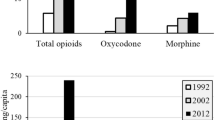
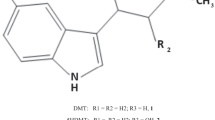
Summary
About 95% of the radioactivity representing imipramine and its metabolites after a 5 μC oral dose of 14C-imipramine could be extracted with tetrahydrofuran-isoamyl alcohol (1∶1) from salt-saturated human urine at pH 12 and pH 5.
By thin-layer chromatography, autoradiography, and various colour tests over 20 metabolites were provisionally identified, including free substances, glucuronides, and a new series of acid-labile conjugates. In free plus conjugated forms 2-hydroxy DMI totalled up to 40%, 2-hydroxy imipramine up to 25%, and 2-hydroxy iminodibenzyl up to 15% of all metabolite excreted. Didesmethylimipramine and its derivatives were present in only small amounts, while free iminodibenzyl and 10-hydroxy DMI each accounted for about 3% of the total metabolite excretion. Metabolism could be described completely in terms of demethylation or dealkylation, and hydroxylation at the 2 or 10 position with subsequent conjugation.
Males seemed to show less demethylation than females. Continued daily treatment was associated with a drop in excretion of free 2-hydroxy compounds and a rise in glucuronides in some individuals only. So far it has not been possible to correlate the individual differences in metabolite excretion with differences in clinical response, whether these be adverse or therapeutic.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adank, K., and W. Hammerschmidt: Dünnschichtchromatographische Untersuchung von Imipramin. Chimia 18, 361–363 (1964).
Bickel, M. H., and M. Baggiolini: The metabolism of imipramine and its metabolites by rat liver microsomes. Biochem. Pharmacol. 15, 1155–1169 (1966).
—, and H. J. Weder: The total fate of a drug: Kinetics of distribution, excretion, and formation of 14 metabolites in rats treated with imipramine. Arch. int. Pharmacodyn. 173, 433–463 (1968).
Christiansen, J., L. F. Gram, B. Kofod, and O. J. Rafaelsen: Imipramine metabolism in man. A study of urinary metabolites after administration of radioactive imipramine. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 11, 255–264 (1967).
Cochin, J., and J. W. Daly: The use of thin-layer chromatography for the analysis of drugs: identification and isolation of phenothiazine tranquillizers and of anti-histamines in body fluids and tissues. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 139, 160–165 (1963).
Crammer, J. L., and B. Scott: New metabolites of imipramine. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 8, 461–468 (1966).
- The excretion of desmethylimipramine and its metabolites in depressive patients. Excerpta Medica I.C.S. No. 150, p. 1942 (Proc IV World Congress of Psychiatry) (1968).
— —, H. Woods, and B. Rolfe: Metabolism of 14C-imipramine. I. Excretion in the rat and in man. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 12, 263–277 (1968).
Dingell, J. V., and E. Sanders: Methylation of desmethylimipramine by rabbit lung in vitro. Biochem. Pharmacol. 15, 599–605 (1966).
Feigl, F.: Spot Tests in organic analysis. 7th English edition. Amsterdam-London-New York: Elsevier 1966.
Hammer, W., and B. B. Brodie: A new approach to the determination of plasma levels of desmethylimipramine and other psychotropic drugs. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 157, 503 (1967).
- C.-M. Ideström, and F. Sjöqvist: Chemical control of antidepressant drug therapy. Proc. 1st. Int. Symp. on Antidepressant Drugs. Milan 1966. Excerpta Medica I.C.S. 122, p. 309 (1966).
Herrmann, B.: Quantitative Methoden zur Untersuchung des Stoffwechsels von Tofranil. Helv. physiol. pharmacol. Acta 21, 402–408 (1963).
—, and R. Pulver: Der Stoffwechsel des Psychopharmakons Tofranil. Arch. int. Pharmacodyn. 126, 454–469 (1960).
Kuhn, R.: Untersuchungen über mögliche Zusammenhänge zwischen Metabolitenausscheidung und Krankheitsverlauf depressiver Zustände unter Imipramin-Medikation. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 8, 201–222 (1965).
McMahon, R. E., F. J. Marshall, H. W. Culp, and W. M. Miller: The metabolism of nortriptyline-N-methyl-14C in rats. Biochem. Pharmacol. 12, 1207 to 1217 (1963).
Pscheidt, G. R.: Demethylation of imipramine in male and female rats. Biochem. Pharmacol. 11, 501–502 (1962).
Smith, Ivor: Chromatographic and electrophoretic techniques. London: Heinemann and New York: Interscience 1960.
Watt, D.C., J. L. Crammer, and A.Elkes: The relation of side-effects to therapeutic outcome of imipramine in depressive illness. Exeerpta Medica I.C.S. No. 180, p. 553 (1969a).
- - - Rate of metabolism and therapeutic response to desmethylimipramine. Proc. 5th. Hungarian Conference for Therapy and Pharmacological Research. Budapest (1969b).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work has been supported by a grant from the Medical Research Council. We are very grateful to Dr. Cyril Maxwell (Geigy Pharmaceuticals [U.K.] Ltd.) for encouragement, information and the gift of reference substances.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Crammer, J.L., Scott, B. & Rolfe, B. Metabolism of 14C-imipramine: II. Urinary metabolites in man. Psychopharmacologia 15, 207–225 (1969). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00411170
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00411170