Summary
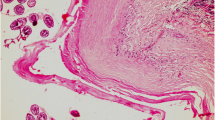
Scolices and brood capsules of healthy hydatid cysts from lungs of human patients were studied with histochemical and histoenzymatic methods.
The subtegumental and flame cells were specially rich in glycogen, RNA and some dehydrogenases such as SDH, MDH, NADH-reductase and G-6-PDH. The rostellar zone or invaginated pole, an area of marked contractile movements, showed intense activity in ATP'ase and simple esterase.
The so-called excretory pole shows strong activity in simple esterases, lipase, β-HBH, α-GDH and NADPH-reductase. Lipids are also abundant in this zone implying the important role of this metabolic path in the development of the parasite.
Intense activity in alkaline phosphatase was observed in cells associated to the calcareous corpuscles. The largest corpuscles were devoid of enzymatic activity. The enzyme could play some role in the calcification of the corpuscles.
Wide enzymatic variations are described according to morphology being orthoscolices the most rich in enzyme activity.
Accumulations of small cells surrounded by specialized cells on the germinal membrane are interpreted as the origin or “embryo” of brood capsules. Some enzymes detected in the wall of mature brood capsules depicted alternating types of cells. Some of them are positive for ATP'ase that may be related to active transport of substances across the brood capsule wall. The intense ATP'ase activity at the stalks of scolices may be similarly interpreted. However, a miosine-like activity is a more feasible explanation since this area showed striking contractile movements in vivo.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agosin, M.: Biochemistry and physiology of Echinococcus. Bull. WHO 39, 115–120 (1968)
Agosin, M., Aravena, L.: Studies on the metabolism of Echinococcus granulosus. III. Glycolysis with special reference to hexokinases and related glycolytic enzymes. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 34, 90–102 (1959)
Agosin, M., Brand, T. von, Rivera, G. F., McMahon, P.: Studies on the metabolism of Echinococcus granulosus. I. General chemical composition and respiratory reactions. Exp. Parasit. 6, 37–51 (1957)
Agosin, M., Repetto, U.: Studies on the metabolism of Echinococcus granulosus. IX. Protein synthesis in scolices. Exp. Parasit. 21, 195–208 (1967)
Agosin, M., Repetto, Y., Dicowsky, L.: Ribonucleic acid of Echinococcus granulosus protoscolices. Exp. Parasit. 30, 233–243 (1971)
Coutelen, F.: Recherches sur le système excréteur des hydatides echinococciques. Ann. Parasit. 9, 423–455 (1931)
Digenis, G. A., Thorson, R. E., Konyalian, A.: Cholesterol biosynthesis and lipid biochemistry in the scolex of Echinococcus granulosus. J. pharmac. Sci. 59, 676–679 (1970)
Frayha, G. J.: A study of the synthesis and absorption of cholesterol in hydatid cysts (Echinococcus granulosus). Short communication. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 27, 875–878 (1968)
Frayha, G. J.: Comparative metabolism of acetate in the taeniid tapeworms Echinococcus granulosus, E. multilocularis and Taenia hydatigena. Short communication. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 39, 167–170 (1971)
Holt, S. J., Hicks, R. M.: Studies on formaline fixation for electron microscopy and cytochemical staining purposes. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 11, 31–45 (1961)
Kilejian, A., Sauer, K., Schwabe, C.: Host-parasite relationships in echinococtosis. VIII. Infrared spectra and chemical composition of the hydatid cyst. Exp. Parasit. 12, 377–392 (1962)
Kilejian, A., Schinazi, L., Schwabe, C.: Host-parasite relationship in echinococcosis. V. Histochemical observations on Echinococcus granulosus. J. Parasit. 47, 181–188 (1961)
Lee, D. L., Rothman, A. H., Senturia, J. B.: Esterases in Hymenolepis and in Hydatigera. Exp. Parasit. 14, 285–295 (1963)
Lozano, W., Siri, A. M., Vercelli Retta, J., Reissenweber, N., Civila, E., Vignale, R.: Immunofluorescencia e hidatidosis. Evaluación de la técnica de anticuerpos fluorescentes para el diagnóstico immunológico de la hidatidosis. V. Congreso Latinoamericano de Microbiología Libro de Resúmes, p. 116. Punta del Este, Uruguay (1971)
Morseth, D. J.: Fine structure of the hydatid cyst and protoscolex of Echinococcus granulosus. J. Parasit. 43, 312–325 (1967)
Panaitesco, D., Bona, C.: Recherches histochimiques sur la structure du sable hydatique. Arch. roum. Path. exp. Microbiol. 24, 817–824 (1965)
Pearse, A. G. E.: Histochemistry. Theoretical and applied. Vol. 1 and 2. Third edition. London: J. & A. Churchill Ltd. 1968, 1972.
Schwabe, C. W., Schinazi, L. A.: Distribution of protonephridial flame cells in larval Echinococcus granulosus. J. Parasit. 44, 558–563 (1958)
Thorson, R. E., Digenis, G. A., Berntzen, A., Konyalian, A.: Biological activities of various lipid fractions from Echinococcus granulosus scolices on in vitro cultures of Hymenolepis diminuta. J. Parasit. 54, 970–973 (1968)
Vercelli Retta, J., Reissenweber, N., Lozano, W., Siri, A. M.: Histochemistry and histoenzymology of the hydatid cyst (Echinococcus granulosus Batsch, 1786). I. The germinal membrane. Z. Parasitenk. 48, 15–23 (1975)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reissenweber, N.J., Vercelli-Retta, J., Siri, A.M. et al. Histochemistry and histoenzymology of the hydatid cyst (Echinococcus granulosus Batsch, 1786). Z. F. Parasitenkunde 48, 25–33 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00389826
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00389826