohol 36:587–596
Moody P (1976) Drinking and smoking behaviour of hospitalized medical patients. J Stud Alcohol 37:1316–1319
Myrsten A, Andersson K (1975) Interaction between effects of alcohol intake and cigarette smoking. Blutalkohol 12:253–265
Myrsten A, Post B, Frankenhaeuser M, Johansson G (1972) Changes in behavioral and physiological activation induced by cigarette smoking in habitual smokers. Psychopharmacologia 27:305–312
Sannita W, Waldeier H, Dolce G (1979) Individual variability in the effects of alcohol on the contingent negative variation in human subjects. Res Commun Psychol Psychiatr Behav 4:97–108
Tecce J, Savignano-Bowman J, Cole J (1978) Drug effects on contingent negative variation and eyeblinks: the distraction-arousal hypothesis. In: Lipton M, Dimascio A, Killman K (eds) Psychopharmacology: A generation of progress, Raven, New York, p 745
Tecce J, Savignano-Bowman J, Meinbresse D (1976) Contingent negative variation and the distinction-arousal hypothesis. Electroenceph Clin Neurophysiol 41:277–286
Thomas C (1973) The relationship of smoking and habits of nervous tension. In: Dunn W (ed) Smoking behaviour: Motives and incentives, Halstead, New York, p 157
Tong J, Knott V, McGraw D, Leigh G (1974) Alcohol, visual discrimination and heart rate: effects of dose, activation and tobacco. J Stud Alcohol 35:1003–1022
Walter W, Cooper R, Aldridge V, McCallum W, Winter A (1964) Contingent negative variation: An electric sign of sensorimotor association and expectance in the human brain. Nature 203:380–384
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Knott, V.J., Venables, P.H. Separate and combined effects of alcohol and tobacco on the amplitude of the contingent negative variation. Psychopharmacology 70, 167–172 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00435309
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00435309