Abstract
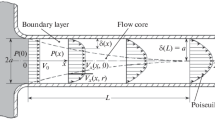
A two-dimensional solution for the velocity and pressure distributions in steady, laminar, isothermal flow of an ideal gas in a long tube is obtained as a double perturbation expension in β, the radius to length ratio, and ε, the relative pressure drop. It is found that simple approximations estimate the exact flow rate-pressure drop relationship accurately.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.B. Bird, W.E. Stewart, and E.N. Lightfoot, Transport Phenomena, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. New York (1960) p. 468.
Ali Bulent Cambel, “Compressible Flow”, Chapter 8 in Handbook of Fluid Dynamics, Victor L. Streeter, Ed., McGraw-Hill Book Company, Inc., New York (1961), pp. 8–38-8–62.
R.B. Bird et al., op. cit., p. 92.
R.B. Bird et al., op. cit., p. 484.
R.B. Bird et al., op. cit., p. 314.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prud'Homme, R.K., Chapman, T.W. & Bowen, J.R. Laminar compressible flow in a tube. Appl. Sci. Res. 43, 67–74 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00385729
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00385729