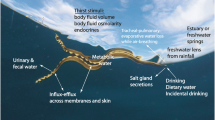
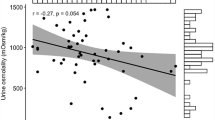
Summary
-
1.
Total body water and exchangeable Na pools have been measured in hatchling and juvenile Estuarine Crocodiles captured from a wide range of salinity (0–64‰). Plasma electrolyte concentrations are presented for hatchlings over the same range of salinity.
-
2.
Plasma electrolyte concentrations in hatchlings are constant across the entire salinity range studied. Hatchlings and juveniles, up to 5 kg body weight, maintain constant weight-corrected total body water pools but show a decline in exchangeable sodium pools with increasing salinity, suggesting a shift in the distribution of electrolytes or water between extra- and intra-cellular fluid compartments.
-
3.
Both water and Na pools scale allometrically with body weight (allometric coefficients of 0.984 and 0.944 respectively). Expression of weight-specific pool sizes in units of ml/100 g or mmol/kg is, therefore, potentially misleading. Demonstration of homeostasis with respect to pool size depends upon the expression of pool size in units of ml or mmol per unit length and upon detailed consideration of weight/length and volume/length scaling relationships. The implications of these findings for future studies of the ecology of C. porosus in saline habitats are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bliss CI (1970) Statistics in Biology. McGraw-Hill, New York
Davies RE, Kornberg HL, Wilson GM (1952) Relation between total and exchangeable sodium in the body. Nature 170:979–980
Dunson WA (1970) Some aspects of electrolyte and water balance in three estuarine reptiles, the Diamondback Terrapin, American and “Salt water” crocodiles. Comp Biochem Physiol 32:161–174
Dunson WA (1982) Osmoregulation of crocodiles: salinity as a possible limiting factor to Crocodylus acutus in Florida Bay. Copeia 1982/2:374–385
Ellis TM (1981) Tolerance of seawater by the American Crocodile, Crocodylus acutus. J Herpetol 15/2:187–192
Evans DH, Ellis TM (1977) Sodium balance in the hatchling American Crocodile, Crocodylus acutus. Comp Biochem Physiol 58A:159–162
Forbes GB (1955) Inorganic chemical heterogony in man and animals. Growth 19:75–87
Green B (1978) Estimation of food consumption in the dingo, Canis familiaris dingo, by means of 22Na turnover. Ecology 59/2:207–210
Green B, Dunsmore JD (1978) Turnover of tritiated water and 22sodium in captive rabbits. J Mammal 59:12–17
Grigg GC (1981) Plasma homeostasis and cloacal urine composition in Crocodylus porosus caught along a salinity gradient. J Comp Physiol 144:261–270
Grigg GC, Taplin LE, Harlow P, Wright J (1980) Survival and growth of hatchling Crocodylus porosus in saltwater without access to fresh drinking water. Oecologia (Berlin) 47:264–266
Grigg GC, Taplin LE, Green B, Harlow P (in prep) Water and sodium turnover in free-ranging Crocodylus porosus under hypo- and hyper-osmotic conditions in northern Australia
Magnusson WE (1980) Habitat required for nesting by Crocodylus porosus (Reptilia: Crocodilidae) in northern Australia. Aust Wildl Res 7:149–156
Magnusson WE (1981) Suitability of two habitats in northern Australia for the release of hatchling Crocodylus porosus from artificial nests. Aust Wildl Res 8:199–202
Magnusson WE, Taylor JA (1981) Growth of juvenile Crocodylus porosus as affected by season of hatching. J Herpetol 15/2:242–245
Messel H, Butler ST (1977) Australian Animals and their Environment. Shakespeare Head Press, Sydney
Messel H, Wells AG, Green WJ et al. (1979–1981) Surveys of tidal river systems in the Northern Territory of Australia and their crocodile populations. A series of 17 monographs. Pergamon Press, Sydney
Moran PAP (1971) Estimating structural and functional relationships. J Multivar Anal 1:232–255
Nagy KA, Costa DP (1980) Water flux in animals: analysis of potential errors in the tritiated water method. Amer J Physiol 238 (Regulatory Integrative comp Physiol 7): R454-R465
Nie NH, Hull CH, Jenkins JG, Steinbrenner K, Bent DH (1975) Statistical Package for the Social Sciences. 2nd Ed. McGraw-Hill, New York
Ogden JC (1978) Status and nesting biology of the American Crocodile, Crocodylus acutus, (Reptilia, Crocodilidae) in Florida. J Herpetol 12/2:183–196
Ricker WE (1973) Linear regressions in fishery research. J Fish Res Board Can 30:409–434
Robinson GD, Dunson WA (1976) Water and sodium balance in the estuarine Diamondback Terrapin, (Malaclemys). J comp Physiol 105:129–152
Taplin LE (1982) Osmoregulation in the Estuarine Crocodile, Crocodylus porosus. Unpubl PhD Thesis, University of Sydney
Taplin LE (1984) Drinking of fresh water but not seawater by the Estuarine Crocodile (Crocodylus porosus). Comp Biochem Physiol (in press)
Taplin LE (submitted) Osmoregulatory mechanisms of the fasted Estuarine Crocodile, Crocodylus porosus, in seawater
Taplin LE, Grigg GC (1981) Salt glands in the tongue of the Estuarine Crocodile, Crocodylus porosus. Science 212:1045–1047
Taylor JA (1979) The foods and feeding habits of sub-adult Crocodylus porosus Schneider in northern Australia. Aust Wildl Res 6:347–359
Underwood AJ (1981) Techniques of analysis of variance in experimental marine biology and ecology. Oceanogr Mar Biol Ann Rev 19:513–605
Webb GJW, Messel H, Magnusson W (1977) The nesting of Crocodylus porosus in Arnhem Land, northern Australia. Copeia 1977/2:238–249
Webb GJW, Messel H, Crawford J, Yerbury MJ (1978) Growth rates of Crocodylus porosus (Reptilia: Crocodilia) from Arnhem Land, northern Australia. Aust Wildl Res 5:385–399
Winer BJ (1971) Statistical Principles in Experimental Design. McGraw-Hill Koga-Kushu, Tokyo
Zar JH (1974) Biostatistical Analysis. Prentice-Hall, New Jersey
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taplin, L.E. Homeostasis of plasma electrolytes, water and sodium pools in the Estuarine Crocodile, Crocodylus porosus, from fresh, saline and hypersaline waters. Oecologia 63, 63–70 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00379786
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00379786