Summary
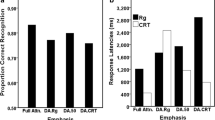
A tentative hypothesis is presented to account for the dissociation of the effects of various centrally-acting drugs and other agents on performance of the Continuous Performance Test (C.P.T.) and the Digit Symbol Substitution Test (D.S.S.T.): L.S.D., secobarbital, pentobarbital meprobamate and phenobarbital produced significantly greater impairment of the D.S.S.T. than of the C.P.T., while chlorpromazine, sleep deprivation and centrencephalic epilepsy had the reverse effect. Psychological, neurophysiological, electroencephalographic and neuropharmacological data were cited which suggested that the tests were affected differently because they are dependent upon the functioning of somewhat different neural organizations which are, in turn, differentially sensitive to the action of various centrally-active agents.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adametz, J. H.: Rate of recovery of functioning in cats with rostral reticular lesions. J. Neurosurg. 16, 85–98 (1959).
Batini, C., G. Moruzzi, M. Palestini, G. F. Rossi and A. Zanchetti: Persistent patterns of wakefulness in the pretrigeminal midpontine preparation. Science 128, 30–32 (1958).
Bjerner, B.: Alpha depression and lowered pulse rate during delayed actions in a serial reaction test. Acta physiol. scand. 19, Suppl. 65 (1949).
Blake, H., R. W. Gerard and N. Kleitman: Factors influencing brain potentials during sleep. J. Neurophysiol. 2, 48–60 (1939).
Bradley, P. B.: The central action of certain drugs in relation to the reticular formation of the brain. In: H. H. Jasper et al. (edits.), Reticular formation of the brain. Boston: Little Brown Co. 1958.
Brazier, M. A. B.: The action of anesthetics on the nervous system. In: E. D. Adrian and H. H. Jasper (edits.), Brain mechanisms and consciousness. Springfield (Ill.): Ch. C. Thomas 1954.
Bremer, F.: Cerveau »isolé« et physiologie du sommeil. C.R. Soc. Biol. (Paris) 118, 1235–1241 (1935).
Caspers, H., u. K. Winkel: Die Beeinflussung der Großhirnrindenrhythmik durch Reizungen im Zwischen- und Mittelhirn bei der Ratte. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol. 259, 334–356 (1954).
Creutzfeldt, O., and R. Jung: Neuronal discharge in the cat's motor cortex during sleep and arousal. In: G. E. W. Wolstenholme and M. O'Connor (edits.), The nature of sleep. Boston: Little Brown Co. 1961.
Dement, W.: The occurrence of low voltage, fast electroencephalogram patterns during behavioral sleep in the cat. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol. 10, 291–296 (1958).
—, and N. Kleitman: Cyclic variations in EEG during sleep and their relation to eye movements, body motility, and dreaming. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol. 9, 673–690 (1957).
Evarts, E. V.: A review of the neurophysiological effects of lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) and other psychotomimetic agents. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 66, 479–495 (1957).
—: Effects of sleep and waking on spontaneous and evoked discharge of single units in visual cortex. Fed. Proc. 19, 828–837 (1960).
—: Effects of sleep and waking on activity of single units in the unrestrained cat. In: G. E. W. Wolstenholme and M. O'Connor (edits.), The nature of sleep. Boston: Little Brown Co. 1961.
—: Activity of neurons in visual cortex of the cat during sleep with low voltage fast activity. J. Neurophysiol. 25, 812–816 (1962).
—, E. Bental, B. Bihari and P. R. Huttenlocher: Spontaneous discharge of single neurons during sleep and waking. Science 135, 726–728 (1962).
Favale, E., C. Loeb, G. F. Rossi and G. Sacco: EEG synchronizing effect of low frequency stimulation of the reticular formation. Abstracts XXI Int. Physiol. Congr. 87 (1959).
French, J. D., R. Hernandez-Peón and R. B. Livingston: Projections from cortex to cephalic brain stem (reticular formation) in monkey. J. Neurophysiol. 18, 74–95 (1955).
—, and H. W. Magoun: Effects of chronic lesions in central cephalic brain stem of monkeys. Arch. Neurol. Psychiat. (Chic.) 68, 591–604 (1952).
—, M. Verzeano and H. W. Magoun: A neural basis of the anesthetic state. Arch. Neurol. Psychiat. (Chic.) 69, 519–529 (1953).
Gantt, W. H.: Effect of alcohol on cortical and subcortical activity measured by the conditioned reflex method. Bull. Johns Hopk. Hosp. 56, 61–83 (1935).
Gliedman, L. H., and W. H. Gantt: The effects of reserpine and chlorpromazine on orienting behavior and retention of conditioned responses. Sth. med. J. (Bgham, Ala.) 49, 880–889 (1956).
Henry, C. E., and W. D. Obrist: The effect of meprobamate on the electroencephalogram. J. nerv. ment. Dis. 126, 268–271 (1958).
Hess, W. R.: The functional organization of the diencephalon. New York: Grune & Stratton 1957.
Hubel, D. H.: Single unit activity in striate cortex of unrestrained cats. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 147, 226–238 (1959).
Huttenlocher, P. R.: Effects of state of arousal on click responses in the mesencephalic reticular formation. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol. 12, 819–827 (1960).
—: Evoked and spontaneous activity in single units of medial brain stem during natural sleep and waking. J. Neurophysiol. 24, 451–468 (1961).
Jasper, H. H.: Diffuse projection systems: the integrative action of the thalamic reticular system. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol. 1, 405–419 (1949).
—: Recent advances in our understanding of ascending activities of the reticular system. In: H. H. Jasper et al. (edits.), Reticular formation of the brain. Boston: Little Brown Co. 1958.
Jouvet, M.: Recherches sur les mécanismes neurophysiologiques du sommeil et de l'apprentissage négatif. In: J. F. Delafresnaye (edit.), Brain mechanisms and learning. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publ. Ltd. 1961.
Killam, K. F., and E. K. Killam: Drug action on pathways involving the reticular formation. In: H. H. Jasper et al. (edits.), Reticular formation of the brain. Boston: Little Brown Co. 1958.
Kornetsky, C.: Effects of meprobamate, phenobarbital and dextro-amphetamine on reaction time and learning in man. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 123, 216–219 (1958).
—, and O. Humphries: Psychological effects of centrally acting drugs in man. Effects of chlorpromazine and secobarbital on visual and motor behavior. J. ment. Sci. 104, 1093–1099 (1958).
— — and E. V. Evarts: A comparison of the psychological effects of certain centrally acting drugs in man. Arch. Neurol. Psychiat. (Chic.) 77, 318–324 (1957).
—, A. F. Mirsky, E. Kessler and J. Dorff: The effects of dextro-amphetamine on behavioral deficits produced by sleep loss in humans. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 127, 46–50 (1959).
Lansdell, H., and A. F. Mirsky: The effects of focal and non-focal epilepsy on the Continuous Performance Test. (To be published) (1963).
Lennox, M.: Effects of sedative drugs on the EEG. Amer. J. Psychiat. 102, 799–804 (1946).
Lindsley, D. B., J. W. Bowden and H. W. Magoun: Effect upon the EEG of acute injury to the brain stem activating system. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol. 1, 475–486 (1949).
—, L. H. Schreiner, W. B. Knowles and H. W. Magoun: Behavioral and EEG changes following chronic brain stem lesions in the cat. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol. 2, 483–498 (1950).
Machne, X., I. Calma and H. W. Magoun: Unit activity of central cephalic brain stem in EEG arousal. J. Neurophysiol. 18, 547–558 (1955).
Magnes, J., G. Moruzzi and O. Pompeiano: Electroencephalogram-synchronizing structures in the lower brain stem. In: G. E. W. Wolstenholme and M. O'Connor (edits.), The nature of sleep. Boston: Little Brown Co. 1961.
Mirsky, A. F., and P. V. Cardon: A comparison of the behavioral and physiological changes accompanying sleep deprivation and chlorpromazine administration in man. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol. 14, 1–10 (1962).
—, D. W. Primac and R. Bates: The effects of chlorpromazine and secobarbital on the continuous performance test. J. nerv. ment. Dis. 128, 12–17 (1959).
— —, C. Ajmone Marsan, H. E. Rosvold and J. R. Stevens: A comparison of the psychological test performance of patients with focal and non-focal epilepsy. Exp. Neurol. 2, 75–89 (1960).
Monroe, R. R., R. G. Heath, W. A. Mickle and W. Miller: A comparison of cortical and subcortical brain waves in normal, reserpine and chlorpromazine sleep. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 61, 56–71 (1955).
Penfield, W., and H. Jasper: Epilepsy and the functional anatomy of the human brain. Boston: Little Brown Co. 1954.
Pfeiffer, C. C., A. J. Riopelle, R. P. Smith, E. H. Jenny and H. L. Williams: Comparative study of the effect of meprobamate on the conditioned response, on strychnine and pentylenetetrazol thresholds, on the normal electroencephalogram, and on polysynaptic reflexes. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 67, 734–745 (1957).
Primac, D. W., A. F. Mirsky and H. E. Rosvold: Effects of centrally-acting drugs on two tests of brain damage. Arch. Neurol. Psychiat. (Chic.) 77, 328–332 (1957).
Rimbaud, L., P. Passouant et J. Cadilhac: Participation de l'hippocampe à la régulation des états de veille et de sommeil. Rev. neurol. 93, 303–308 (1955).
Rosvold, H. E., A. F. Mirsky, I. Sarason, E. B. Bransome jr. and L. H. Beck: A continuous performance test of brain damage. J. cons. Psychol. 20, 343–350 (1956).
Shagass, C., H. Azima and J. Sangowicz: Effect of meprobamate in sustained high dosage on the electroencephalogram and sedation threshold. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol. 11, 275–283 (1959).
Sharpless, S., and H. H. Jasper: Habituation of the arousal reaction. Brain 79, 655–680 (1956).
Sprague, J. M., W. W. Chambers and E. Stellar: Attentive, affective and adaptive behavior in the cat. Science 133, 165–173 (1961).
Toman, J. E. P., and J. P. Davis: The effects of drugs upon the electrical activity of the brain. Pharmacol. Rev. 1, 425–492 (1949).
Townsend A. M., III, and A. F. Mirsky: A comparison of the effects of meprobamate, phenobarbital and d-amphetamine on two psychological tests. J. nerv. ment. Dis. 130, 212–216 (1960).
Unna, K. R.: A review of the neurophysiological effects of psychotherapeutic drugs. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 66, 777–783 (1957).
Villablanca, J.: Electroencephalogram in the permanently isolated forehrain of the cat. Science 138, 44–46 (1962).
Wechsler, D.: The measurement of adult intelligence, Ed. 3. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins Co. 1944.
Weitzman, E. D.: A note on the EEG and eye movements during behavioral sleep in monkeys. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol. 13, 790–794 (1961).
Williams, H. L., A. Lubin and J. J. Goodnow: Impaired performance with acute sleep loss. Psychol. Monogr. 73, 1–26 (1959).
Wolff, H. G., and W. H. Gantt: Caffeine sodiobenzoate, sodium iso-amylethyl barbiturate, sodium bromide and chloral hydrate. Effect on the highest integrative functions. Arch. Neurol. Psychiat. (Chic.) 33, 1030–1057 (1935).
Yamamoto, S., and U. Schaeppi: Effects of pentothal on cortex and brain stem. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol. 13, 248–256 (1961).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The studies referred to in this paper involving the Digit Symbol Substitution and Continuous Performance Tests were conducted in the Laboratory of Clinical Science, and in the Section on Neuropsychology, Laboratory of Psychology, National Institute of Mental Health, and in the Surgical Neurology Branch of the National Institute of Neurological Diseases and Blindness. The authors wish to express their appreciation to the numerous members of the staff of these laboratories who provided advice, assistance and facilities for these studies. Part of the costs of preparing this work for publication were borne by grant M-6015 from the National Science Foundation, grants GMK3-1759 and K3-14 915 from the National Institute of Mental Health and grant 61-241 from the Foundations Fund for Research in Psychiatry.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mirsky, A.F., Kornetsky, C. On the dissimilar effects of drugs on the digit symbol substitution and continuous performance tests. Psychopharmacologia 5, 161–177 (1964). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00413239
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00413239