Summary
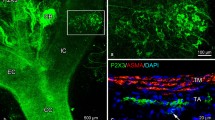
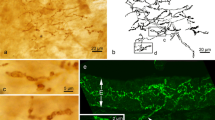
The ontogeny of substance P, CGRP (calcitonin gene-related peptide), and VIP (vasoactive intestinal polypeptide) containing nerve fibers in the carotid labyrinth of the bullfrog, Rana catesbeiana, was examined by the peroxidase-antiperoxidase method. The time of appearance of these three peptides was different for each. First, CGRP fibers appeared in the wall of the carotid arch and external carotid arteries, and in a thin septum between these two arteries at an early stage of larval development (stage III). At stage V, substance P immunoreactive fibers appeared, and VIP fibers were detected at the early metamorphic stage (stage XXII). Up to the completion of metamorphosis, the number of these fibers remained low. From 1 to 5 weeks after metamorphosis, substance P, CGRP, and VIP fibers increased in number to varying degrees. By 8 weeks after metamorphosis, the distribution and abundance of these fibers closely resembled those of the adults. Some CGRP and VIP immunoreactive glomus cells were found at the stages immediately before and after the completion of metamorphosis. These findings suggest that substance P, CGRP, and VIP fibers during larval development and metamorphosis may be nonfunctional, and start to participate in vascular regulation only after metamorphosis. The transient CGRP and VIP in some glomus cells may be important for the development of the labyrinth, or may take part in vascular regulation through the close apposition of the glomus and smooth muscle cells (g-s connection).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams WE (1958) The comparative morphology of the carotid body and carotid sinus. Thomas, Springfield, Illinois, pp 202–214
Brain SD, Williams TJ, Tippins JR, Moris HR, MacIntyre I (1985) Calcitonin gene-related peptide is a potent vasodilator. Nature 313:54–56
Buijs RM, Velis DN, Swaab DF (1980) Ontogeny of vasopressin and oxytocin in the fetal rat: early vasopressinergic innervation of the fetal brain. Peptides 1:315–324
Carman JB (1955) The carotid labyrinth in the Hyla aurea, with a note on that in Leiopelma hochstettri. J Anat 89:503–525
Carman JB (1967a) The carotid labyrinth in the anuran Breviceps mossambicus. Trans R Soc New Zeal Zool 10:1–15
Carman JB (1967b) The morphology of the carotid labyrinth in Bufo bufo and Leiopelma hochstetteri. Trans R Soc New Zeal Zool 10:71–76
Cho HJ, Shiotani Y, Shiosaka S, Inagaki S, Kubota T, Kiyama H, Umegaki K, Tateishi K, Hashimura E, Hamaoka T, Tohyama M (1983) Ontogeny of cholecystokinin-8-containing neuron system of the rat: an immunohistochemical analysis. I. Forebrain and upper brain stem. J Comp Neurol 218:25–41
Edvinsson L, Uddman R (1982) Immunohistochemical localization and dilatory effects of substance P on human cerebral vessels. Brain Res 232:466–471
Emson PC, Girbert RFT, Loren I, Fahrenkrug J, Sundler F, Schaffalitzky de Muckadell OB (1979) Development of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) containing neurons in the rat brain. Brain Res 177:437–444
Hara Y, Shiosaka S, Senba E, Sakanaka M, Inagaki S, Takagi, Kawai Y, Takatsuki K, Matsuzaki T, Tohyama M (1982) Ontogeny of the neurotensin-containing neuron system of the rat: Diencephalon. J Comp Neurol 208:177–195
Heistad DD, Marcus MI, Said SI, Gross PM (1980) Effect of acetylcholine and vasoactive intestinal peptide on cerebral blood flow. Am J Physiol 238:H73-H80
Ishida S (1954) So-called carotic body of the Amphibia. Igaku Kenkyu (Fukuoka) 24:1024–1050
Ishii K, Ishii K (1973) Fiber composition and derivation of afferent and efferent nerve fibers in the carotid nerve innervating the carotid labyrinth of the toad. Tohoku J Exp Med 109:323–337
Ishii K, Kusakabe T (1982) The glomus cell of the carotid labyrinth of Xenopus laevis. Cell Tissue Res 224:459–463
Ishii K, Oosaki T (1969) Fine structure of the chemoreceptor cell in the amphibian carotid labyrinth. J Anat 104:263–280
Ishii K, Honda K, Ishii K (1966) The function of the carotid labyrinth in the toad. Tohoku J Exp Med 88:103–116
Kameda Y (1990) Ontogeny of the carotid body and glomus cells distributed in the wall of the common carotid artery and its branches in the chicken. Cell Tissue Res 261:525–537
Khachaturin HK, Sladek JR Jr (1980) Simultaneous monoamine histofluorescence and neuropeptide immunohistochemistry: III. Ontogeny of catecholamine varicosities and neurophysin neurons in the rat supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei. Peptides 1:77–95
Kobayashi S (1971) Comparative cytological studies of the carotid body. 2. Ultrastructure of the synapse on the chief cell. Arch Histol Jpn 33: 397–420
Kobayashi S, Murakami T (1975) Scanning electron microscopic observation of the fine three-dimensional distribution of the blood vessels in the frog carotid labyrinth. In: Purves MJ (ed) The peripheral chemoreceptors. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 301–313
Kondo H, Yamamoto M (1988) Occurrence, ontogeny, ultrastructure and some plasticity of CGRP (calcitonin gene-related peptide)-immunoreactive nerves in the carotid body of rats. Brain Res 473:283–293
Kusakabe T (1990a) Comparative studies on the vascular organization of carotid labyrinths of anurans and caudates. J Morphol 204:47–55
Kusakabe T (1990b) Ultrastructural studies of the carotid labyrinth in the newt Cynops pyrrhogaster. Zool Sci 7:201–208
Kusakabe T (1991a) The occurrence of melanosomes in the newt glomus cell. Arch Histol Cytol 54:81–87
Kusakabe T (1991b) Morphogenesis of the carotid labyrinth of the bullfrog, Rana catesbeiana, during larval development and metamorphosis. Anat Embryol 184:133–139
Kusakabe T (1992a) Intimate apposition of the glomus and smooth muscle cells (g-s connection) in the carotid labyrinth of juvenile bullfrogs. Anat Embryol 185:39–44
Kusakabe T (1992b) Ultrastructural characteristics of glomus cells in the external carotid artery during larval development and metamorphosis in bullfrogs, Rana catesbeiana. Anat Rec (in press)
Kusakabe T, Ishii K, Ishii K (1987) A possible role of the glomus cell in controlling vascular tone of the carotid labyrinth of Xenopus laevis. Tohoku J Exp Med 151:395–408
Kusakabe T, Anglade P, Tsuji S (1991) Localization of substance P, CGRP, VIP, and somatostatin immunoreactive nerve fibers in the carotid labyrinths of some amphibian species. Histochemistry 96:255–260
McGregor GP, Woodhams PL, O'shaughnessy DJ, Ghatei MA, Polak JM, Bloom SR (1982) Developmental changes in bombesin, substance P, somatostatin and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in the rat brain. Neurosci Lett 28:21–27
Noguchi R, Kobayashi S (1977) On the vascular architecture of the carotid labyrinth in Cynops pyrrhogaster and Onychodactylus japonicus. Arch Histol Jpn 40:347–360
Palmer MR, Miller RJ, Olson L, Seiger A (1982) Prenatal ontogeny of neurons with enkephalin-like immunoreactivity in the rat central nervous system: an immunohistochemical mapping investigation. Med Biol 60:61–88
Pickel VM, Sumal KK, Reis DJ, Miller RJ, Hervonen A (1980) Immunohistochemical localization of enkephalin and substance P in the dorsal tegmental nuclei in human fetal brain. J Comp Neurol 193:805–814
Poullet-Krieger M (1973) Innervation du labyrinthe carotidien du crapaud Bufo bufo: étude ultrastructurale et histochimique. J Microscopie 18:55–64
Rogers DC (1963) Distinct cell types in the carotid labyrinth. Nature 200:492–493
Samnegård H, Thulin L, Tydén G, Johansson C, Muhrberg O, Bjorklund C (1978) Effect of synthetic substance P on internal carotid artery blood flow in man. Acta Physiol Scand 104:492–495
Scheibner T, Read DJC, Sullivan CE (1988) Distribution of substance P-immunoreactive structures in the developing cat carotid body. Brain Res 453:72–78
Senba E, Shiosaka S, Hara Y, Inagaki S, Sakanaka M, Takatsuki K, Kawai Y, Tohyama M (1982) Ontogeny of the peptidergic system in the rat spinal cord: Immunohistochemical analysis. J Comp Neurol 208:54–66
Shiosaka S, Takatsuki K, Sakanaka M, Inagaki S, Takagi H, Senba E, Kawai Y, Tohyama M (1981) Ontogeny of somatostatin-containing neuron system of the rat: immunohistochemical observations. I. Lower brainstem. J Comp Neurol 203:173–188
Sternberger LA (1979) Immunocytochemistry, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
Taylor AC, Kollros JJ (1946) Stages in the normal development of Rana pipiens larvae. Anat Rec 94:7–23
Toews D, Shelton G, Boutilier R (1982) The amphibian carotid labyrinth: some anatomical and physiological relationships. Can J Zool 60:1153–1160
Wilson DA, O'Neill JT, Saido SI, Traystman RJ (1981) Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide and canine cerebral circulation. Circ Res 48:138–148
Yamano M, Inagaki S, Tateishi N, Hamaoka T, Tohyama M (1984) Ontogeny of neuropeptides in the nucleus ventromedialis. Dev Brain Res 16:253–262
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kusakabe, T. Ontogeny of substance P-, CGRP-, and VIP-containing nerve fibers in the amphibian carotid labyrinth of the bullfrog, Rana catesbeiana . Cell Tissue Res 269, 79–85 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00384728
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00384728