Abstract
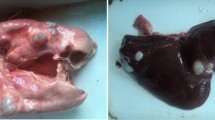
A total of 2100 sheep, slaughtered or spontaneously dead, from various areas of Kashmir valley were screened for the presence of hydatidosis. Out of 2100 cases, 85 were positive for hydatidosis. Histopathologicallly, the cyst wall consisted of the inner germinal, middle lamellated, and outer fibrous layer. Inflammatory reaction around the cyst was variable and was characterized by an inner zone of loosely arranged fibroblasts infiltrated with mononuclear cells and densely packed fibroblasts mixed with mononuclear cells; and an outer layer of concentrically packed fibrous connective tissue. Mast cell reaction was observed mainly in the bronchiolar, peribronchiolar, and inflammatory zones in the lungs; while in the liver, mast cells were noted in portal triads and bile ducts and were least evident in the vicinity of the cysts. Qualitative increase was observed for acid mucopolysaccharides in fibroblasts, inflammatory cells, and bronchial epithelium, especially hyperplastic epithelial cells. Masson’s trichrome revealed intense formation of collagen fibers in the pericystic connective tissue. The calcareous corpuscles of the protoscolices were distinct when stained with combined Alcian blue PAS and toluidine stains but were not visible when stained with H & E and Masson’s trichrome stains.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad ME, Rahim MA, Fatima MA (2011) Hydatid disease, a morbid drop needs awareness. Sudan Med J 47:1
Anwar Z (1997) The effect of echinococcosis on rabbit and sheep along with its control by indigenous plants of Pakistan. Ph.D. thesis. Department of Zoology, university of Punjab, Lahore
Anwar Z, Tanveer A, Bashir S (1999) Echinococcus granulosus: histopathology of naturally infected sheep liver. Punjab Univ. J Zool 14:105–111
Bancroft JD, Gamble M (2002) Theory and practice of histological techniques, 5th edn. Harcout Publishers Limited, London, pp 181–182
Barnes TS, Hinds LA, Jenkins DJ, Bielefeldt-Ohmann H, Lightowlers MW, Coleman GT (2011) Comparative pathology of pulmonary hydatid cysts in macropods and sheep. J Comp Pathol 144(2-3):113–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcpa.2010.07.003
Darzi MM, Mir MS, Khan M (2003) Concurrent anthracosis and parasitic pneumonia in a sheep. SKUAST-J Res 5:213–216
Da-Silva A (2010) Human echinococcosis: a neglected disease. Gastroenterol Res Pract 2010:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/583297
Endalew D, Nurradis I (2013) Prevalence and economic importance of echinococcosis in cattle slaughtered at North Gonder Elfora Abattoir. Eur. J Appl Sci 5:29–35
Gupta V, Kaira V, Sharma J, Sen R, Sangwaiya A (2014) Primary hydatid cyst of spleen: a rare entity. J Trop Dis 2:2
Humason GL (1979) Staining cellular elements. In animal tissue techniques, fourth Edn. San Francisco, W.H. Freeman pp. 319-320. Indian J Anim Res 37(1): 57–58
Ibrahim SEA, Gameel AA (2014) Pathological, histochemical and immunohistochemical studies of lungs and livers of cattle and sheep infected with hydatid disease. The 5th annual conference-agricultural and veterinary research - February 2014, Khartoum, Sudan, Conference Proceedings 2: 1–17
Jakubowski MS, Barnard DE (1971) Anaphylactic shock during operation for hydatid disease. Anesthesiol 34(2):197–199. https://doi.org/10.1097/00000542-197102000-00029
Kebede N, Mitiku A, Tilahun G (2009) Echinococcosis of slaughtered animals in Bahir Dar Abattoir, Northwestern Ethiopia. Trop Anim Health Prod 41(1):43–50. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11250-008-9152-3
Kilejian A, Kenneth S, Schwabe CW (1962) Host-parasite relationships in echinococcosis, VIII. Infrared spectra and chemical composition of the hydatid cyst. Exp Parasitol 12: 377–392
Kilejian A, Schwabe CW (1971) Host-parasite relationships in echinococcosis, VIII. Infrared spectra and chemical composition of the hydatid cyst. Exp Parasitol 12:377–392
Kul O, Yildiz K (2010) Multivesicular cysts in cattle: characterisation of unusual hydatid cyst morphology caused by Echinococcus granulosus. Vet Parasitol 170(1-2):162–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2010.01.045
Lascano EF, Coltorti EA, Varela-Diaz VM (1975) Fine structure of the germinal membrane of Echinococcus granulosus cysts. The. J Parasitol 61(5):853–860. https://doi.org/10.2307/3279219
Luna LG (1968) Manual of histologic staining methods of the Armed Forces, Institute of Pathology, 3rd edn. Mc Graw Hill Book Company, New York
Lupu NG, Velican D, Velican C, Olinescu V (1959) The action exerted by pneumoconiotic factors upon the acid mucopolysaccharide contents of pulmonary macrophages. Brit J Indutr Med 16:244
Maxova H, Herget J, Vízek M (2012) Lung mast cells and hypoxic pulmonary hypertension. Physiol Res 61(1):1–11
Migally NB, Tucker A, Greenlees K, Wright M, Zambernard J (1983) Density and ultrastructure of mast cells in lung vessels of aging rats exposed to and recovering from chronic hypoxia. Cell Tissue Res 232(3):601–608. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00216432
Mitrea IL (1998) Research regarding immunodiagnostics, immune response and immune prophylaxis in hydatidosis in ruminants [In Romanian]. PhD thesis, USAMV Bucharest, Romania
Morseth DJ (1967) Fine structure of the hydatid cyst and protoscolex of Echinococcus granulosus. J Parasitol 53(2):312–325. https://doi.org/10.2307/3276582
Ould CB, Schneegans F, Chollet JY, Jemli MH (2010) Prevalence and aspects of lesions of echinococcosis in camel in Northern Mauritania. Rev Elev Méd Vét Pays Trop 63:23–28
Pejler G, Ronnberg E, Waern I, Wernersson S (2010) Mast cell proteases: multifaceted regulators of inflammatory disease. Blood 115(24):4981–4990. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2010-01-257287
Rashed AA, Omer HM, Fouad MAH, Al-Shareef AMF (2004) The effect of severe cystic hydatidosis on the liver of a Najdi sheep with special reference to the cyst histology and histochemistry. J Egypt Soc Parasitol 34(1):297–304
Sakamoto T, Gutierrez C (2005) Pulmonary complications of cystic echinococcosis in children in Uruguay. Pathol Int 55(8):497–503. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1827.2005.01859.x
Sanjay OP, Tauro DI, Kilpadi K (2003) Intra-operative anaphylaxis caused by a pulmonary hydatid cyst. J Thor Cardiov Surg 19(2):128–129. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12055-003-0029-9
Solcan C, Solcan G, Ioniţă M, Hristescu DV, Mitrea IL (2010) Histological aspects of cystic echinococcosis in goats. Sci Parasitol 11(4):191–198
Taherkhani H (2001) Analysis of the Echinococcus granulosus laminated layer carbohydrates by Lectin blotting. Iran Biomed J 5(1):47–51
Thompson RCA, Lymbery AJ (1988) The nature, extent and significance of variation within the genus Echinococcus. Adv Parasitol 27:209–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-308X(08)60356-5
Torgerson PR (2003) The economic effects of echinococcosis. Acta Trop 85(2):113–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0001-706X(02)00228-0
Tucker A, Mcmurtry I, Alexander AF, Reeves JT, Grover RF (1977) Lung mast cell density and distribution in chronically hypoxic animals. J Appl Physiol 42(2):174–178
Veerappan A, O’Connor NJ, Brazin J, Reid AC, Jung A, McGee D, Summers B, Branch-Elliman D, Stiles B, Worgall S, Kaner RJ, Silver RB (2013) Mast cells: a pivotal role in pulmonary fibrosis. DNA Cell Bio 32(4):206–218. https://doi.org/10.1089/dna.2013.2005
Verma Y, Swamy M (2009) Prevalence and pathology of hydatidosis in buffalo liver. Buffalo Bull 28(4):207–211
Wygrecka M, Dahal BK, Kosanovic D, Petersen F, Taborski B, Gerlach S, Didiasova M, Zakrzewicz D, Preissner KT, Schermuly RT, Philipp M (2013) Mast cells and fibroblasts work in concert to aggravate pulmonary fibrosis role of transmembrane SCF and the PAR-2/PKC-a/Raf-1/p44/42 signaling pathway. Am J Pathol 182(6):2094–2108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajpath.2013.02.013
Young ED (2005) Brucella species. In: Mandell, Douglos, Bennett, editors. Principles and practice of infectious disease, 6th edn. Churchill Livingstone, Pensylvania, pp 3290–3292
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors do not have any conflict of interest with themselves or with any other organization.
Ethical approval
During all stages of our research, all applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. In addition, this article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors. There has been no significant financial support for this research work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beigh, A.B., Darzi, M.M., Bashir, S. et al. Pathological and histochemical studies of the effects of cystic echinococcosis in sheep. Comp Clin Pathol 27, 407–412 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-017-2606-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-017-2606-0