Summary
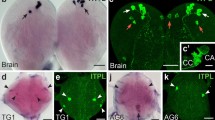
In the pond snail Lymnaea stagnalis, the growth regulating system consists of (1) about 200 neuroendocrine light green cells, located in four clusters in the cerebral ganglia, and (2) the paired canopy cells, located in the lateral lobes. These cells express genes encoding the molluscan insulin-related peptides (MIPs). Six MIP genes have previously been identified. Four of these (I, II, III and V) are expressed in the light green cells and the canopy cells. The MIP-VI gene is a pseudogene. In the present in situ hybridization study, using oligonucleotide probes specific to the transcripts of MIP-I,-II,-III,-IV, and-V, no signal was obtained with the MIP-IV probe, indicating that gene IV is also a pseudogene. With the other four probes, two types of light green cells were distinguished. Type-A cells express all four MIP genes, whereas type-B cells do not (or only faintly) express the MIP-I gene. Gene III is relatively strongly expressed in type-B cells. Genes II and V are moderately expressed in both cell types. Type-A cells are mainly located in the periphery of the clusters, whereas type-B cells are present in the center. The canopy cell resembles type-A light green cells. The expression levels of the MIP-II and MIP-V genes are low in the canopy cell. The expression pattern of the MIP genes correlates with the staining pattern of the anti-MIP-C antibody, which has been raised to a synthetic C-fragment shared by MIP-I,-II and-V. Type-A cells stain more intensely with the antibody than type-B cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benjamin PR, Swindale NV, Slade CT (1976) Electrophysiology of identified neurosecretory neurones in the pond snail Lymnaea stagnalis (L.) In: Salanki J (ed) Neurobiology of invertebrates — Gastropoda brain. Akadémiai Kiadó, Budapest, pp 85–100
Boer HH (1965) A cytological and cytochemical study of neurosecretory cells in Basommatophora, with particular reference to Lymnaea stagnalis (L.). Arch Neerl Zool 16:313–386
Boer HH, Groot C, Jong-Brink M de, Cornelisse CJ (1977) Polyploidy in the freshwater snail Lymnaea stagnalis (Gastropoda, Pulmonata). A cytophotometric analysis of the DNA in neurons and some other cell types. Neth J Zool 27:245–252
De With ND, Slootstra JW, Schors RC van der (1988) The bioelectrical activity of the body wall of the pulmonate freshwater snail Lymnaea stagnalis: effects of neurotransmitters and the sodium influx stimulating neuropeptides. Gen Comp Endocrinol 70:216–223
Dirks RW, Raap AK, Van Minnen J, Vreugdenhil E, Smit AB, Van der Ploeg M (1989) Detection of mRNA molecules coding for neuropeptide hormones of the pond snail Lymnaea stagnalis by radioactive and non-radioactive in situ hybridization; a model study for mRNA detection. J Histochem Cytochem 37:7–14
Geraerts WPM (1976) Control of growth by the neurosecretory hormone of the light green cells in the freshwater snail Lymnaea stagnalis. Gen Comp Endocrinol 29:61–71
Geraerts WPM, Smit AB, Joosse J (1989) Peptide messenger in evolution: the invertebrate contribution. Proc. 4th ENEA Conference, Santiago de Compostella, Spain, 28–30 June 1989, pp 3–14
Geraerts WPM, Smit AB, Li KW, Vreugdenhil E, Heerikhuizen H van (1990) Neuropeptide gene families that control reproductive behaviour and growth in molluscs. In: Osborne NN (ed) Current aspects of the neurosciences. MacMillan, London, pp 255–304
Girbau M, Gomez JA, Lesniak MA, Pablo F de (1987) Insulin and insulin-like growth factor I both stimulate metabolism, growth, and differentiation in the postneurula chick embryo. Endocrinology 121:1477–1482
Herrington CS, Graham AD, Flannery DMJ, Burns J, Mc Gee JO'D (1990) Discrimination of closely homologous HPV types by non isotopic in situ hybridization: definition and derivation of tissue melting temperatures. Histochem J 22:545–554
Heyner S, Smith RM, Schultz GA (1989) Temporally regulated expression of insulin and insulin-like growth factors and their receptors in early mammalian development. Bioessays 11:171–176
Joosse J (1964) Dorsal bodies and dorsal neurosecretory cells of the cerebral ganglia of Lymnaea stagnalis (L.) Arch Neerl Zool 15:1–103
Joosse J (1988) The hormones of molluscs. In: Laufer H, Downer GH (eds) Invertebrate endocrinology, vol 3. Endocrinology of selected invertebrate types. Liss, New York, pp 89–140
Manialis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J (1982) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
Mizoguchi A, Hatta M, Sato S, Nagasawa H, Suzuki A, Ishizaki H (1990) Developmental change of bombyxin content in the brain of the silk moth Bombyx mori. J Insect Physiol 36:655–664
Puro DG, Agardh E (1984) Insulin mediated regulation of neuronal maturation. Science 225:1170–1172
Recio-Pinto E, Ishii DN (1988) Insulin and related growth factors: effects on the nervous system and mechanism for neurite growth and regeneration. Neurochem Int 12:397–414
Roubos EW (1985) Intracellular and extracellular control of neuroendocrine activity in the freshwater snail Lymnaea stagnalis. In: Lofts B, Holmes WN (eds) Current trends in comparative endocrinology. Hong Kong University Press, Hong Kong, pp 47–49
Roubos EW, Van der Wal-Divendal RM (1980) Ultrastructural analysis of peptide-hormone release by exocytosis. Cell Tissue Res 207:267–275
Roubos EW, Van der Wal-Divendal RM (1982) Sensory input to growth stimulating neuroendocrine cells of Lymnaea stagnalis. Cell Tissue Res 227:371–386
Smit AB (1990) The organization, neuronal expression and evolution of a family of insulin-related genes in the mollusc Lymnaea stagnalis. Thesis, Vrije Universiteit, Amsterdam
Smit AB, Vreugdenhil E, Ebberink RHM, Geraerts WPM, Klootwijk J, Joosse J (1988) Growth-controlling molluscan neurons produce the precursor of an insulin-related peptide. Nature 331:535–538
Straus DS (1984) Growth-stimulatory actions of insulin in vitro and in vivo. Endocrin Rev 5:356–369
Van Heumen WRA, Roubos EW (1990) Ultrastructural evidence for synthesis, storage and relase of insulin-related peptides in the central nervous system of Lymnaea stagnalis. Neuroscience 39:493–500
Van Minnen J, Schallig HDFH (1990) Demonstration of insulinrelated substances in the central nervous systems of pulmonates and Aplysia californica. Cell Tissue Res 260:381–386
Van Minnen J, Reichelt D, Lodder JC (1979) An ultrastructural study of the neurosecretory canopy cell of the pond snail Lymnaea stagnalis (L), with the use of the horseradish peroxidase tracer technique. Cell Tissue Res 204:453–462
Van Minnen J, Smit AB, Joosse J (1989) Central and peripheral expression of genes coding for egg laying inducing and insulin-related peptides in a snail. Arch Histol Cytol 52 [Suppl]:241–252
Wendelaar Bonga SE (1970) Ultrastructure and histochemistry of neurosecretory cells and neurohaemal areas in the pond snail Lymnaea stagnalis. Z Zellforsch 108:190–224
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meester, I., Ramkema, M.D., van Minnen, J. et al. Differential expression of four genes encoding molluscan insulin-related peptides in the central nervous system of the pond snail Lymnaea stagnalis . Cell Tissue Res 269, 183–188 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00384739
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00384739