Abstract
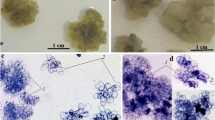
In suspension-cultured cells of Glycine max and Catharanthus roseus, marked callose synthesis can be induced by digitonin and chitosan. Leakage of a limited pool of electrolytes precedes callose formation, K+ representing the major cation lost. Poly-L-ornithine, as well as the ionophores A 23187 and ionomycin, also induces some callose synthesis but to a lesser extent. Digitonin increases the net uptake of Ca2+ from the external buffer with a time course parallel to callose synthesis but lagging behind the leakage of K+. Nifedipine partly blocks callose synthesis as well as the digitonin-induced increase in net Ca2+ uptake. Taken together, the data support the hypothesis that addition of the various substances might indirectly lead to membrane perturbation causing the common event of an increase in net Ca2+ uptake which results in callose deposition by a direct activition of the Ca2+-dependent and plasma-membane-located 1,3-β-glucan synthase.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrejauskas, E., Hertel, R., Marmé, D. (1985) Specific binding of the calcium antagonist (3H)verapamil to membrane fractions from plants. J. Biol. Chem. 260, 5411–5414
Blaschek, W., Semler, U., Franz, G. (1985) The influence of potential inhibitors on the in vivo and in vitro cell wall β-glucan biosynthesis in tobacco cells. J. Plant Physiol. 120, 457–470
Delmer, D.P., Cooper, G., Alexander, D., Cooper, J., Hajashi, T., Nitsche, C., Thelen, M. (1985) New approaches to the study of cellulose biosynthesis. J. Cell Sci., Suppl. 2, 33–50
Eschrich, W. (1965) Physiologie der Siebröhrencallose. Planta 65, 280–300
Fink, J., Jeblick, W., Blaschek, W., Kauss, H. (1987) Ca2+ and polyamines activate the plasma membrane-located 1,3-β-glucan synthase. Planta 171 130–135
Gillerey M.J., Ranjeva, R. (1985) Characterization of calcium channels in carrot cells: In: Molecular and cellular aspects of calcium in plant development, pp. 421–422, Trewavas, A.J., ed. Plenum Press, New York London
Hepler, P.K., Wayne, R.O. (1985) Calcium and plant development. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 36, 397–439
Hetherington, A.M., Trewavas, A.J. (1984) Binding of nitrendipine, a calcium channel blocker, to pea shoot membranes. Plant Sci. Lett. 35, 109–113
Kauss, H. (1987a) Some aspects of calcium-dependent regulation in plant metabolism. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 38, 47–72
Kauss, H. (1987b) Callose-Synthese: Regulation durch induzierten Ca2+-Einstrom in Pflanzenzellen. Naturwissenschaften 74, 275–281
Kauss, H., Jeblick, W. (1986a) Influence of free fatty acids, lysophosphatidylcholine, platelet-activating factor, acylcarnitine, and Echinocandin B on 1,3-β-D-glucan synthase and callose synthesis. Plant Physiol 80, 7–13
Kauss, H., Jeblick, W. (1986b) Synergistic activation of 1,3-β-D-glucan synthase by Ca2+ and polyamines. Plant Sci. Lett. 43, 103–107
Kauss, H., Jeblick, W. (1987) Solubilization, affinity chromatography and Ca2+/polyamine activation of the plasma membrane-located 1,3-β-D-glucan synthase. Plant Sci. 48, 63–69
Kauss, H., Köhle, H., Jeblick, W. (1983) Proteolytic activation and stimulation by Ca2+ of glucan synthase from soybean cells. FEBS Lett. 158, 84–88
Köhle, H., Jeblick, W., Poten, F., Blaschek, W., Kauss, H. (1985) Chitosan-elicited callose synthesis in soybean cells as a Ca2+-dependent process. Plant Physiol. 77, 544–551
Lee, K.S., Tsien, R.W. (1983) Mechanism of calcium channel blockade by verapamil, D 600, diltiazem and nitrendipine in single dialysed heart cells. Nature 302, 790–794
Lehtonen, J. (1984) The significance of Ca2+ in the morphogenesis of Micrasterias studied with EGTA, verapamil, LaCl3 and calcium, ionophore A 23187. Plant Sci. Lett. 33, 53–60
Linsmaier, E.M., Skoog, F. (1965) Organic growth factor requirements of tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant. 18, 100–127
Morrow, D.L., Lucas, W.T. (1986) 1→3)-β-D-glucan synthase from sugar beet. Plant Physiol. 81, 171–176
Reiss, H.D., Herth, W. (1985) Nifedipine-sensitive calcium channels are involved in polar growth of lily pollen tubes. J. Cell Sci. 76, 247–254
Reuveni, M., Lerner, H.R., Poljakoff-Mayber, A. (1985) Changes in membrane potential as a demonstration of selective pore formation in the plasmalemma by poly-L-lysine treatment. Plant Physiol. 79, 406–410
Rincon, M., Hanson, J.B. (1986) Controls on calcium ion fluxes in injured or shocked corn root cells: Importance of proton pumping and cell membrane potential. Physiol. Plant. 67, 576–583
Saunders, M.J., Hepler, P.K. (1983) Calcium antagonists and calmodulin inhibitors block cytokinin-induced bud formation in Funaria. Dev. Biol. 99, 41–49
Young, D.H., Kauss, H. (1983) Release of calcium from suspension-cultured Glycine max cells by chitosan, other polycations, and polyamines in relation to effects on membrane permeability. Plant Physiol. 73, 698–702
Young, D.H., Köhle, H., Kauss, H. (1982) Effect of chitosan on membrane permeability of suspension-cultured Glycine max and Phaseolus vulgaris cells. Plant Phsiol. 70, 1449–1454
Zocchi, G., Rogers, S.A., Hanson, J.B. (1983) Inhibition of proton pumping in corn roots is associated with increased phosphorylation of membrane proteins. Plant Sci. Lett. 31, 215–221
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Waldmann, T., Jeblick, W. & Kauss, H. Induced net Ca2+ uptake and callose biosynthesis in suspension-cultured plant cells. Planta 173, 88–95 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00394492
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00394492