Abstract
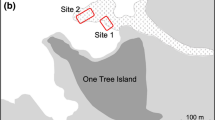
A total of 34 zooplanktonic taxa were common in emergence trap, reentry trap, and net-tow samples taken in the lagoon of Heron Reef, Great Barrier Reef, between 27 February and 22 March and between 11 June and 4 July 1985. Twenty-nine of these taxa were classified as demersal (17 taxa), meroplanktonic and larval (10 taxa), or incidental (2 taxa). The remaining five multispecific groups yielded variable results. Differences were observed between two locations separated by 200 m, with emergence 2 to 62 times greater for 22 taxa at a deeper site with larger coral formations. Most zooplankters were more common (2 to 122 times) in samples from 1 m2 areas around 0.25 to 0.5 m2 patches of branching coral. However, two species of copepods, Pseudodiaptomus colefaxi and Metis holothuriae, were taken in greater numbers (3 to 12 times) from open sand. Seasonal increases (2 to 322 times) were observed for 13 adult taxa and 8 classes of larvae or juveniles in the summer and for 10 adult taxa and one larval group in the winter. Fourteen of the 17 demersal taxa and 4 groups of large larvae or juveniles emerged in numbers 2 to 323 times greater during lunar quarters or new moons. In contrast, 6 larval taxa and 4 groups of small or transparent adults displayed significant emergence during full moons. Five diurnal emergence patterns were shown by 27 taxa, with patterns varying primarily among lunar periods. The variety of taxon-specific patterns observed in this study highlight a need for caution when generalizing about demersal zooplankton.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Alheit, J. (1981). Feeding interactions between coral reef fishes and the zoobenthos. Proc. 4th int. Symp. coral Reef, 2: 545–552 [Gomez, E.D. et al. (eds.) Marine Sciences Center, University of the Philippines, Quezon City]
Alldredge, A. L. (1985). Abundance of demersal zooplankton on tropical seagrass meadows. Res. Rep. natn. geogr. Soc., Wash. 19: 95–101
Alldredge, A. L., King, J. M. (1977). Distribution, abundance, and substrate preference of demersal reef zooplankton at Lizard Island Lagoon, Great Barrier Reef. Mar. Biol. 41: 317–333
Alldredge, A. L., King, J. M. (1980). Effects of moonlight on the vertical migration patterns of demersal zooplankton. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 44: 133–156
Alldredge, A. L., King, J. M. (1985). The distance demersal zooplankton migrate above the benthos: implications for predation. Mar. Biol. 84: 253–260
Ambrose, W. G. Jr. (1986). Experimental analysis of density dependent emigration of the amphipod Rhepoxynius abronis. Mar. Behav. Physiol. 12: 209–216
Anger, K. C., Valentin, C. (1976). In situ studies on the diurnal activity pattern of Diastylis rathkei (Cumacea, Crustacea) and its importance for the “hyperbenthos”. Helgoländer wiss. Meeresunters. 28: 138–144
Emery, A. R. (1968). Preliminary observations on coral reef plankton. Limnol. Oceanogr. 13: 293–303
Birkeland, C., Smalley, T. L. (1981). Comparisons of demersal plankton from comparable substrata from a high island and an atoll. Proc. 4th int. Symp. coral Reefs 1: 437–442 [Gomez, E. D. et al. (eds.) Marine Sciences Center, University of the Philippines, Quezon City]
Fancett, M. S., Kimmerer, J. W. (1985). Vertical migration of the demersal copepod Pseudodiaptomus as a means of predator avoidance. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 88: 31–43
Feeley, M. T., Filer, D. L., Schwartz, L. (1979). Zooplankton emerging from a Philippine coral reef: a preliminary study. J. Asian Ecol. 1: 51–56
Goswami, S. C. (1979). Diel variations of zooplankton at Kavaratti Atoll (Lakshadweep). Indian J. mar. Sci. 8: 247–251
Griffiths, A. M., Frost, B. W. (1976). Chemical communication in the marine planktonic copepods Calanus pacificus and Pseudocalanus sp. Crustaceana 30: 1–8
Hamner, W. M., Carleton, J. H. (1979). Copepod swarms: attributes and role in coral reef ecosystems. Limnol. Oceanogr. 24: 1–4
Hobson, E. S., Chess, J. R. (1978). Trophic relationships among fishes and plankton in the lagoon at Enewetak Atoll, Marshall Islands. Fish. Bull. U.S. 76: 133–153
Hobson, E. S., Chess, J. R. (1979). Zooplankton that emerge from the lagoon floor at night at Kure and Midway Atolls, Hawaii. Fish. Bull. U.S. 77: 275–280
Jacoby, C. A., Youngbluth, M. J. (1983). Mating behavior in three species of Pseudodiaptomus (Copepoda: Calanoida). Mar. Biol. 76: 77–86
Johnson, M. W. (1949). Zooplankton as an index of water exchange between Bikini Lagoon and the open sea. Trans. Am. geophys. Un. 30: 238–244
Katona, S. K. (1973). Evidence for sex pheromones in planktonic copepods. Limnol. Oceanogr. 18: 574–583
Kern, J. C., Taghon, G. L. (1986). Can passive recruitment explain harpacticoid copepod distributions in relation to epibenthic structure?. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 101: 1–23
Mather, P., Bennett, I. (1978). A coral reef handbook. A guide to the fauna, flora and geology of Heron Island and adjacent reefs and cays. Handbk Ser. Gt Barrier Reef Comm. 1: 1–92
McWilliam, P. S., Sale, P. F., Anderson, D. T. (1981). Seasonal changes in resident zooplankton sampled by emergence traps in One Tree Lagoon, Great Barrier Reef. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 52: 185–203
Mills, E. L. (1967). The biology of an ampeliscid amphipod crustacean sibling species pair. J. Fish. Res. Bd Can. 24: 305–355
Ohlhorst, S. L. (1982). Diel migration patterns of demersal reef zooplankton. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 60: 1–15
Porter, J. W., Porter, K. G. (1977). Quantitative sampling of demersal plankton migrating from different coral reef substrates. Limnol. Oceanogr. 22: 553–556
Porter, J. W., Porter, K. G., Catalan, Z. B. (1977). Quantitative sampling of Indo-Pacific demersal reef zooplankton. Proc. 3rd int. Symp. coral Reefs 1: 105–112 [Taylor, D. L. (ed.) School of Marine and Atmospheric Sciences, University of Miami, Miami, Fla.]
Randall, R. H., Birkeland, C., Amesbury, S. S., Lassuy, D., Eads, J. R. (1978). Marine survey of a proposed resort site at Arakabesan Island, Palau. Tech. Rep. Univ. Guam mar. Lab. 44: 1–66
Renon, J. P., Dudemaine, M., Drouet, J. (1985) Une piège à émergence à collecteurs multiples pour l'étude des migrations planctoniques verticales en milieu corallien. J. Plankton Res. 7: 19–34
Robichaux, D. M., Cohen, A. C., Reaka, M. L., Allen, D. (1981). Experiments with zooplankton on coral reefs, or, will the real demersal zooplankton please come up? Mar. Ecol. 2: 77–94 (Paul Parey, Berlin)
Sale, P. F., McWilliam, P. S., Anderson, D. T. (1976). Composition of the near-reef zooplankton at Heron Reef, Great Barrier Reef. Mar. Biol. 34: 59–66
Sale, P. F., McWilliam, P. S., Anderson, D. T. (1978). Faunal relationships among the near-reef zooplankton at three locations on Heron Reef, Great Barrier Reef, and seasonal changes in this fauna. Mar. Biol. 49: 133–145
SAS Institute Inc. (1985). SAS/STAT guide for personal computers. 6 edn. SAS Inst. Inc., Cary, North Carolina
Stretch, J. J. (1985). Quantitative sampling of demersal zooplankton: reentry and airlift dredge comparisons. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 91: 125–136
Tranter, D. J., Bulleid, N. C., Campbell, R., Higgins, H. W., Rowe, F., Tranter, H. A., Smith, D. F. (1981). Nocturnal movements of phototactic zooplankton in shallow waters. Mar. Biol. 61: 317–326
Ueda, H. (1987). Small-scale ontogenetic and diel vertical distributions of neritic copepods in Maizuru Bay, Japan. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 35: 65–73
Underwood, A. J. (1981). Techniques of analysis of variance in experimental marine biology and ecology. Oceanogr. mar. Biol. A. Rev. 19: 513–605
Walter, T. C., Pasamonte, J. N., Talaue, L. (1981). A preliminary quantitative study on emergence of reef associated zooplankton from a Philippine coral reef. Proc. 4th int. Symp. coral Reefs 1: 443–451 [Gomez, E. D. et al. (eds.) Marine Sciences Center, University of the Philippines, Quezon City]
Youngbluth, M. J. (1982a). Sampling demersal zooplankton: a comparison of field collections using three different emergence traps. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 61: 111–124
Youngbluth, M. J. (1982b). Demersal zooplankton: diel emergence patterns from subtropical seagrass habitats. EOS Trans., Am. geophys. Un. 63, p. 964
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by G. F. Humphrey, Sydney
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jacoby, C.A., Greenwood, J.G. Spatial, temporal, and behavioral patterns in emergence of zooplankton in the lagoon of Heron Reef, Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Mar. Biol. 97, 309–328 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00397762
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00397762