Summary
-
1.
The distribution of K, Ca, Sr and P in the vegetative organs of Zea Mays was examined.
-
2.
The ions were detected localized in cryostat sections with the X-ray microanalyzer.
-
3.
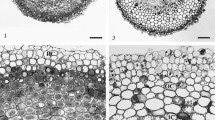
In meristems (root tip, intercalary meristem in internodes) P is distributed rather uniformly, and K is mainly accumulated in tissues which are about to undergo or are undergoing differentiation. The content of Ca and Sr in meristematic cells is low.
-
4.
Root hairs accumulate ions intensively.
-
5.
The vascular bundle of the root and the big bundles in the sheath and midrib of the oldest leaves show a high ion content.
-
6.
In the vascular bundles, the ions are mainly localized in sclerenchyma and xylem. The phloem always contains much P and in part it also contains a considerable amount of K.
-
7.
The ions are mainly localized to the cell walls in differentiated cells. Cations are partly adsorbed to cell walls or may be bound chemically. Part of the Ca and Sr deposited in cell walls is found as phosphate.
-
8.
A barrier to lateral transport of ions across the root is located in the plasmalemma of the outermost cortex layer. After the transfer across the barrier, ions move in the symplams to the vascular tissue.
-
9.
Translocation of K and P in the root is basipetal in xylem and acropetal in phloem; translocation of Ca and Sr is mainly basipetal.
-
10.
The ions are accumulated in the oldest leaves. P and K may be retranslocated from these leaves in the phloem and later on redistributed to younger leaves.
-
11.
The deposition of ions in the epidermis and bundlesheaths of the shoot is interpreted as salt exeretion.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Bell, C. W., and O. Biddulph: Translocation of calcium: Exchange versus mass flow. Plant Physiol. 38, 610–614 (1963).
Biddulph, O., S. F. Biddulph, F. Cory, and H. Koontz: Circulation patterns for P32, S35, and Ca45 in the bean plant. Plant Physiol. 33, 293–300 (1958).
—, and J. Markle: Translocation of radiophosphorus in the phloem of the cotton plant. Amer. J. Bot. 31, 65–70 (1944).
Bieleski, R. L.: Accumulation of phosphate, sulfate and sucrose by excised phloem tissues. Plant Physiol. 41, 447–454 (1966).
Brouwer, R.: Ion absorption and transport in plants. Ann. Rev. Plant Physiol. 16, 241–266 (1965).
Bukovac, H. J., and S. H. Wittwer: Absorption and mobility of foliar applied nutrients. Plant Physiol. 32, 428–435 (1957).
Charles, A.: Uptake of dyes into cut leaves. Nature (Lond.) 171, 435–436 (1953).
Clowes, F. A. L.: Nucleic acids in root apical meristems of Zea. New Phytologist 55, 29–35 (1956).
— Apical meristems. Oxford: Blackwell 1961.
Emmert, F. H.: Forces involved in retention and movement of non-metabolic strontium in Phaseolus vulgaris. Plant and Soil 22, 136–142 (1965).
Esau, K.: Ontogeny of the vascular bundle in Zea Mays. Hilgardia 15, 327–368 (1943).
—: Plant anatomy. New York: John Wiley & Sons 1953.
Evans, E. C.: Polar transport of calcium in the primary root of Zea Mays. Science 144, 174–177 (1964).
Frey-Wyssling, A.: Die pflanzliche Zellwand. Berlin-Göttingen-Heidelberg: Springer 1959.
Gahan, P. B., and A. K. Rajan: The autoradiographic detection of ions in plant tissues. J. exp. Bot. 17, 34–43 (1966).
Gielink, A. J., G. Sauer, and A. Ringoet: Histoautoradiographic localization of calcium in oat plant tissues. Stain Technol. 41, 281–286 (1966).
Handley, R., and R. Overstreet: Uptake of calcium and chlorine in roots of Zea Mays: Plant Physiol. 36, 766–769 (1961).
——: Uptake of strontium by roots of Zea Mays. Plant Physiol. 38, 180–184 (1963).
Husain, S. M., and A. J. Linck: Relationship of apical dominance to the nutrient accumulation pattern in Pisum sativum var. Alaska. Physiol. Plant. 19, 992–1010 (1966).
James, W. O., and N. L. Penston: Studies of the physiological importance of the mineral elements in plants. IV. The quantitative distribution of potassium in the potato plant. Ann. Bot. 47, 279–293 (1933).
Kaufmann, P. B., S. J. Cassell, and P. A. Adams: On nature of intercalary growth and cellular differentiation in internodes of Avena sativa. Bot. Gaz. 126, 1–13 (1965).
Läuchli, A.: Über die Aufnahme von Strontium durch höhere Pflanzen. Ber. Schweiz. bot. Ges. 72, 147–197 (1962).
—: Cryostat technique for fresh plant tissues and its application in enzyme histochemistry. Planta (Berl.) 70, 13–25 (1966).
—: Nachweis von Calcium-Strontiumablagerungen im Fruchtstiel von Pisum sativum mit der Röntgen-Mikrosonde. Planta (Berl.) 73, 221–227 (1967).
—, and H. Schwander: X-ray microanalyser study on the localization of minerals in native plant tissue sections. Experientia (Basel) 22, 503–505 (1966).
Lüttge, U.: Mikroautoradiographischer Nachweis der Aufnahme von 35SO4" in die Wurzelhaare von Ahornkeimlingen. Naturwissenschaften 51, 296–297 (1964).
—, and G. G. Laties: Dual mechanism of ion absorption in relation to long distance transport in plants. Plant Physiol. 41, 1531–1539 (1966).
—, u. J. Weigl: Zur Mikroautoradiographie wasserlöslicher Substanzen. Planta (Berl.) 64, 28–36 (1965).
Myttenaere, C., et J. M. Mousny: Application de la méthode histoautoradiographique à l'étude de la localisation histologique du calcium et du strontium présents dans les tissues végétaux. Int. J. appl. Radiat. 17, 287–292 (1966).
O'Brien, T. P. O., N. Feder, and M. E. McCully: Polychromatic staining of plant cell walls by toluidine blue O. Protoplasma (Wien) 59, 368–373 (1964).
Overstreet, R., and L. Jacobson: The absorption by roots of rubidium and phosphate ions at extremely small concentrations as revealed by experiments with Rb86 and P32 prepared without intert carrier. Amer. J. Bot. 33, 107–112 (1946).
Penston, N. L.: Studies of the physiological importance of the mineral elements in plants. III. A study by microchemical methods of the distribution of potasium in the potato plants. Ann. Bot. 45, 673–692 (1931).
Schilling, G.: Der Einfluß von Alterungsprozessen auf die Verteilung von Calcium und Strontium im Erbsenblatt. Biol. Zbl. 80, 33–36 (1961).
Steward, F. C., and F. K. Millar: Salt accumulation in plants: A reconsideration of the role of growth and metabolism. Symp. Soc. Exp. Biol. 8, 367–406 (1954).
Stout, P. R., and D. R. Hoagland: Upward and lateral movement of salt in certain plants as indicated by radioactive isotopes of potassium, sodium and phosphorus absorbed by roots. Amer. J. Bot. 26, 320–324 (1939).
Sutcliffe, J. F.: Mineral salts absorption in plants. Oxford: Pergamon Press 1962.
Tousimis, A. J.: Scanning electron probe microanalysis of biological specimens. Biomed. Sci. Instr. 1, 249–261 (1963).
Weigl, J., u. U. Lüttge: Mikroautoradiographische Untersuchungen über die Aufnahme von 35SO4" durch Wurzeln von Zea Mays L. Die Funktion der primären Endodermis. Planta (Berl.) 59, 15–28 (1962).
Wiebe, H. H., and P. J. Kramer: Translocation of radioactive isotopes from various regions of roots of barley seedlings. Plant Physiol. 29, 342–348 (1954).
Ziegler, H.: Untersuchungen über die Leitung und Sekretion der Assimilate. Planta (Berl.) 47, 447–500 (1956).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Läuchli, A. Untersuchungen über Verteilung und Transport von Ionen in Pflanzengeweben mit der Röntgen-Mikrosonde. Planta 75, 185–206 (1967). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00386319
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00386319