Summary
-
1.
A careful replication of the Minz and Walaszek test failed to demonstrate its reliability as a clinical tool for diagnosing schizophrenia.
-
2.
Human serum contains substances toxic to rabbits. There is some indication that schizophrenic serum has greater toxicity than nonschizophrenic sera.
-
3.
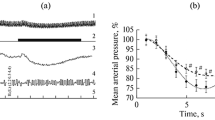
Local application of a 5% epinephrine solution to the cerebral cortex causes a rise in blood pressure in about half the rabbits treated with normal serum.
-
4.
Effects of some tests with psychoactive drugs on the local epinephrine responses are reported.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baldi, F.: Ricerche sperimentali sul sangue dei dementi precoci. I. Neurologica (Napoli) 3, 91–111 (1926).
Chamorro, A., et B. Minz: Localisation d'une activité ocytocique dans l'hypothalamus postérieur du lapin. C.R. Soc. Biol. (Paris) 151, 496–499 (1957).
Delgado, José M. R.: Circulatory effects of cortical stimulation. Physiol. Rev. 40, Suppl. No 4, 146–171 (1960).
Gerard, R. W.: The nosology of schizophrenia. Amer. J. Psychiat. 1963 (in press).
Green, H. D., and E. C. Hoff: Effects of faradic stimulation of the cerebral cortex on limb and renal volumes in the cat and monkey. Amer. J. Physiol. 118, 641–658 (1937).
Harrison, F., and A. Goth: Effect of reserpine on the hypothalamic pressor response. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 116, 262–267 (1956).
Hoff, E. C., and H. D. Green: Cardiovascular reactions induced by electrical stimulation of the cerebral cortex. Amer. J. Physiol. 117, 411–422 (1936).
Howell, W. H., and M. F. Austin: The effect of stimulation of various portions of the cortex cerebri, caudata nucleus, and dura mater upon blood pressure. Amer. J. Physiol. 3, 22–23 (1899).
Kety, S. S.: Biochemical theories of schizophrenia. Part II of a two part critical review of current theories and of the evidence used to support them. Science 129, 1590–1596 (1959).
Kremer, W. F.: Blood pressure changes in response to electrical and chemical (Acetyl-β-methylcholine) stimulation of the cerebral cortex in dogs. Amer. J. Physiol. 152, 314–323 (1948).
Lovatt-Evans, C.: Starling's principles of human physiology. Philadelphia: Lea and Febiger 1956.
Minz, B.: Actions de drogues tranquillisantes sur la réaction du cortex cérébral à l'adrenaline. C.R. Soc. Biol. (Paris) 151, 432–436 (1957).
—, P. Buser et D. Albe-Fessard: Effet presseur de l'adrenaline appliquée localement sur le cortex du lapin. C.R. Soc. Biol. (Paris) 147, 1154–1156 (1953).
—, et A. Chamorro: Sur une action corticohypothalamique déclenchée par l'adrenaline. C.R. Acad. Sci. (Paris) 240, 454–455 (1955).
— —: Sensibilisation à distance par l'adrenaline appliquee sur le cortex cerebral du lapin. C.R. Soc. Biol. (Paris) 150, 299–303(1956a).
— —: Diffèrenciation pharmacodynamique d'effets corticaux et périphériques de l'adrenaline. C.R. Soc. Biol. (Paris) 150, 849–853 (1956b).
—, et E. J. Walaszek: Sur le mécanisme de l'inhibition de la réaction corticale à l'adrenaline chez des lapins traités avec du sérum de schizophrénes. C.R. Acad. Sci. (Paris) 246, 1326–1328 (1958a).
— —: Tropic action of epinephrine on the cerebral cortex of rabbits pretreated with serum from schizophrenics. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 122, 53A (1958b).
Sjövall, T.: Preliminary studies on a possible serum toxicity in schizophrenia. Acta psychiat. scand., Suppl. 47, 105–117 (1947).
Stricker, S.: Untersuchungen über die Gefäßnervenzentren im Gehirn und Rückenmark. Med. Jb. 1, 1–19 (1886).
Trapold, J. H., A. T. Plummer and F. F. Yonkman: Cardiovascular and respiratory effects of serpasil, a new crystallin alkaloid from rauwolfia serpentina benth., in the dog. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 110, 205–214 (1954).
Walaszek, E. J.: Personal communication 1959.
—, and B. Minz: Neurohormonal changes in brains of rabbits pretreated with serum from schizophrenics. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 122, 80A (1958).
— — and C. M. Smith: Effects of serum from schizophrenic patients on neurohumors in rabbit brain. Fed. Proc. 17, No 1, 1645 (1958).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by United States Public Health Service grants MY-1971 and MY-1972, R. W. Gerard, M.D., Ph.D. Principal Investigator.
With technical assistance of Neil V. Williams.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fujita, S., Rosenzweig, N. Use of the cortical epinephrine pressor response in rabbits as a diagnostic test for schizophrenia. Psychopharmacologia 4, 367–376 (1963). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00405247
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00405247