Abstract
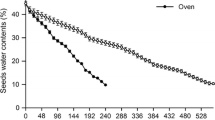
Commercially obtained fruits of Corylus avellana exhibit the characteristic loss of dormancy of this seed following chilling under moist conditions. The activities of cytosolic and organellar enzymes of pentose phosphate pathway in cotyledonary tissue were assayed throughout stratification and over a similar period in damp vermiculite at 20° C. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PDH) and 6-phosphogluconic acid dehydrogenase (6PGDH) were both found in cytosolic extracts in all treatments; only 6PGDH was present in the organellar fraction.
The enzyme activities monitored in seeds at 20° C remained relatively constant over the course of the investigation except in the case of cytosolic 6PGDH where it is suggested an inhibitor of the enzyme accumulated. This inhibitor was removed by the partial purification procedure. Increases in the activities of the enzymes occurred during stratification, the major increase coinciding exactly with dormancy breakage but prior to the initiation of germination. The marked increase in G6PDH and 6PGDH concurrent with the change in germination potential of the chilled seed may have considerable biochemical significance in breaking down the dormant state.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- G6P:
-
glucose-6-phosphate
- G6PDH:
-
glucose-6 phosphate dehydrogenase
- NADP:
-
nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
- 6 PGDH:
-
6-phosphogluconic acid dehydrogenase
- PPP:
-
pentose phosphate pathway
References
Bradbeer, J.W., Colman, B.: Studies in seed dormancy. I. The metabolism of [2-14C]acetate by chilled seeds of Corylus avellana. New Phytol. 66, 5–15 (1967)
Brown, A.P., Wray, J.L.: Correlated changes of some enzyme activities and cofactor and substrate contents of Pea cotyledon tissue during germination. Biochem. J. 108, 437–444 (1968)
Colman, B.: Metabolic Aspects of Dormancy. Ph. D. Thesis, University of Wales 1961
Eggleston, L.V., Krebs, H.A.: Regulation of pentose phosphate cycle. Biochem. J. 138, 425–435 (1974)
Filner, P., Wray, J.L., Varner, J.E.: Enzyme induction in higher plants. Science 165, 358–367 (1969)
Frankland, B., Wareing, P.F.: Hormonal regulation of seed dormancy in Hazel (Corylus avellana) and Beech (Fagus sylvatica). J. Exp. Bot. 17, 596–611 (1966)
Gosling, P.G., Ross, J.D.: Characterisation of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase and 6-phosphogluconic acid dehydrogenase from Hazel cotyledons. Phytochemistry 18, 1441–1445 (1979)
Horecker, B.L.: Pathways of carbohydrate metabolism and their physiological significance. J. Chem. Edu. 42, 244–253 (1965)
Kovacs, M.I.P., Simpson, G.N.: Dormancy and enzyme levels in seeds of wild oats. Phytochemistry 15, 455–458 (1976)
La Croix, L.J., Jaswal, A.S.: Metabolic changes in after-ripening seed of Prunus cerasus. Plant Physiol. 42, 479–480 (1967)
Roberts, E.H.: Seed Dormancy and Oxidation Processes. S.E.B. Symposia 23, 161–192 (1969)
Roberts, E.H.: Oxidative processes and the control of seed germination. In: Seed Ecology, pp. 189–218. Heydecker, W. ed.
Roberts, E.H., Smith, R.D.: Dormancy and the pentose phosphate pathway. In: The Physiology and Biochemistry of Seed Dormancy and Germination, Khan, A.A., ed. pp. 385–411. Amsterdam Elsevier 1977
Ross, J.D., Bradbeer, J.W.: Concentrations of gibberellin in chilled hazel seeds. Nature (London) 220, 85–86 (1968)
Ross, J.D., Bradbeer, J.W.: Studies in seed dormancy. VI. The effects of growth retardants on the gibberellin content and germination of chilled seeds of Corylus avellana. Planta 100, 303–308 (1971)
Sedmak, J.H., Grossberg, S.E.: A rapid sensitive and versatile assay for protein using Coomassie brilliant blue G 250. Anal. Biochem. 79, 544–552 (1977)
Simcox, P.D., Dennis, D.T.: 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase isoenzymes from the developing endosperm of Riccinus communis. Plant Physiol. 62, 287–290 (1978)
Williams, P.M., Ross, J.D., Bradbeer, J.W.: Studies in seed dormancy. VII. The abscisic acid content of the seeds and fruits of Corylus avellana L. Planta 110, 303–310 (1973)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gosling, P.G., Ross, J.D. Pentose phosphate metabolism during dormancy breakage in Corylus avellana L.. Planta 148, 362–366 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00388124
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00388124