Summary
-
1.
We staged predatory encounters between snakes and salamanders in the laboratory.
-
2.
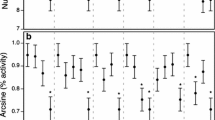
Both snakes and salamanders accumulated significant quantities of lactic acid (0.3–2.3 mg/g) during predatory encounters. In a typical 14.4 min encounter, lactate concentration reached 260% of resting levels in snake predators and 880% of resting levels in salamander prey. This is one of the first demonstrations of anaerobiosis during natural ‘burst’ activity in both predator and prey.
-
3.
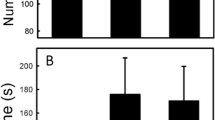
Salamander responses to snake attack were surprisingly variable, and included writhing, thrashing, tail wrapping, tail autotomy, and biting. Antipredator responses were effective in nearly one third of trials. Lactate concentration was significantly correlated with duration of predatory encounters (r=0.57), snake mass, and salamander mass (Table 3).
-
4.
Our calculations suggest that attack and ingestion of prey may cost snakes less than 1% of energy assimilated from prey.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnold SJ (1982) A quantitative approach to antipredator performance: salamander defense against snake attack. Copeia 1982: in press
Bennett AF (1978) Activity metabolism of the lower vertebrates. Ann Rev Physiol 40:444–469
Bennett AF (1980) The metabolic foundations of vertebrate behavior. BioScience 30:452–456
Bennett AF (1981) The energetics of reptilian activity. In: C Gans, FH Pough (eds), Biology of the Reptilia, Vol 12 Academic Press, New York in press
Bennett AF, Dawson WR (1976) Metabolism. In: C Gans, WR Dawson (eds), Biology of the Reptilia, Vol 5 (Physiology A). Academic Press, New York, p 127–223
Bennett AF, Licht P (1972) Anaerobic metabolism during activity in lizards. J comp Physiol 81:277–288
Bennett AF, Licht P (1974) Anaerobic metabolism during activity in amphibians. Comp Biochem Physiol 48A:319–327
Bennett AF, Gleeson TT, Gorman GC (1981) Anaerobic metabolism in a lizard (Anolis bonairensis) under natural conditions. Physiol Zool 54:237–241
Carpenter CC (1952) Comparative ecology of the common garter snake (Thamnophis s. sirtalis), the ribbon snake (Thamnophis s. sauritus) and Butler's garter snake (Thamnophis butleri). Ecol Mongor 22:235–258
Cushman JR, Packard GC, Boardman TJ (1976) Concentrations of lactic acid in neotenic and transformed tiger salamanders (Ambystoma tigrinum) before and after activity. J comp Physiol 112: 273–281
Feder ME, Olsen LE (1978) Behavioral and physiological correlates of recovery from exhaustion in the lungless salamander Batrachoseps attenuatus (Amphibia: Plethodontidae). J comp Physiol 128: 101–107
Gatten RE (1981) Anaerobic metabolism in freely diving painted turtles. J exp Zool 216:377–385
Gratz RK, Hutchison VH (1977) Energetics for activity in the diamondback water snake, Natrix rhombifera. Physiol Zool 50:99–114
Hillman SS, Shoemaker VH, Putnam RW, Withers PC (1979) Reassessment of aerobic metabolism in amphibians during activity. J. comp Physiol 129B:309–313
Hochachka PW, Somero GN (1973) Strategies of biochemical adaptation. WB Saunders Co. Philadelphia
Hutchison VH, Turney LD, Gratz RK (1977) Aerobic and anaerobic metabolism during activity in the salamander Ambystoma tigrinum. Physiol Zool 50:189–202
Jackson DC, Prange HD (1979) Ventilation and gas exchange during rest and exercise in adult green sea turtles. J comp Physiol 134:315–319
Porter WP, Mitchell JW, Beckman WA, Tracy CR (1975) Environmental constraints on some predator-prey interactions. In: DM Gates, R Schmerl (eds), Perspectives in biophysical ecology. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, p 347–364
Pough FH (1977) Ontogenetic change in blood transport capacity and endurance in garter snakes (Thamnophis sirtalis). J comp Physiol 116B:337–345
Pough FH (1978) Ontogenetic changes in endurance in water snakes (Natrix sipedon): physiological correlates and ecological consequences. Copeia 1978:268–272
Pough FH (1981) Amphibians and reptiles as low energy systems. In: WP Aspey, S Lustick (eds), Behavioral energetics: vertebrate costs of survival. Ohio State Univ Press, Columbus in press
Ruben JA (1976) Aerobic and anaerobic metabolism during activity in snakes. J comp Physiol 109:147–157
Smith GC (1976) Ecological energetics of three species of ectothermic vertebrates. Ecology 57:252–264
Taigen TL, Pough FH, Emerson SB (1982) Ecological correlates of anuran exercise physiology. Oecologia (Berl) in press
Whitford WG, Hutchison VH (1965) Gas exchange in salamanders. Physiol Zool 38:228–242
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feder, M.E., Arnold, S.J. Anaerobic metabolism and behavior during predatory encounters between snakes (Thamnophis elegans) and salamanders (Plethodon jordani). Oecologia 53, 93–97 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00377141
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00377141