Abstract
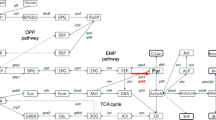
Theoretical calculations of the NADPH requirement for biomass formation indicate that in yeasts this parameter is strongly dependent on the carbon and nitrogen sources used for growth. Enzyme surveys of NADPH-generating metabolic pathways and radiorespirometric studies demonstrate that in yeasts the HMP pathway is the major source of NADPH. Furthermore, radiorespirometric data suggest that in yeasts the HMP pathway activities are close to the theoretical minimum. It may be concluded that the mitochondrial NADPH oxidation, which in yeasts may yield ATP, is quantitatively not an important process.
The inability of C. utilis to utilize the NADH produced in formate oxidation as an extra source of NADPH strongly suggests that transhydrogenase activity is absent. Furthermore, the absence of xylose utilization under anaerobic conditions in most facultatively fermentative yeasts indicates that also in these organisms transhydrogenase activity is absent. This conclusion is supported by the observation that anaerobic xylose utilization is observed only in those yeasts which possess a high activity of an NADH-linked xylose reductase. Hence in these organisms the redox-neutral conversion of xylose to ethanol is possible, since the second step in xylose metabolism is mediated by an NAD+-linked xylitol dehydrogenase.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
Atkinson, D. E. (1977) Cellular Energy Metabolism and its Regulation. Academic Press, London
Blumenthal, H. J., Lewis, K. F. & Weinhouse, S. (1954) An estimation of pathways of glucose catabolism in yeasts. J. Amer. Chem. Soc. 76: 6093–6097
Bruinenberg, P. M., vanDijken, J. P. & Scheffers, W. A. (1983a) A theoretical analysis of NADPH production and consumption in yeasts. J. Gen. Microbiol. 129: 953–964
Bruinenberg, P. M., vanDijken, J. P. & Scheffers, W. A. (1983b) An enzymic analysis of NADPH production and consumption in Candida utilis CBS621. J. Gen. Microbiol. 129: 965–971
Bruinenberg, P. M., deBot, P. H. M., vanDijken, J. P. & Scheffers, W. A. (1983c) The role of redox balances in the anaerobic fermentation of xylose by yeasts. Eur. J. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 18: 287–292
Bruinenberg, P. M., deBot, P. H. M., vanDijken, J. P. & Scheffers, W. A. (1984) NADH-linked aldose reductase: the key to anaerobic alcoholic fermentation of xylose by yeasts. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 19: 256–269
Bruinenberg, P. M., vanDijken, J. P., Kuenen, J. G. & Scheffers, W. A. (1985a) Oxidation of NADH and NADPH by mitochondria from the yeast Candida utilis. J. Gen. Microbiol. 131: 1043–1051
Bruinenberg, P. M., Jonker, R., vanDijken, J. P. & Scheffers, W. A. (1985b) Utilization of formate as an additional energy source by glucose-limited chemostat cultures of Canadida utilis CBS 621 and Saccharomyces cerevisiae CBS 8066. Evidence for the absence of transhydrogenase activity in yeasts. Arch. Microbiol. 142: 302–306.
Bruinenberg, P. M., vanDijken, J. P. & Scheffers, W. A. (1986a) A radiorespirometric study on the contribution of the hexose monophosphate pathway to glucose metabolism in Candida utilis CBS 621 grown in glucose-limited chemostat cultures. J. Gen. Microbiol. 131: 221–229
Bruinenberg, P. M., Waslander, G. W., vanDijken, J. P. & Scheffers, W. A. (1986b) A comparative radiorespirometric study of glucose metabolism in yeasts. Yeasts 2: 117–121
Chakravorty, M., Veiga, L. A., Bacila, M. & Horecker, B. L. (1962) Pentose metabolism in Canadida II. The diphosphopyridine nucleotide-specific polyol dehydrogenase of Candida utilis. J. Biol. Chem. 237: 1014–1020
Chance, B. & Williams, G. R. (1956) The respiratory chain and oxidative phosphorylation. Adv. Enzymol. 17: 65–134
Dekker, R. F. H. (1982) Ethanol production from D-xylose and other sugars by the yeast Pachysolen tannophilus. Biotechnol. Lett. 4: 411–416
Dekkers, J. G. J., deKok, H. E. & Roels, J. A. (1981) Energetics of Saccharomyces cerevisiae CBS 426: comparison of anaerobic and aerobic glucose limitation. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 23: 1023–1035
Djavadi, F. H. S., Moradi, M. & Djavadi-Ohaniance, L. (1980) Direct oxidation of NADPH by submitochondrial particles from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eur. J. Biochem. 107: 501–504.
DuPreez, J. C. & van derWalt, J. P. (1983) Fermentation of D-xylose to ethanol by a strain of Candida shehatea. Biotechnol. Lett. 5: 357–362
Evans, T. C., Mackler, B. & Grace, R. (1985) Pyridine nucleotide transhydrogenations in yeast. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 243: 492–503
Gancedo, J. M. & Lagunas, R. (1973) Contribution of the pentosephosphate pathway to glucose metabolism in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: a critical analysis on the use of labelled glucose. Plant Science Lett. 1: 193–200
Haas, E., Hoerecker, B. L. & Hogness, T. R. (1940) The enzymatic reduction of cytochrome c. Cytochrome c reductase. J. Biol. Chem. 136: 747–774
Hirai, M., Shiotani, T., Tanaka, A. & Fukui, S. (1976) Intracellular localization of several enzymes in Candida tropicalis grown on different carbon sources. Agric. Biol. Chem. 40: 1979–1985
Höfer, M. (1968) Estimation of pathways of glucose catabolism in Rhodotorula gracilis. Folia Microbiol. (Prague) 13: 373–378
Jeffries, T. W. (1981) Conversion of xylose to ethanol under aerobic conditions by Candida tropicalis. Biotechnol. Lett. 3: 213–218
Katz, J. & Wood, H. G. (1963) The use of C14O2 yields from glucose-1 and -6-C14 for the evaluation of the pathways of glucose metabolism. J. Biol. Chem. 238: 517–523
Lehninger, A. L. (1951) Oxidative phosphorylation in diphosphopyridine nucleotide-linked systems. pp. 344–366. In: W. D.McElroy & B.Glass (Eds), Phosphorus Metabolism. A symposium on the role of phosphorus in the metabolism of plants and animals. Vol. I. The Johns Hopkins Press, Baltimore
Ligthelm, M. E., Prior, B. A. & du Preez, J. C. (1986) The effect of inoculum age upon the anoxic fermentation of xylose by yeast. In: XIth International Specialized Symposium on Yeasts, p. 81. Lisbon
Mackler, B., Haynes, B., Person, R. & Palmer, G. (1980) Electron transport systems of Candida utilis. Purification and properties of the respiratory chain-linked external NADH dehydrogenase. Biochim. biophys. acta 591: 289–297
Mackler, B., Bevan, C., Person, R. & Davis, K. A. (1981) Purification and properties of the respiratory chain-linked internal NADH dehydrogenase of Candida utilis. Biochem. Intern. 3: 9–17
Margaritis, A., & Bajpaj, P. (1982) Direct fermentation of D-xylose to ethanol by Kluyveromyces marxianus strains. Appl. Environm. Microbiol. 44: 1039–1041
Mian, F. A., Fencl, Z., Prokop, A., Mohagheghi, A. & Fazeli, A. (1974) Effect of growth rate on the glucose metabolism of yeast grown in continuous culture. Radiorespirometric studies. Folia Microbiol. (Prague) 19: 191–198
Ragan, C. I. & Garland, P. B. (1971) Spectroscopic studies of flavoproteins and non-haem iron proteins of submitochondrial particles of Torulopsis utilis modified by iron- and sulfate-limited growth in continuous culture. Biochem. J. 124: 171–187
Schneider, H, Wang, P. Y., Chan, Y. K. & Maleszka, R. (1981) Conversion of D-xylose into ethanol by the yeast Pachysolen tannophilus. Biotechn. Lett. 3: 89–92
Schuurmans Stekhoven, F. M. A. H. (1966) Studies on yeast mitochondria. I. Existence of three phosphorylation sites along the respiratory chain of isolated yeast mitochondria. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 115: 555–568
Stouthamer, A. H. (1973) A theoretical study on the amount of ATP required for synthesis of microbial cell material. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 39: 545–565
Stouthamer, A. H. (1977) Theoretical calculations on the influence of the inorganic nitrogen source on parameters of aerobic growth of microorganisms. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 43: 351–367
Suihko, M. L. & Dražić, M. (1983) Pentose fermentation by yeasts. Biotechnol. Lett. 5: 107–112
Toivola, A., Yarrow, D., van denBosch, E., vanDijken, J. P. & Scheffers, W. A. (1984) Alcoholic fermentation of D-xylose by yeasts. Appl. Environm. Microbiol. 47: 1221–1223
Tottmar, S. O. C. & Ragan, C. I. (1971) The purification and properties of the respiratory-chain reduced nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide dehydrogenase of Torulopsis utilis. Biochem. J. 124: 853–865
Verduyn, C., Frank, J., vanDijken, J. P. & Scheffers, W. A. (1985a) Multiple forms of xylose reductase in Pachysolen tannophilus CBS 4044. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 30: 313–317.
Verduyn, C., vanKleef, R., Frank, J., Schreuder, H., vanDijken, J. P. & Scheffers, W. A. (1985) Properties of the NAD(P)H-dependent xylose reductase from the xylose-fermenting yeast Pichia stipitis. Biochem. J. 226: 669–677
VonJagow, G. & Klingenberg, M. (1970) Pathways of hydrogen in mitochondria of Saccharomyces carlsbergensis. Eur. J. Biochem. 12: 583–592
Wang, C. H. & Krackov, J. K. (1962) The catabolic fate of glucose in Bacillus subtilis. J. Biol. Chem. 237: 3614–3622
Warburg, O. & Christian, W. (1932) Über ein neues Oxydationsferment und sein Absorptionsspektrum. Biochem. Zeitschr. 254: 438–458
Warburg, O. & Christian, W. (1936) Pyridin, der wasserstofübertragende Bestandteil von Gärungsfermenten. (Pyridin-Nucleotide). Biochem. Zeitschr. 287: 291–328
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This paper is adapted from a treatise by the same author, entitled: ‘The NADP(H) redox couple in yeast metabolism’, that was awarded the Kluyver prize 1986 by the Netherlands Society of Microbiology
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bruinenberg, P.M. The NADP(H) redox couple in yeast metabolism. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 52, 411–429 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00393469
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00393469