Abstract
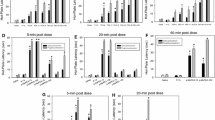
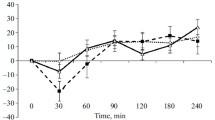
The effect of reserpine, α-methyl-dl-m-tyrosine (α-MT) and p-chlorophenylalanine (p-ClPhe) pretreatment on meperidine analgesia has been studied by various methods in male mice. The ED50 of meperidine was significantly increased by all methods when the animals were pretreated with reserpine. α-methyl-mtyrosine significantly increased the ED50 of meperidine only by the clip method. P-chlorophenylalanine pretreatment significantly increased the ED50 of meperidine by the clip (both in acute and chronic treatments) and shock methods (only after chronic treatment). Possible explanations for the different findings are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bianchi, C., Franceschini, J.: Experimental observations on Haffner's method for testing analgesic drugs. Brit. J. Pharmacol. 9, 280–284 (1954).
Brodie, B. B., Shore, P. A.: A concept for a role of serotonin and norepinephrine or chemical mediator in the brain. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 66, 631–642 (1957).
— —, Pletscher, A.: Serotonin releasing activity limited to Rauwolfia alkaloid with tranquillising action. Sciences 123, 992–993 (1956).
Costa, E., Gessa, G. L., Kuntzman, R., Brodie, B. B.: The effects of drugs on storage and release of serotonin and catecholamines in the brain. First Int. Pharmacol. Meeting, Vol. 8, pp. 43–69. Ed. by Uvnas, B. Oxford: Pergamon Press 1962.
Grewal, R. S.: A method for testing analgesics in mice. Brit. J. Pharmacol. 7, 433–437 (1952).
Hanson, L. C. F.: The disruption of conditioned avoidance response following selective depletion of brain catecholamines. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 8, 100–110 (1965).
Koe, B. K., Weissman, A.: p-chlorphenylalanine: A specific depletor of brain serotonin. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 154, 499–516 (1966).
Litchfield, J. T., Wilcoxon, F.: A simplified method of evaluating dose-effect experiments. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 96, 99–113 (1949).
Medakovic, M., Banic, B.: The action of reserpine and α-methyl-m-tyrosine on the analgesic effect of morphine in rats and mice. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 16, 198–206 (1964).
Ross, J.A., Ashford, A.: The effect of reserpine and α-methyldopa on the analgesic action of morphine in the mouse. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 19, 709–713 (1967).
Schneider, J. A.: Reserpine antagonism of morphine analgesia in mice. Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. (N. Y.) 87, 614–615 (1954).
Schumann, W., Beeinflussung der analgetischen Wirkung der Morphine durch Reserpine. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. exp. Path. Pharmak. 235, 1–9 (1958).
Shore, P. A., Brodie, B. B.: Influence of various drugs on serotonin and norepinephrine in the brain. In Psychotropic drugs, pp. 423–427. (Garattini, S., V. Ghetti). Amsterdam: Elsevier 1957.
Sigg, E. B., Caprio, G., Schneider, J. A.: Syndrgism of amines and antagonism of reserpine to morphine analgesia. Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. (N. Y.) 97, 97–100 (1958).
Spector, S., Sjoerdsma, A., Udenfriend, S.: Blockade of endogenous NE synthesis by α-methyl-tyrosine an inhibitor of hydroxylase. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 147, 86–95 (1966).
Tenen, S. S.: Antagonism of the analgesic effect of morphine and other drugs by p-chlorophenylalanine a serotonin depletor. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 12, 278–285 (1968).
Takagi, H., Takashima, T., Kimura, K.: Antagonism of morphine in mice by tetrabenazine and reserpine. Arch. int. Pharmacodyn. 149, 484–492 (1964).
Tsoukong, Tu. Zeng-Hong: Acta physiol. sin. 26, 360–366 (1963). Quoted by Ross and Ashford (1967).
Verri, R. A., Graeff, F. G., Corrado, A. P.: Antagonism of morphine analgesia by reserpine and α-methyl-tyrosine and the role played by catecholamines in morphine analgesic action. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 19, 264–265 (1967).
— — —: Effect of reserpine and alpha-methyl-tyrosine on morphine analgesia. Int. J. Neuropharmacol. 7, 283–292 (1968).
Volicer, L.: Correlation between behavioural and biochemical effects of p-chlorophenylalanine in mice and rats. Int. J. Neuropharmacol. 8, 361–364 (1969).
Wolf, H. H., Rollins, D. E., Rowland, C. R., Reigle, T. G.: The importance of endogenous catecholamines in the activity of some CNS stimulants. Int. J. Neuropharmacol. 8, 319–328 (1969).
Woolf, G., MacDonald, A. D.: The evaluation of the analgesic action of pethidine hydrochloride (Demerol). J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 80, 300–307 (1944).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sethy, V.H., Pradhan, R.J., Mandrekar, S.S. et al. Role of brain amines in the analgesic action of meperidine hydrochloride. Psychopharmacologia 17, 320–326 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00404237
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00404237