Abstract
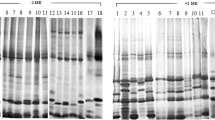
Since there is some question as to whether or not legumin is glycosylated, this storage protein was isolated by various procedures from developing cotyledons of Pisum sativum L. supplied with [14C]-labeled glucosamine and analyzed by sodium dodecylsulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Legumin isolated by the classical method of Danielsson [(1949) Biochem. J. 44, 387–400] a procedure in which globulins extracted with a buffered salt solution are precipitated with ammonium sulfate (70% saturation) and legumin separated from vicilin by isoelectric precipitation, was labeled. The glucosamine incorporated into legumin was associated with low-molecular-weight polypeptides. In contrast, legumin isolated by the method of Casey [(1979) Biochem. J. 177, 509–520], a procedure where legumin is prepared by zonal isoelectric precipitation from globulins precipitated with 40–70% ammonium sulfate, was not labeled. However, the globulin fraction precipitated with 40% ammonium sulfate was labeled and the radioactive glucosamine was associated with low-molecular-weight polypeptides. Legumin isolated from protein bodies [Thomson et al. (1978) Aust. J. Plant Physiol. 5, 263–279] was not extensively labeled. However, the saltinsoluble fraction of protein body extracts was labeled and the radioactivity was associated with low-molecular-weight polypeptides. These results indicate that protein bodies contain a glycoprotein of low-molecular-weight that co-purifies with legumin isolated by the method of Danielsson but that is discarded when isolation methods developed more recently are used.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bailey, C.J., Boulter, D. (1970) The structure of legumin, a storage protein of broad bean (Vicia faba) seeds. Eur. J. Biochem. 17, 460–466
Basha, S.M.M., Beevers, L. (1975) The development of proteolytic activity and protein degradation during germination of Pisum sativum L. Planta 124, 77–87
Basha, S.M.M., Beevers, L. (1976) Glycoprotein metabolism in the cotyledons of Pisum sativum during development and germination. Plant Physiol. 57, 93–97
Beevers, L., Mense, R.M. (1977) Glycoprotein biosynthesis in cotyledons of Pisum sativum L.: Involvement of lipid-linked intermediates. Plant Physiol. 60, 703–708
Braconnot, H. (1827) Memoire sur un principe particular aux graines de la famille des legumineuses, et analyse des pois et des haricots. Ann. Chim. Phys. 34, 68–85
Browder, S.K., Beevers, L. (1978) Characterization of the glycopeptide bond in legumin from Pisum sativum L. FEBS Lett. 89, 145–148
Casey, R. (1979) Immunoaffinity chromatography as a means of purifying legumin from Pisum (pea) seeds. Biochem. J. 177, 509–520
Croy, R.R.D., Derbyshire, E., Krishma, T.G., Boulter, D. (1979) Legumin of Pisum sativum and Vicia faba. New Phytologist 83, 29–35
Danielsson, L.E. (1949) Seed globulins of the gramineae and leguminosae. Biochem. J. 44, 387–400
Davey, R.A., Dudman, W.F. (1979) The carbohydrate of storage glycoproteins from seeds of Pisum sativum: Characterization and distribution of component polypeptides. Aust. J. Plant Physiol. 6, 435–447
Davies, H.M., Delmer, D.P. (1979) Seed reserve-protein glycosylation in an in vitro preparation from developing cotyledons of Phaseolus vulgaris. Planta 146, 513–520
Derbyshire, E., Wright, D.J., Boulter, D. (1976) Legumin and vicilin, storage proteins of legume seeds. Phytochemistry 15, 3–24
Gatehouse, J.A., Croy, R.R.D., Boulter, D. (1980) Isoelectric-focusing properties and carbohydrate content of pea (Pisum sativum) legumin. Biochem. J. 185, 497–503
Larkins, B.A., Hurkman, W.J. (1978) Synthesis and deposition of zein in protein bodies of maize endosperm. Plant Physiol. 62, 256–263
Lowry, O.H., Rosenbrough, N.J., Farr, A.L., Randall, R.J. (1951) Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 193, 265–275
Millerd, A. (1975) Biochemistry of legume seed proteins. Ann. Rev. Plant Physiol. 26, 53–72
Osborne, T.B., Campbell, G.F. (1898) Proteids of the pea. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 20, 348–362
Roberts, R.M., Pollard, W.E. (1975) The incorporation of D-glucosamine into glycolipids and glycoproteins of membrane preparations from Phaseolus aureus hypocotyls. Plant Physiol. 55, 431–436
Scholz, G., Richter, J., Manteuffel, R. (1974) Studies on seed globulins from legumes. I. Separation and purification of legumin and vicilin from Vicia faba L. by zone precipitation. Biochem. Physiol. Pflanzen 166, 163–172
Thomson, J.A., Schroeder, H.E., Dudman, W.F. (1978) Cotyledonary storage proteins in Pisum sativum I. Molecular heterogeneity. Aust. J. Plant Physiol. 5, 263–279
Weber, K., Osborn, M. (1969) The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J. Biol. Chem. 244, 4406–4412
Weyl, T. (1876) Beiträge zur Kenntniss thierischer und pflanzlicher Eiweisskörper. Pflügers Arch. 12, 635–638
Weyl, T. (1877) Beitrage zur Kenntniss thierischer und pflanzlicher Eiweisskörper. Z. Physiol. Chem. 1, 72–100
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hurkman, W.J., Beevers, L. What is pea legumin — Is it glycosylated?. Planta 150, 82–88 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00385618
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00385618