Abstract
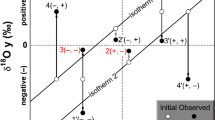
Late Carboniferous (Hercynian) tectonism in the Pyrenees generated extremely steep thermal gradients at 8–14 km depth in the continental crust, producing andalusite- and sillimanite-grade metamorphism and partial melting of Lower Paleozoic metasediments under water-rich conditions. At the same time, amphibolite- and granulitefacies “basal gneisses” were equilibrated under dryer conditions at pressures of 4 to 7 kbar (14–25 km depth), beneath these higher-level rocks. We present 95 new oxygen isotopic analyses of samples from the Agly, St. Barthelemy, Castillon and Trois Seigneurs Massifs, highlighting contrasting 18O/16O systematics at different structural levels in the Hercynian crust, here termed Zones 1, 2, and 3. The unmetamorphosed, fossiliferous, Paleozoic shales and carbonates of Zone 1 have typical sedimentary δ 18O values, mostly in the range +14 to +16 for the pelitic rocks and +20 to +25 for the carbonates. The metamorphosed equivalents of these rocks in Zone 2 all have strikingly uniform and much lower δ 18O values; the metapelites mostly have δ 18O=+10 to +12, and interlayered metacarbonates from the Trois Seigneurs Massif have δ 18O of about +12 to +14. Typically, the Zone 3 “basal gneisses” are isotopically heterogeneous with variable δ 18O values ranging from +6 in mafic lithologies to +22 in carbonate-rich lithologies. Steep gradients in δ 18O (as much as 10 per mil over a few cm) are preserved at the margins of some metacarbonate layers. These data indicate that the Zone 3 gneisses were infiltrated by much smaller volumes of metamorphic pore fluids than were the overlying Zone 2 rocks, and that circulation of surface-derived H2O (either seawater or formation waters, as evidenced by high δD values) was mainly confined to the Paleozoic supracrustal sedimentary pile. This is compatible with an overall reduction of interconnected porosity with increasing depth, but perhaps even more important, the extensive partial melting at the base of Zone 2 may have produced a ductile, impermeable barrier to downward fluid penetration.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allaart JH (1959) The geology and petrology of the Trois Seigneurs Massif, France. Leidse Geol Med 11:97–214
Autran A, Fonteilles M, Guitard G (1966) Discordance du Paleozoique inferieur metamorphique sur un socle gneissique antehercynien dans le massif des Alberes (Pyrenees Orientales). C R Acad Sci 263:317–320
Autran A, Barriere B, Bonin B, Didier J, Fluck P, Fourcade S, Giraud P, Jonin J, Lameyre J, Orsini J-B, Vivier G (1980) Les granitoides de France. In: Evolutions Geologiques de la France. Bull Geol Rech Mineral Mem 107; Colloque C7:51–97
Baertschi P (1957) Messung und Deutung relativer Häufigkeitsvariationen von 18O und 13C in Karbonatgesteinen und Mineralien. Schweiz Mineral Petrogr Mitt 37:73–151
Bard J-P, Briand B, Cantagrel J-M, Guitard G, Kienast J-R, Kornprobst J, Lasnier B, LeCorre C, Santallier D (1980) Le metamorphisme en France. In: Evolutions Geologiques de la France. Bull Geol Rech Mineral Mem 107:161–189
Ben Othman D, Fourcade S, Allegre CJ (1984) Recycling processes in granite-granodiorite complex genesis: the Querigut case studied by Nd-Sr isotope systematics. Earth Planet Sci Lett 69:290–300
Bottinga Y (1968) Calculation of fractionation factors for carbon and oxygen isotopic exchange in the system calcite-carbon dioxide-water. J Phys Chem 72:800–808
Condomines M, Gronvold K, Hooker PJ, Muehlenbachs K, O'Nions RK, Oskarsson N, Oxburgh ER (1983) Helium, oxygen, strontium and neodymium isotopic relationships in Icelandic volcanics. Earth Planet Sci Lett 66:125–136
Criss RE, Taylor HP Jr (1983) An 18O/16O and D/H study of Tertiary hydrothermal systems in the southern half of the Idaho batholith. Bull Geol Soc Am 94:640–663
Etheridge MA, Wall VJ, Vernon RH (1983) The role of the fluid phase during regional metamorphism and deformation. J Met Geol 1:205–227
Ferry JM (1976) P, T, \({\text{f}}_{{\text{CO}}_{\text{2}} } \) and \({\text{f}}_{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}} {\text{O}}} \) during metamorphism of calcareous sediments in the Waterville-Vassalboro area, SouthCentral Maine. Contrib Mineral Petrol 57:119–43
Ferry JM (1980) A case study of the amount and distribution of heat and fluid during metamorphism. Contrib Mineral Petrol 77:373–85
Ferry JM (1983) Regional metamorphism of the Vassalboro formation, South-Central Maine, USA: a case study of the role of fluid in metamorphic petrogenesis. J Geol Soc Lond 140:551–76
Fleck RJ, Criss RE (1985) Strontium and oxygen isotopic variations in Mesozoic and Tertiary plutons of central Idaho. Contrib Mineral Petrol 90:291–308
Fonteilles M (1970) Geologie des terrains metamorphiques et granitiques du massif hercynien de l'Agly (Pyrenees orientales). Bull Bur Rech Geol Minières (2) Sect 4:21–72
Fonteilles M (1981) Anatexis of a metagraywacke series in the Agly Massif, Eastern Pyrenees, France. J Fac Sci Tokyo Univ 20:181–240
Fyfe WS, Price NJ, Thompson AB (1978) Fluids in the earth's crust. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Garlick GD, Epstein S (1966) Oxygen isotope ratios in coexisting minerals of regionally metamorphosed rocks. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 31:181–214
Graham CM, Greig KM, Sheppard SMF, Turi B (1983) Genesis and mobility of the H2O-CO2 fluid phase during greenschist and epidote-amphibolite fades metamorphism: a petrological and stable isotope study in the Scottish Dalradian. J Geol Soc London 140, Part 4:577–599
Guitard G (1970) Le metamorphisme hercynien mesozonal et les gneiss oeilles du massif du Canigou (Pyrenees Orientales). Mem Bur Rech Geol Minières 63:1–349
Hattori K, Muehlenbachs K (1982) Oxygen isotope ratios of the Icelandic crust. J Geophys Res 87:6559–6565
Koslovsky YA (1984) The world's deepest well. Sci Am 251(6):98–105
Magaritz M, Taylor HP Jr (1976) Oxygen, hydrogen and carbon isotope studies of the Franciscan formation, Coast Ranges, California. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 40:215–234
Matthews A, Kolodny Y (1978) Oxygen isotope fractionation in decarbonation metamorphism: the Mottled Zone Event. Earth Planet Sci Lett 39:179–192
Matthews A, Schliestedt M (1984) Evolution of the blueschist and greenschist facies rocks of Sifnos, Cyclades, Greece. Contrib Mineral Petrol 88:150–163
McCrea JM (1950) On the isotopic chemistry of carbonates and a paleotemperature scale. J Chem Physics 18:849–857
Nabelek PI, Labotka TC, O'Neil JR, Papike JJ (1984) Contrasting fluid/rock interaction between the Notch Peak granitic intrusion and argillites and limestones in western Utah: evidence from stable isotopes and phase assemblages. Contrib Mineral Petrol 86:25–34
Norton D, Taylor HP Jr (1979) Quantitative simulation of the hydrothermal systems of crystallizing magmas on the basis of transport theory and oxygen isotope data: An analysis of the Skaergaard intrusion. J Petrol 20:421–486
Passchier CW (1982) Mylonitic deformation in the Saint-Barthelemy Massif, French Pyrenees. GUA Papers of Geology No 16
Passchier CW (1984) Mylonite-dominated footwall geometry in a shear zone, central Pyrenees. Geol Mag 121:429–436
Roux L (1977) L'évolution des roches du facies granulite et le probleme des ultramafites dans le massif de Castillon (Ariege). These d'Etat, Toulouse, pp 487
Rumble D, Ferry JM, Hoering TC, Boucot AJ (1982) Fluid flow during metamorphism at the Beaver Brook fossil locality. Am J Sci 282:886–919
Rye RO, Schuiling RD, Rye DM, Jansen JBH (1976) Carbon, hydrogen and oxygen isotope studies of the regional metamorphic complex at Naxos, Greece. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 40:1031–1049
Sharma T, Clayton RN (1965) Measure of 18O/16O ratios of total oxygen from carbonates. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 29:1347–1353
Shieh YN, Schwarcz HP (1974) Oxygen isotope studies of granite and migmatite, Grenville Province of Ontario, Canada. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 38:21–45
Shieh YN, Taylor HP Jr (1969a) Oxygen and hydrogen isotope studies of contact metamorphism in the Santa Rosa range, Nevada, and other areas. Contrib Mineral Petrol 20:306–356
Shieh YN, Taylor HP Jr (1969b) Oxygen and carbon isotope studies of contact metamorphism of carbonate rocks. J Petrol 10:307–331
Soula J-C (1982) Characteristics and mode of emplacement of gneiss domes and plutonic domes in the central-eastern Pyrenees. J Struct Geol 4:313–42
Taylor HP Jr (1969) Oxygen isotope studies of anorthosites, with particular reference to the origin of bodies in the Adirondack Mountains, New York. Origin of Anorthosite, NY State Mus Sci Serv Mem 18:111–34
Taylor HP Jr (1974) The application of oxygen and hydrogen isotope studies to problems of hydrothermal alteration and ore deposition. Econ Geol 69:843–883
Taylor HP Jr (1977) Water/rock interactions and the origin of H2O in granitic batholiths. J Geol Soc London 133:509–558
Taylor HP Jr, Epstein S (1962) Relationships between 18O/16O ratios in coexisting minerals of igneous and metamorphic rocks. Part I: principles and experimental results. Bull Geol Soc Am 73:461–480
Taylor HP Jr, Forester RW (1979) An oxygen and hydrogen isotope study of the Skaergaard intrusion and its country rocks: a description of a 55-m.y. old fossil hydrothermal system. J Petrol 20:355–419
Tracy RJ, Rye DM, Hewitt DA, Schiffries CM (1983) Petrologic and stable isotopic studies of fluid-rock interactions, south central Connecticut: I. The role of infiltration in producing reaction assemblages in impure marbles. Am J Sci 283 A:589–616
Valley JW (1986) Stable isotope geochemistry of metamorphic rocks. In: Valley JW, Taylor HP Jr, O'Neil JR (eds) Stable isotopes in high temperature geological processes. Min Soc Am Rev Mineral 16:445–489
Valley JW, O'Neil JR (1984) Fluid heterogeneity during granulite facies metamorphism in the Adirondacks: stable isotope evidence. Contrib Mineral Petrol 85:158–173
Veizer J, Hoefs J (1976) The nature of 18O/16O and 13C/12C secular trends in sedimentary carbonate rocks. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 47:697–706
Verhoef PNW, Vissers RLM, Zwart HJ (1984) A new interpretation of the structural and metamorphic history of the western Aston massif (Central Pyrenees, France). Geol Mijnb 63:399–410
Vielzeuf D (1984) Relations de phases dans le facies granulite et implications geodynamiques. L'exemple des granulites des Pyrenees. Annales Scientifiques Université Clermont II Vol 79:189
Vitrac-Michard A, Allegre CJ (1975) A study of the formation and history of a piece of continental crust by 87Sr/86Sr method; the case of the French oriental Pyrenees. Contrib Mineral Petrol 50:257–85
Vitrac-Michard A, Albarede F, Dupuis C, Taylor HP Jr (1980) The genesis of Variscan (Hercynian) plutonic rocks: inferences from Sr, Pb, and O studies on the Maladeta igneous complex, Central Pyrenees, Spain. Contrib Mineral Petrol 72:57–72
Wickham SM (1984) Crustal anatexis in the Trois Seigneurs Massif, Pyrenees, France. Unpublished Ph.D. thesis, University of Cambridge
Wickham SM (1987a) Crustal anatexis and granite petrogenesis during low pressure regional metamorphism; the Trois Seigneurs Massif, Pyrenees, France. J Petrol (in press)
Wickham SM (1987b) The segregation and emplacement of granitic magmas. J Geol Soc London (in press)
Wickham SM, Oxburgh ER (1985) Continental rifts as a setting for regional metamorphism. Nature 318:330–333
Wickham SM, Taylor HP Jr (1985) Stable isotopic evidence for large-scale seawater infiltration in a regional metamorphic terrane; the Trois Seigneurs Massif, Pyrenees, France. Contrib Mineral Petrol 91:122–137
Wickham SM, Oxburgh ER (1986) A rifted tectonic setting for Hercynian high thermal gradient metamorphism in the Pyrenees. In: Banda E, Wickham SM (eds) The geological evolution of the Pyrenees. Tectonophysics 129:53–69
Wickham SM, Oxburgh ER (1987) Low pressure regional metamorphism in the Pyrenees and its implications for the thermal evolution of rifted continental crust. Philos Trans R Soc London A321:219–243
Zwart HJ (1954) La geologie du massif du Saint Barthelemy, Pyrenees, France. Leidse Geol Med 18:1–228
Zwart HJ (1959) Metamorphic history of the Central Pyrenees, part 1. Arize, Trois Seigneurs and Saint Barthelemy Massifs. Leidse Geol Med 22:419–490
Zwart HJ (1979) The geology of the Central Pyrenees. Leidse Geol Med 50.1:1–74
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Contribution No. 4287, Publication of the Division of Geological and Planetary Sciences, California Institute of Technology
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wickham, S.M., Taylor, H.P. Stable isotope constraints on the origin and depth of penetration of hydrothermal fluids associated with Hercynian regional metamorphism and crustal anatexis in the Pyrenees. Contr. Mineral. and Petrol. 95, 255–268 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00371841
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00371841