Abstract
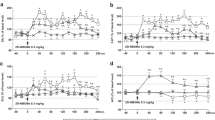
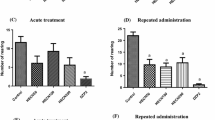
Physiological disposition of isoergine (d-isolysergamide, iso-LA) obtained from the seeds of Argyreia nervosa (Burm. f.) Bojer were determined in rat liver, brain and plasma. Method of determination involved the extraction of the drug from biological samples and quantitation of the compound by fluorometric analysis. The injection of 5 mg/kg, i.p., of iso-LA resulted after 5 min in peak levels in the liver (7.2 μg/g) and after 15 min in peak levels in the brain (1.2 μg/g) and plasma (1.9 μg/ml). After 120 min, 90% of the compound had disappeared from the tissues and plasma. The minimal dose required to produce a significant decrease in the conditioned avoidance response (CAR) was somewhat less than 5 mg/kg. The minimal brain level which interfered with the CAR was approximately 1 μg/g. Brain levels of iso-LA seem to correlate directly with changes in behavior suggesting that iso-LA, and not a metabolite, is the psychoactive agent.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Axelrod, J., Brady, R. O., Witkop, B., Evarts, E. V.: The distribution and metabolism of lysergic acid diethylamide. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 66, 435–444 (1957).
Chao, J. M.: A pharmacognostic investigation of Argyreia nervosa (Burm. f.) Bojer and allied species, and a biosynthetic study of ergoline alkaloids in Ipomoea violacea L., Ph. D. thesis, Philadelphia College of Pharmacy and Science 1970.
Clarke, E. G. C.: Isolation and Identification of drugs. First Ed. London. The Pharmaceutical Press 1969.
Cohen, S.: Psychotomimetic agents. Ann. Rev. Pharmacol. 7, 301–318 (1967).
Der Marderosian, A.: Psychotomimetic indoles in the convolvulaceae. Am. J. Pharm. 139, 19–26 (1967).
Heim, E., Heimann, H., Lukacs, G.: Die psychische Wirkung der mexikanischen Droge „Ololiuqui“ am Menschen. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 13, 35–48 (1968).
Hofmann, A.: The active principles of the seeds of Rivea Corymbosa and Ipomoea violacea. Botanical Museum Leaflets (Harvard Univ.) 20, 6, 194–211 (1963).
Isbell, H., Gorodetsky, C. W.: Effect of alkaloids of Ololuiqui in man. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 8, 331–339 (1966).
Rice, W. B., Genest, K.: Acute toxicity of morning glory seeds in mice. Nature (Lond.) 207, 302–303 (1965).
Smythies, J. R., Johnston, V. S., Bradley, R. J.: Behavioral model of psychosis. Brit. J. Psychiat. 115, 55–68 (1969).
—, Sykes, E. A.: The effect of mescaline upon the conditioned avoidance response in the rat. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 6, 163–172 (1964).
Solms, H.: Relationships between chemical structure and psychoses with the use of psychotoxic substances. J. clin. exp. Psychopath. 17, 429–433 (1956).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vogel, W.H., Carapellotti, R.A., Evans, B.D. et al. Physiological disposition of isoergine [from Argyreia nervosa (Burm. f.) Bojer Convolvulaceae] and its effect on the conditioned avoidance response in rats. Psychopharmacologia 24, 238–242 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00403643
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00403643