Abstract
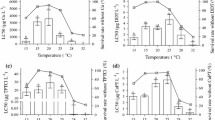
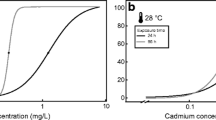
The developmental stages from megalopa to third crab of the blue crab Callinectes sapidus Rathbun were tested in 12 combinations of cadmium (0, 50, and 150 ppb) and salinity (10, 20, 30, and 40‰) at 25°C. A reduction in survival and a significant delay in development from megalopa to third crab occurred within each salinity regime in 50 ppb compared with the control. Comparison of the delay in development within each salinity regime revealed that the sublethal effect of cadmium was most pronounced in the salinities normally preferred by C. sapidus. A similar comparison within each cadmium concentration, however, showed that the developmental time from megalopa to third crab was approximately the same irrespective of salinity. The developmental stages from hatch to first crab of the mud-crab Rhithropanopeus harrisii (Gould) were examined in 63 combinations of cadmium (0, 50, and 150 ppb), salinity (10, 20, and 30‰), constant temperature (20°, 25°, 30°, and 35°C) and cycling temperature (20° to 25°C, 25° to 30°C, and 30° to 35°C). The results indicated that cycling temperatures may have a stimulating effect on survival of the larvae compared to constant temperatures, both in the presence and in the absence of cadmium. Effects of cadmium and salinity and their interaction on the survival of the larvae from zoeae to megalopa were documented at most of the temperatures by analyses of variance. The zoeal larvae were more susceptible to cadmium than the megalopa. Effects of different combinations of cadmium and salinity on the duration of larval development were assessed by a t-test.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Ayling, G.M.: Uptake of cadmium, zinc, copper, lead and chromium in the pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas, grown in the Tamar River, Tasmania. Wat. Res. 8, 729–738 (1974)
Bailey, N.T.J.: Statistical methods in biology, 200 pp. London: English University Press 1959
Ball, I.R.: The toxicity of cadmium to rainbow trout (Salmo gairdnerii Richardson). Wat. Res. 1, 805–806 (1967)
Benayoun, G., S.W. Fowler and B. Oregioni: Flux of cadmium through euphausiids. Mar. Biol. 27, 205–212 (1974)
Bengtsson, B.E., C.H. Carlin, Å. Larsson and O. Svanberg: Vertebral damage in minnows, Phoxinus phoxinus L., exposed to cadmium. Ambio 4, 166–168 (1975)
Benijts, C.C. and F. Benijts: The effect of low lead and zinc concentrations on the larval development of the mud-crab Rhithropanopeus harrisii Gould. In: Sublethal effects of toxic chemicals on aquatic animals, pp 43–52. Ed. by J.H. Koeman and J.J.T.W.A. Strik. Elsevier Scientific Publishing Co. 1975
Bookhout, C.G. and J.D. Costlow, Jr.: Nutritional effects of Artemia from different locations on larval development of crabs. Helgoländer wiss. Meersunters. 20, 435–442 (1970)
—, A.J. Wilson, T.W. Duke and J.I. Lowe: Effects of mirex on the larval development of two crabs. Wat. Air Soil Pollut. 1, 165–180 (1972)
Calabrese, A., R.S. Collier, D.A. Nelson and J.R. MacInnes: The toxicity of heavy metals to embryos of the American oyster Crassostrea virginica. Mar. Biol. 18, 162–166 (1973)
Christiansen, M.E. and J.D. Costlow, Jr.: The effect of salinity and cyclic temperature on larval development of the mud-crab Rhithropanopeus harrisii (Brachyura: Xanthidae) reared in the laboratory. Mar. Biol. 32, 215–221 (1975)
Costlow. J.D., Jr.: The effect of salinity and temperature on survival and metamorphosis of megalops of the blue crab Callinectes sapidus. Helgoländer wiss. Meeresunters. 15, 84–97 (1967)
— and C.G. Bookhout: The larval development of Callinectes sapidus Rathbun reared in the laboratory. Biol. Bull. mar. biol. Lab., Woods Hole 116, 373–396 (1959)
——: The effect of cyclic temperatures on larval development in the mudcrab Rhithropanopeus harrisii. In: Fourth European Marine Biology Symposium, pp 211–220. Ed. by D.J. Crisp. London: Cambridge Univ. Press 1971
—— and R.J. Monroe: Studies on the larval development of the crab, Rhithropanopeus harrisii (Gould). I. The effect of salinity and temperature on larval development. Physiol. Zoöl. 39, 81–100 (1966)
Eisler, R.: Cadmium poisoning in Fundulus heteroclitus (Pisces: Cyprinodontidae) and other marine organisms. J. Fish. Res. Bd Can. 28, 1225–1234 (1971)
—, G.E. Zaroogian and R.J. Hennekey: Cadmium uptake by marine organisms. J. Fish. Res. Bd Can. 29, 1367–1369 (1972)
Flick, D.F., H.F. Kraybill and J.M. Dimitroff: Toxic effects of cadmium: a review. Envir. Res. 4, 71–85 (1971)
Förster, U. and G. Müller: Heavy metal accumulation in river sediments: a response to en-environmental pollution. Geoforum 14, 53–61 (1973)
Friberg, L., M. Piscator and G. Nordberg: Cadmium in the environment, 168 pp. Cleveland, Ohio: CRC Press 1971
Holmes, C.W., E.A. Slade and C.J. McLerran: Migration and redistribution of zinc and cadmium in marine estuarine system. Envir. Sci. Technol. 8, 255–159 (1974)
Jones, M.B.: Synergistic effects of salinity, temperature and heavy metals on mortality and osmoregulation in marine and estuarine isopods (Crustacea). Mar. Biol. 30, 13–20 (1975)
Kerfoot, W.B. and S.A. Jacobs: Cadmium accrual in a combined wastewater treatment-aquaculture system. In: Proceedings of the First Annual NSF Trace Contaminants Conference, Ed. by W. Fulkerson, R.J. Van Hook and W.D. Schults. Oak Ridge, Tennesse: In press
Kinne, O.: The effects of temperature and salinity on marine and brackish water animals. II. Salinity and temperature salinity combinations. Oceanogr. mar. Biol. A. Rev. 2, 281–339 (1964)
Nordberg, G.F.: Health hazards of environmental cadmium pollution. Ambio 3, 55–66 (1974)
O'Hara, J.: Cadmium uptake by fiddler crabs exposed to temperature and salinity stress. J. Fish. Res. Bd Can. 30, 846–848 (1973)
Pavicić, J. and T. Järvenpää: Cadmium toxicity in adults and early larval stages of the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis Lam. In: Comparative studies of food and environmental contamination, pp 179–188. Vienna, Austria: International Atomic Energy Agency 1974
Vallee, B.L. and D.D. Ulmer: Biochemical effects of mercury, cadmium, and lead. A. Rev. Biochem 41, 91–128 (1972)
Vernberg, W.B., P.J. Decoursey and W.J. Padgett: Synergistic effects of environmental variables on larvae of Uca pugilator. Mar. Biol. 22, 307–312 (1973)
Williams, A.B.: Marine decapod crustaceans of the Carolinas. Fishery Bull. Fish Wildl. Serv. U.S. 65, 1–298 (1965)
Westernhagen, H. von, H. Rosenthal and K.R. Sperling: Combined effects of cadmium and salinity on development and survival of herring eggs. Helgoländer wiss. Meeresunters. 26, 416–433 (1974)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by O. Kinne, Hamburg
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rosenberg, R., Costlow, J.D. Synergistic effects of cadmium and salinity combined with constant and cycling temperatures on the larval development of two estuarine crab species. Mar. Biol. 38, 291–303 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00391369
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00391369