Abstract
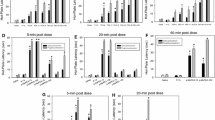
The analgesic effect of etorphine was compared with that of morphine in rats with electrolytic lesions of the nucleus medianus raphe or injected intraventricularly with 6-hydroxydopamine.
The effect of both compounds was markedly reduced in animals with raphe lesions, but not significantly modified in those receiving 6-hydroxy-dopamine. Etorphine and morphine significantly increased the forebrain levels of 5-hydroxyindolacetic acid when administered subcutaneously at doses of 5 mg/kg and 2 μg/kg, respectively. Neither drug significantly affected the forebrain levels of monoamines.
It is concluded that, as for morphine, the integrity of the serotoninergic system in the brain is important for the full analgesic effect of etorphine.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adler, M., Kostowski, W., Recchia, M., Samanin, R.: Anatomical specificity as the critical determinant of the interrelationship between raphe lesions and morphine analgesia. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 32, 39–44 (1975)
Ayhan, I. H.: Effect of 6-hydroxydopamine on morphine analgesia. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 25, 183–188 (1972)
Blane, G. F., Boura, A. L. A., Fitzgerald, A. E., Lister, R. E.: Actions of etorphine hydrochloride (M 99): a potent morphine-like agent. Br. J. Pharmacol. Chemother. 30,11–22 (1967)
Bläsig, J., Herz, A., Reinhold, K., Zieglgänsberger, S.: Development of physical dependence on morphine in respect to time and dosage and quantification of the precipitated withdrawal syndrome in rats. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 33, 19–38 (1973)
Blundell, C., Slater, P.: The effect of 6-hydroxydopamine on the antinociceptive action of analgesics in mice. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 29, 306–307 (1977)
Bowers, M. B., Kleber, H. D.: Methadone increases mouse brain 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid. Nature 229, 134–135 (1971)
Breese, G. R., Traylor, T. D.: Depletion of brain noradrenaline and dopamine by 6-hydroxydopamine. Br. J. Pharmacol. 42, 88–99 (1971)
Buxbaum, D. M., Yarbrough, G. G., Carter, M. E.: Biogenic amines and narcotic effects. I. Modification of morphine-induced analgesia and motor activity after alterations of cerebral amine levels. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 185, 317–327 (1973)
Chang, C. C.: A sensitive method for spectrophotofluorometric assay of catecholamines. Int. J. Neuropharmacol. 3, 643–649 (1964)
Clouet, D. H., Ratner, M.: Catecholamine biosynthesis in brains of rats treated with morphine. Science 168, 854–856 (1970)
Cox, B. M., Ginsburg, M., Osman, O. H.: Acute tolerance to narcotic analgesic drugs in rats. Br. J. Pharmacol. 33, 245–256 (1968)
Curzon, G., Green, A. R.: Rapid method for the determination of 5-hydroxytryptamine and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid in small regions of rat brain. Br. J. Pharmacol. 39, 653–655 (1970)
Elchisak, M. A., Rosecrans, J. A.: Effect of central catecholamine depletions by 6-hydroxydopamine on morphine antinociception in rats. Res. Commun. Chem. Pathol. Pharmacol. 6, 349–352 (1973)
Goodlet, I., Sugrue, M. F.: Effect of acutely administered analgesic drugs on rat brain serotonin turnover. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 29, 241–248 (1974)
Haubrich, D. R., Blake, D. E.: Modification of serotonin metabolism in rat brain after acute or chronic administration of morphine. Biochem. Pharmacol. 22, 2753–2759 (1973)
Koe, B. K., Weissman, A.: p-Chlorophenylalanine: a specific depletor of brain serotonin. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 154, 499–516 (1966)
König, J. F. R., Klippel, R. A.: The rat brain. A stereotaxic atlas of the forebrain and lower parts of the brain stem. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins 1963
Kuschinsky, K., Hornykiewicz, O.: Morphine catalepsy in the rat: relation to striatal dopamine metabolism. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 19, 119–122 (1972)
Laverty, R., Taylor, K. M.: The fluorometric assay of catecholamines and related compounds: improvements and extensions to the hydroxyindole technique. Anal. Biochem. 22, 269–279 (1968)
Lorens, S. A., Yunger, L. M.: Morphine analgesia, two-way avoidance, and consummatory behavior following lesions in the midbrain raphe nuclei of the rat. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2, 215–221 (1974)
Major, C. T., Pleuvry, B. J.: Effect of α-methyl-p-tyrosine, p-chlorphenylalamine, L-β-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)alanine, 5-hydroxytrpptophan and diethyldithiocarbamate on the analgesic activity of morphine and methylamphetamine in the mouse Br. J. Pharmacol. 42, 512–521 (1971)
Nakamura, K., Kuntzman, R., Maggio, A. C., Augulis, V., Conney, A. H.: Influence of 6-hydroxydopamine on the effect of morphine on the tail-flick latency. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 31, 177–189 (1973)
Noble, E. P., Wurtman, R. J., Axelrod, J.: A simple and rapid method for injecting H3-norepinephrine into the lateral ventricle of the rat brain. Life Sci. 6, 281–291 (1967)
Pérez-Cruet, J., Thoa, N. B., Ng, L. K. Y.: Acute effects of heroin and morphine on newly synthesized serotonin in rat brain. Life Sci. 17, 349–362 (1975)
Price, M. T. C., Fibiger, H. C.: Ascending catecholamine systems and morphine analgesia. Brain Res. 99, 189–193 (1975)
Reinhold, K., Bläsig, J., Herz, A.: Changes in brain concentration of biogenic amines and the antinociceptive effect of morphine in rats. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 278, 69–80 (1973)
Samanin, R., Bendotti, C., Gradnik, R., Miranda, F.: The effect of localized lesions of central monoaminergic neurons on morphine analgesia and physical dependence in rats. In: Proceedings of the Thirty-Seventh Annul Scientific Meeting Committee on Problems of Drug Dependence, pp. 690–697. Washington, May 19–21, 1975
Samanin, R., Bernasconi, S.: Effects of intraventricularly injected 6-OH dopamine of midbrain raphe lesion on morphine analgesia. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 25, 175–182 (1972)
Samanin, R., Ghezzi, D., Mauron, C., Valzelli, L.: Effect of midbrain raphe lesion on the antinociceptive action of morphine and other analgesics in rats. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 33, 365–368 (1973)
Samanin, R., Gumulka, W., Valzelli, L.: Reduced effect of morphine in midbrain raphe lesioned rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 10, 339–343 (1970)
Samanin, R., Miranda, F., Mennini, T.: Serotonergic mechanisms of narcotic action. In: Factors affecting the action of narcotics, M. W. Adler, L. Manara, R. Samanin, eds. New York: Raven (in press) 1977
Samanin, R., Valzelli, L.: Increase of morphine-induced analgesia by stimulation of the nucleus raphe dorsalis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 16, 298–302 (1971)
Sasa, M., Munekiyo, K., Osumi, Y., Takaori, S.: Attenuation of morphine analgesia in rats with lesions of the locus coeruleus and dorsal raphe nucleus. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 42, 53–62 (1977)
Sawa, A., Oka, T.: Effects of narcotic analgesics on serotonin metabolism in brain of rats and mice. Jpn. J. Pharmacol. 26, 599–605 (1976)
Sethy, V. H., Pradhan, R. J., Mandrekar, S. S., Sheth, U. K.: Role of brain amines in the analgesic action of meperidine hydrochloride. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 17, 320–326 (1970)
Sewell, R. D. E., Spencer, P. S. J.: Anti-nociceptive activity of narcotic agonists and partial agonists in mice given biogenic amines by intracerebroventricular injection. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 42, 67–71 (1975)
Tenen, S. S.: Antagonism of the analgesic effect of morphine and other drugs by p-chlorophenylalanine, a serotonin depletor. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 12, 278–285 (1968)
Uretsky, N. J., Iversen, L. L.: Effects of 6-hydroxydopamine on catecholamine containing neurones in the brain. J. Neurochem. 17, 269–278 (1970)
Yarbrough, G. G., Buxbaum, D. M., Sanders-Bush, E.: Biogenic amines and narcotic effects. II. Serotonin turnover in the rat after acute and chronic morphine administration. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 185, 328–335 (1973)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miranda, F., Candelaresi, G. & Samanin, R. Analgesic effect of etorphine in rats with selective depletions of brain monoamines. Psychopharmacology 58, 105–109 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00426798
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00426798