Abstract
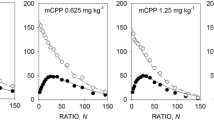
Rats were trained to respond on a geometric progressive ratio schedule until performance was stable. They were then injected with the anticholinergic drug scopolamine at doses of 0.05, 0.1, 0.25, 1.0 and 2.0 mg/kg. Control animals were administered atropine methyl nitrate (1–20 mg/kg). Increasing doses of scopolamine typically produced first an increase, then a decrease in behavior compared with baseline levels, measured by total number of responses, total number of reinforcements, and final completed ratio, per session. Atropine methyl nitrate had no effect on the behaviour of the control animals.
This indicates that the effects of scopolamine are due to its central action. The inverted-U dose-response curve found for scopolamine resembles that found for chlordiazepoxide, phenobarbital, and d-amphetamine on progressive schedules.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berger, B. D.: Conditioning of food aversions by injections of psychoactive drugs. J. comp. physiol. Psychol. 81, 21–26 (1972)
Bignami, G., Rosic, G.: The nature of disinhibitory phenomena caused by central cholinergic (muscarinic) blockade. In: Advances in Neuropsychopharmacology. O. Vinar, Z. Votava and P. B. Bradley, Eds., pp. 481–495. Amsterdam: North-Holland Publ. 1971
Bignami, G., Rosic, G.: Acquisition and performance effects of scopolamine and of treatment withdrawal in avoidance situations. Physiol. Behav. 8, 1127–1134 (1972)
Boren, J. J., Navarro, A. P.: The action of atropine, benactyzine and scopolamine upon FI and FR behavior. J. exp. Anal. Behav. 2, 107–115 (1959)
Carlton, P. L.: Some effects of scopolamine, atropine and amphetamine in three behavioral situations. Pharmacologist 3, 60 (1961)
Carlton, P. L.: Cholinergic mechanisms in the control of behavior by the brain. Psychol. Rev. 70, 19–39 (1963)
Carlton, P. L.: Brain acetylcholine and inhibition. In: Reinforcement and Behavior. J. T. Tapp, Ed., pp. 286–327. London: Academic Press 1969
Dews, P. B.: Studies on behavior: II, The effect of phenobarbitol, methamphetamine and scopolamine on performances in pigeons involving discriminations. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 115, 380–389 (1955)
Findley, J. D.: Preference and switching under concurrent schedules. J. exp. Anal. Behav. 1, 123–144 (1958)
Gaines, S., Thompson, D. M., Woods, J. H.: Escape from a progressive work schedule as functions of deprivation and amount of reinforcement. Virginia J. Sci. 14, 358–359 (1964)
Goldberg, M. E., Ciofalo, V. B.: Alternation of the behavioural effect of amphetamine by agents which modify cholinergic function. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 14, 142–149 (1969)
Hearst, E.: Drug effects on stimulus generalization gradients in the monkey. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 6, 57–70 (1964)
Heise, G. A., Lilie, M. L.: Effects of scopolamine, atropine and amphetamine on internal and external control of responding on non-reinforced trials. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 18, 38–49 (1970)
Heise, G. A., Laughlin, N., Keller, C.: A behavioral and pharmacological analysis of reinforcement withdrawal. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 16, 345–368 (1970)
Herrnstein, R. J.: Effects of scopolamine on a multiple schedule. J. exp. Anal. Behav. 1, 351–358 (1958)
Hodos, W.: Progressive ratio as a measure of reward strength. Science 134, 943–944 (1961)
Hodos, W.: Motivational properties of long duration of rewarding brain stimulation. J. comp. physiol. Psychol. 59, 219–224 (1965)
Hodos, W., Kalman, G.: Effects of increment size and reinforcer volume on progressive ratio performance. J. exp. Anal. Behav. 6, 387–392 (1963)
Kessey, R. E., Goldstein, M. D.: Use of progressive fixed ratio procedures in the assessment of ICS reinforcement. J. exp. Anal. Behav. 11, 293–301 (1968)
Ketchum, J. S., Sidell, F. R., Crowell, E. B.: Atropine, scopolamine and ditran: comparative pharmacology and antagonists in man. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 28, 121–145 (1973)
Khavari, K. A.: Adrenergic-cholinergic involvement in modulation of learned behaviour. J. comp. physiol. Psychol. 74, 281–291 (1971)
Laties, V. G., Weiss, B.: The influence of drugs on behavior controlled by external and internal stimuli. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 152, 388–396 (1966)
Leaf, R. C., Muller, S. A.: Central cholinergic response inhibition during massed free-operant and discrete-trial avoidance acquisition. In: Proceedings of the VIth International Congress of the Colloquium Internationale Neuropsychopharmacologicum, Washington 1966; H. Brill, Ed. Excepta Medica, I.C.S. 129, 1043–1050 (1967)
Leaton, R. N., Kreindler, M.: Effects of physostigmine and scopolamine on operant brightness discrimination in the rat. Physiol. Behav. 9, 121–123 (1972)
McKim, W. A.: The effects of scopolamine on fixed-interval behavior in the rat: a rate-dependency effect. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 32, 255–264 (1973)
Pradham, S. N., Dutta, S. N.: Behavioural effects of arecoline in rats. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 17, 49–58 (1970)
Pradham, S. N., Roth, T.: Comparative behavioural effects of several anticholinergic agents in rats. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 12, 358–366 (1968)
Stein, L.: Anticholinergic drugs and the central control of thirst. Science 139, 46–48 (1963)
Stein, L.: Amphetamine and neural reward mechanism. In: Animal behaviour and drug action. H. Steinberg, Ed. London: Churchill 1964
Stein, L.: Chemistry of purposive behaviour. In: Reinforcement and behaviour. J. Tapp, Ed., pp. 328–355. London: Academic Press 1969
Tapp, J. T.: Cholinergic mechanisms in operant responding. J. comp. physiol. Psychol. 59, 469–472 (1965)
Thompson, D. M.: Enhancement of progressive ratio performance by chlordiazepoxide and phenobarbital. J. exp. Anal. Behav. 17, 287–293 (1972a)
Thompson, D. M.: Effects of d-amphetamine on the “breaking point” of progressive ratio performance. Psychon. Sci. 29, 282–284 (1972b)
Warburton, D. M.: Behavioural effects of central and peripheral changes in acetylcholine systems. J. comp. physiol. Psychol. 68, 56–64 (1969)
Warburton, D. M.: The cholinergic control of internal inhibition: In: Inhibition and learning. R. A. Boakes and M. S. Halliday, Eds., pp. 431–460. London: Academic Press 1972
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Research supported by grants C70/20, 70/44, and 72/24 to N.M.B. Preparation of the paper was aided by a grant to W.J.S. from the Canterbury Branch, N.Z. Psychological Society. An early version of this paper was presented to the Annual Conference, N.Z. Ps. S., Auckland, 1973. Research reported was performed in partial fulfilment of the requirements of the M. Sc. degree by W. J. S.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stewart, W.J., Blampied, N.M. & Hughes, R.N. The effects of scopolamine on performance on a geometric progressive ratio schedule. Psychopharmacologia 38, 55–66 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00421287
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00421287