Abstract
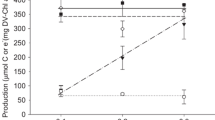
Air-grown cells of the marine diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum showed only 10% of the carbonic-anhydrase activity of air-grown Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Measurement of carbonic-anhydrase activity using intact cells and cell extracts showed all activity was intracellular in Phaeodactylum. Photosynthetic oxygen evolution at constant inorganic-carbon concentration but varying pH showed that exogenous CO2 was poorly utilized by the cells. Sodium ions increased the affinity of Phaeodactylum for HCO -3 and even at high HCO -3 concentrations sodium ions enhanced HCO -3 utilization. The internal inorganic-carbon pool (HCO -3 +CO2] was measured using a silicone-oil-layer centrifugal filtering technique. The internal [HCO -3 +CO2] concentration never exceeded 15% of the external [HCO -3 +CO2] concentration even at the lowest external concentrations tested. It is concluded that an internal accumulation of inorganic carbon relative to the external medium does not occur in P. tricornutum.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Hepes:
-
4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazineethane-sulfonic acid
References
Badger, M.R., Kaplan, A., Berry, J.A. (1980) Internal inorganic carbon pool of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii Evidence for a carbon dioxide concentrating mechanism. Plant Physiol. 66, 407–413
Beardall, J., Morris, I. (1975) Effect of environmental factors on photosynthesis patterns in Phaeodactylum tricornuutum (Bacillariophyceae). II. Effect of oxygen. J. Phycol. 11, 430–434
Beardall, J., Mukerji, D., Glover, H.E., Morris, I. (1976) The path of carbon is photosynthesis by marine phytoplankton. J. Phycol. 12, 409–417
Beardall, J., Raven, J.A. (1981) Transport of inorganic carbon and the CO2 concentrating mechanism in Chlorella emersonii (Chlorophyceae) J Phycol. 19, 134–141
Berry, J., Boynton, J., Kaplan, A., Badger, M. (1976) Growth and photosynthesis of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii as a function of CO2 concentration. Carnegie Inst. Washington yearb. 75, 423–432
Bliss, G.I., James, A.T. (1966) Fitting the rectangular hyperbola. Biometrics 22,573–602
Birmingham, B.C., Coleman, B. (1979) Measurement of carbon dioxide compensation points of freshwater algae. Plant Physiol. 64, 892–895
Briggs, C.E., Whittingham, C.P. (1952) Factors affecting the rate of photosynthesis of Chorella at low concentrations of carbon dioxide and in high illumination. New Phytol. 51, 236–249
Codd, G.A., Lord, J.M., Merrett, M.J. (1969) The glycolate oxidising enzyme of algae. FEBS Lett. 5, 341–342
Coleman, J.R., Berry, J.A., Togasaki, R.K., Grossman, R.A. (1984) Identification of extracellular carbonic anhydrase of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Physiol. 76, 472–477
Findenegg, G.R. (1976) Correlations between accessibility of carbonic anyhdrase for external substrate and regulation of photosynthetic use of CO2 and HCO3 by Scenedesmus obliquus. Z. Pflanzenphysiol. 79, 428–437
Findenegg, G.R., Fischer, K. (1978) Apparent photorespiration of Scenedesmus obliquus: increase during adaptation to low CO2 level. Z. Pflanzenphysiol. 89, 363–371
Hartree, E.F. (1972) A modification of the Lowry method that gives a linear photometric response. Anal. Biochem. 48, 422–427
Holdsworth, E.S., Bruck, K. (1977) Enzymes concerned with β-carboxylation in marine phytoplankter. Purfication and properties of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 182, 87–94
Kaplan, A., Volokita, M., Zenvirth, D, Reinhold, L. (1984) An essential role for sodium in the bicarbonate transporting system of the cyanobacterium Anabaena variabilis. FEBS Lett. 176, 166–168
Kerby, N.W., Raven, J.A. (1985) Transport and fixation of inorganic carbon by marine algae. Adv. Bot. Res. 11, 71–123
Kimpel, D.L., Togasaki, R.K., Miyachi, S. (1983) Carbonic anhydrase in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. I. Localization. Plant Cell Physiol. 24, 255–259
Lloyd, N.D.H., Canvin, D.T., Culver, D.A. (1977) Photosynthesis and photorespiration in algae. Plant Physiol. 59, 936–940
Marcus, Y., Volokita, M., Kaplan, A. (1984) The location of the transporting system for inorganic carbon and the nature of the form translocated in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. J. Exp. Bot. 35, 1136–1144
Miller, A.G., Canvin, D.T. (1985) Distinction between HCO -3 and CO2-dependent photosynthesis in the cyanobacterium Synechococcus leopoliensis based on the selective response of HCO -3 transport to Na+. FEBS Lett. 187, 29–32
Miller, A.G., Turpin, D.H., Canvin, D.T. (1984) Na+ requirement for growth, photosynthesis, and pH regulation in the alkalotolerant cyanobacterium Synechococcus leopoliensis. J. Bacteriol. 159, 100–106
Moroney, J.V., Husic, H.D., Tolbert, N.E. (1985) Effect of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors an inorganic carbon accumulation by Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Physiol. 79, 177–183
Patel, B.N., Merrett, M.J. (1986) Regulation of carbonic anhydrase activity, inorganic carbon uptake and photosynthetic biomass yield in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Planta (in press)
Provasoli, L., McLaughlin, J.J.A., Droop, M.R. (1957) The development of artificial media for marine algae. Arch. Mikrobiol. 25, 392–428
Rees, T.A.V. (1984) Sodium dependent photosynthetic oxygen evolution in a marine diatom. J. Exp. Bot. 35, 332–337
Reinhold, L., Volokita, M., Zenvirth, D., Reinhold, L. (1984) Is HCO -3 transport in Anabaena a Na+ symport? Plant Physiol. 76, 1090–1092
Shelp, B.J., Canvin, D.T. (1980) Utilization of exogenous inorganic carbon species in photosynthesis by Chlorella pyrenoidosa. Plant Physiol. 65, 774–779
Shelp, B.J., Canvin, D.T. (1985) Inorganic carbon accumulation and photosynthesis by chlorella pyrenoidosa. Can. J. Bot. 63, 1249–1254
Spalding, M.H., Ogren, W.L. (1983) Evidence for a saturable transport component in the inorganic carbon uptake of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. FEBS Lett. 154, 335–338
Spalding, M.H., Spreitzer, R.J., Ogren, W.L. (1983) Carbonic anhydrase-deficient mutant of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii requires elevated carbon dioxide concentration for photoautotrophic growth. Plant Physiol. 73, 268–272
Skirrow, G. (1985) The dissolved gases — carbon dioxide. In: Chemical oceanography, pp 1–181, Riley, J.P., Skirrow, G., eds. Academic Press, London New York
Wilbur, K.M., Anderson, N.G. (1948) Electrometric and colorimetric determination of carbonic anhydrase. J. Biol. Chem. 176, 147–154
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Patel, B.N., Merrett, M.J. Inorganic-carbon uptake by the marine diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum . Planta 169, 222–227 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00392318
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00392318