Abstract
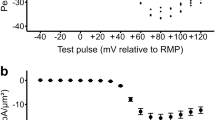
In ferret ventricular myocytes the rate of intracellular Ca concentration [Ca]i decline and relaxation is remarkably fast (compared with rabbit and rat) under conditions where both the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca uptake and Na/Ca exchange are inhibited. Here we explore the possibility that this rapid [Ca]i decline in ferret cells is attributable to the sarcolemmal Ca ATPase by using carboxyeosin (a potent inhibitor of the sarcolemmal Ca-ATPase). We compare the effects of carboxyeosin with those of elevated extracellular [Ca] ([Ca]o) (a thermodynamic approach to limit Ca transport by the sarcolemmal Ca ATPase). In rabbit cells, carboxyeosin and high [Ca]o slowed [Ca]i decline similarly and both virtually abolished [Ca]i decline when mitochondrial Ca uptake was also inhibited. In ferret cells, carboxyeosin treatment produced these same effects on [Ca]i decline, but high [Ca]o did not mimic them. Moreover, only in carboxyeosintreated ferret cells did additional inhibition of mitochondrial Ca uptake nearly abolish [Ca]i decline. We conclude that, carboxyeosin loading can inhibit the sarcolemmal Ca-ATPase in intact myocytes; that this pump seems likely to be responsible for the much faster relaxation observed in ferret cells after block of SR Ca accumulation and Na/Ca exchange transport and that the sarcolemmal Ca pump apparently has different characteristics in rabbit and ferret ventricular myocytes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen DG, Morris PG, Orchard CH, Pirolo JS (1985) A nuclear magnetic resonance study of metabolism in the ferret heart during hypoxia and inhibition of glycolysis. J Physiol (Lond) 361:185–204
Bassani RA, Bassani JWM, Bers, DM (1992) Mitochondrial and sarcolemmal Ca2+ transport reduce [Ca2+]i during caffeine contractures in rabbit cardiac myocytes. J Physiol (Lond) 453:591–608
Bassani JWM, Bassani RA, Bers DM (1993) Ca2+ cycling between sarcoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria in rabbit cardiac myocytes. J Physiol (Lond) 460:603–621
Bassani JWM, Bassani RA, Bers DM (1994) Relaxation in rabbit and rat cardiac cells: species-dependent differences in cellular mechanisms. J Physiol (Lond) 476:279–293
Bassani RA, Bassani JWM, Bers DM (1994) Relaxation in ferret ventricular myocytes: unusual interplay among calcium transport systems. J Physiol (Lond) 476:295–308
Bers DM (1991) Excitation-contraction coupling and cardiac contractile force. Kluwer Academic Press, Amsterdam, pp 258
Bers DM, Bridge JHB (1989) Relaxation of rabbit ventricular muscle by Na-Ca exchange and sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca-pump: ryanodine and voltage-sensitivity. Circ Res 65:334–342
Bers DM, Bassani RA, Bassani JWM, Baudet S, Hryshko LV (1993) Paradoxical twitch potentiation after rest in cardiac muscle: increased fractional release of SR calcium. J Molec Cell Cardiol 25:1047–1057
Carafoli E (1991) Calcium pump of the plasma membrane. Physiol Rev 71:129–153
Caroni P, Carafoli E (1981) The Ca2+ pumping ATPase of heart sarcolemma. Characterization, calmodulin dependence and partial purification. J Biol Chem 256:3263–3270
Dixon DA, Haynes DH (1989) Kinetic characterization of the Ca2+-pumping ATPase of cardiac sarcolemma in four states of activation. J Biol Chem 264:13612–13622
Gatto C, Milanick MA (1993) Inhibition of the red blood cell calcium pump by eosin and other fluorescein analogues. Am J Physiol 264:C1577-C1586
Gatto C, Hale CC, Xu W, Milanick MA (1995) Eosin, a potent inhibitor of the plasma membrane Ca pump, does not inhibit the cardiac Na-Ca exchanger. Biochemistry 34:965–972
Grynkiewicz G, Poenie M, Tsien RY (1985) A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem 250:3440–3450
Hove-Madsen L, Bers DM (1993) Passive Ca buffering and SR Ca uptake in permeabilized rabbit ventricular myocytes. Am J Physiol 264:C677-C686
Negretti N, O'Neill SC, Eisner DA (1993) The relative contributions of different intracellular and sarcolemmal systems to relaxation in rat ventricular myocytes. Cardiovasc Res 27:1826–1830
O'Neill SC, Valdeolmillos M, Lamont C, Donoso P, Eisner DA (1991) The contribution of Na-Ca exchange to relaxation in mammalian cardiac muscle. Ann NY Acad Sci 639:444–452
Skou JC, Esmann M (1981) Eosin, a fluorescent probe of ATP binding to the (Na++K+)-ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta 647:232–240
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Present address: Centro de Engenharia Biomédica Caixa Postal 6040, Universidade Estadual de Campinas (UNICAMP), 13081 Campinas, SP, Brazil
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bassani, R.A., Bassani, J.W.M. & Bers, D.M. Relaxation in ferret ventricular myocytes: role of the sarcolemmal Ca ATPase. Pflugers Arch. 430, 573–578 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00373894
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00373894