Summary
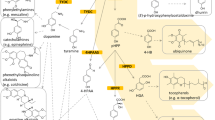
Germinating jack bean cotyledons liberated 14CO2 when fed 14C-guanidoxy-canavanine but did not accumulate any 14C-compounds other than the applied canavanine. This suggested that the canavanine was being degraded by the action of canavanase to canaline and urea, the urea then being converted to ammonia and carbon dioxide by the action of urease. Hydroxyurea and acetohydroxamic acid (both inhibitors of urease activity) strongly inhibited the liberation of 14CO2 from 14C-guanidoxy-canavanine by the cotyledons but neither compound induced the accumulation of 14C-urea within the tissues. This inhibitory action of hydroxyurea on 14CO2 output was thought to be due at least in part, to this inhibition of canavanase activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Archibald, R. M.: Colorimetric determination of canavanine. J. biol. Chem. 165, 169–178 (1946).
Bell, E. A.: Canavanine and related compounds in Leguminosae. Biochem. J. 70, 617–619 (1958).
—: Canavanine in Leguminosae. Biochem. J. 75, 618–620 (1960).
Birdsong, B. A., Alston, R., Turner, B. L.: Distribution of canavanine in the family Leguminosae as related to phyletic grouping. Canad. J. Bot. 38, 499–505 (1960).
Cuppy, D., Crevasse, L.: An assembly for 14CO2 collection in metabolic studies for liquid scintillation counting. Analyt. Biochem. 5, 462–463 (1963).
Fearon, W. R., Bell, E. A.: Canavanine: detection and occurrence in Colutea arborescens. Biochem. J. 59, 221–224 (1955).
Johnstone, J. H.: Nitrogen metabolism in the jack bean (Canavalia ensiformis). Biochem. J. 64, 21 P (1956).
Meister, A.: Biochemistry of the amino acids, vol. 1 and 2. New York and London: Academic Press 1965.
Nakatsu, S., Haratake, S., Sakurai, A., Zoi, N., Nishihara, Z., Hayasida, M.: The change of quantity of canavanine in leguminous plants in the process of germination, growth and fructification. Seikagaku 8, 35–39 (1964).
Topfer, R. v., Miersch, J., Reinbothe, H.: Untersuchungen zum Abbau von Canavanin in Fabaceae. Biochem. Physiol. Pflanzen 161, 231–242 (1970).
Tschiersch, B.: Über Canavanin. Flora (Jena) 147, 405–416 (1959).
Turner, B. L., Harborne, J. B.: Distribution of canavanine in the plant kingdom. Phytochem. 6, 863–866 (1967).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Whiteside, J.A., Thurman, D.A. The degradation of canavanine by jack bean cotyledons. Planta 98, 279–284 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00380228
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00380228