Abstract
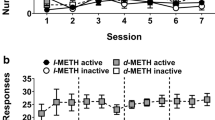
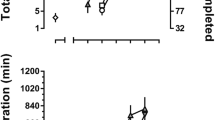
Drug-naive dogs were trained to respond for intravenous infusions of either d-amphetamine, phenmetrazine, or methylphenidate until a stable response rate per 4-hr daily session was achieved. The magnitude of reinforcement (i.e., mg/kg/infusion) was then varied systematically across a wide range for each drug. An inverse relationship between unit dose and number of self-administered infusions per session was seen. Thus, total drug intake per session remained relatively constant and was independent of unit dose. Using a parallel line bioassay design, the relative potencies of d-amphetamine, phenmetrazine, and methylphenidate to maintain self-administration were estimated. By comparing the unit doses of d-amphetamine which yielded the same rate of self-administration it was found that 1 mg of phenmetrazine is equivalent to 0.1 mg of d-amphetamine. It was also determined that 1 mg of methylphenidate is equivalent to 0.75 mg of d-amphetamine. These data indicate the dog can be used to assess the reinforcing properties of psychomotor stimulants.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angrist, B., Gershon, S.: Amphetamine abuse in New York City—1966 to 1968. Semin. Psychiat. 1, 195–207 (1969)
Cappell, H., Le Blanc, A.: Punishment of saccharin drinking by amphetamine in rats and its reversal by chlordiazepoxide. J. comp. physiol. Psychol. 85, 97–104 (1973)
Ellinwood, E., Duarte-Escalante, O.: Chronic methamphetamine intoxication in three species of experimental animals. In: Current Concepts on Amphetamine Abuse, E. H. Ellinwood and S. Cohen, eds., pp. 59–68. Rockville, Maryland: National Institute of Mental Health 1972
Ferris, R. M., Tang, F. L. M., Maxwell, R. A.: A comparison of the capacities of isomers of amphetamine, deoxypipradol, and methylphenidate to inhibit the uptake of tritiated catecholamines into rat cerebral cortex slices, synaptosomal preparations of rat cerebral cortex, hypothalamus and striatum and into adrenergic nerves of rabbit aorta. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 181, 407–416 (1972)
Finney, D. J.: Statistical method in biological assay. London: Griffin 1971
Headlee, C. P., Coppock, H. W., Nichols, J. R.: Apparatus and technique involved in a laboratory method of detecting the addictiveness of drugs. J. Amer. pharm. Ass., sci. Ed. 44, 222–231 (1955)
Inghe, G.: The present status of abuse and addiction to stimulant drugs in Sweden. In: Abuse of Central Stimulants, F. Sjöquist and M. Tottie, eds., pp. 187–225. New York: Raven Press 1969
Jones, B. E., Prada, J.: Relapse to morphine use in dog. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 30, 1–12 (1973)
Kramer, J. C., Fischman, V. S., Littlefield, D. C.: Amphetamine abuse: Pattern and effects of high doses taken intravenously. J. Amer. med. Ass. 201, 305–309 (1967)
Martin, W. R., Sloan, J. W., Sapira, J. D., Jasinski, D. R.: Physiologic, subjective, and behavioral effects of amphetamine, methamphetamine, ephedrine, phenmetrazine, and methylphenidate in man. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 12, 245–258 (1971)
Maxwell, R. A., Plummer, A. J., Ross, S. D., Paytas, J. J., Dennis, A. D.: Antihypertensive effect of the central nervous stimulant, methylphenidate. Arch. int. Pharmacodyn. 112, 26–35 (1957)
Maxwell, R. A., Plummer, A. J., Ross, S. D., Daniel, A. I.: Studies concerning the cardiovascular actions of the central nervous stimulant, methylphenidate. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 123, 22–27 (1958)
Moore, K. E., Carr, L. A., Dominic, J. A.: Functional significance of amphetamine-induced release of brain catecholamines. In: Amphetamines and Related Compounds, E. Costa and S. Garattini, eds., pp. 371–384. New York: Raven Press 1970
National Society for Medical Research: India cuts Rhesus exports; regulations pose additional threats. Nat. Soc med. Res. Bull. 25, 1 (1974)
Pickens, R., Harris, W. C.: Self-administration of d-amphetamine by rats. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 12, 158–163 (1968)
Randrup, A., Munkvad, I.: Stereotyped activities produced by amphetamine in several animal species and man. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 11, 300–310 (1967)
Russo, J. R., Ed.: Amphetamine abuse. Springfield, Ill.: Ch. C. Thomas 1968
Rylander, G.: Addiction to preludin intravenously injected. Excerpta Medica International Congress Series No. 150, Proceedings of the IV World Congress of Psychiatry Madrid, pp. 1363–1365 (5–11 September 1966)
Rylander, G.: Clinical and medici-criminological aspects of addiction to central stimulatory drugs. In: Abuse of Central Stimulants, F. Sjöquist and M. Tottie, eds., pp. 251–273. New York: Raven Press 1969
Schuster, C. R., Thompson, T.: Self administration of and behavioral dependence on drugs. Ann. Rev. Pharmacol. 9, 483–502 (1969)
Thöma, O., Wick, H.: über einige Tetrahydro-1,4-oxazine mit sympathicomimetischen Eigenschaften. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. exp. Path. Pharmak. 222, 540–554 (1954)
Thompson, T., Pickens, R.: Stimulus properties of drugs. New York: A. C. C. 1971
Wallach, M. B., Gershon, S.: The induction and antagonism of central nervous system stimulant-induced stereotyped behavior in the cat. Europ. J. Pharmacol. 18, 22–26 (1972)
Weeks, J. R.: Experimental morphine addiction: Method for automatic intravenous injections in unrestrained rats. Science 138, 143–144 (1962)
Wilner, J. H., Samach, M., Angrist, B., Wallach, M., Gershon, S.: Drug-induced stereotyped behavior and its antagonism in dogs. Commun. Behav. Biol. 5, 135–141 (1970)
Wilson, M., Hitomi, M., Schuster, C.: Psychomotor stimulant self-administration as a function of dosage per injection in the rhesus monkey. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 22, 271–281 (1971)
Yanagita, R., Deneau, G. A., Seevers, M. H.: Physical dependence to opiates in the monkey, with demonstration. Reported to the Committee on Drug Addiction and Narcotics, Ann Arbor, Michigan 1963
Yokel, R. A., Pickens, R.: Drug level of d- and l-amphetamine during intravenous self-administration. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 34, 255–264 (1974)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Risner, M.E., Jones, B.E. Self-administration of CNS stimulants by dog. Psychopharmacologia 43, 207–213 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00429252
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00429252