Abstract
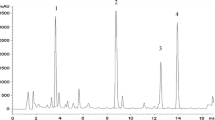
The studies for production of saikosaponins by tissue culture of Bupleurum falcatum L. were carried out to produce saikosaponins with several kinds of media and plant hormones. Among the media and plant hormones studied, Gamborg's B-5 [23] medium containing 0.5 ppm kinetin (k) and 1.0 ppm 3-indolebutyric acid (IBA) was the most effective medium and hormone for production of saikosaponins. The highest content of saikosaponin-d in the dried cells was 0.26%, which was similar to a concentration of Bupleuri Radix.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MS :
-
medium used by Murashige and Skoog [22]
- G :
-
medium used by Gamborg (B 5) [23]
- W :
-
medium used by White [24]
- NN :
-
medium used by Nitsch and Nitsch [25]
- k :
-
Kinetin
- BAP :
-
6-Benzylaminopurine
- 2,4 D :
-
2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid
- NAA :
-
α-Naphtylacetic acid
- IBA :
-
3-Indolebutyric acid
- IAA :
-
3-Indoleacetic acid
- ssd :
-
saikosaponin-d
- PM :
-
Production medium
- dw:
-
Dry weight
References
Furuya, T., et al.: Isolation of saponins and sapogenins from callus tissue of Panax ginseng. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 21 (1973) 98
Furuya, T., et al.: Saponin production in cell suspension cultures of Panax ginseng. Planta Medica 48 (1983) 83
Tabata, M., et al.: Pigment formation in callus cultures of Lithospermum Erythrorhizon. Phytochemistry 13, (1974) 927
Mizukami, H., et al.: Effect of nutritional factors on shikonin derivative formation in Lithospermum callus cultures. Phytochemistry 16 (1977) 1183
Mizukami, H., et al.: Variation in pigment production in Lithospermum Erythrorhizon callus cultures. Phytochemistry 17 (1978) 95
Fujita, Y., et al.: Production of Shikonin derivatives by cell suspension cultures of Lithospermum Erythrorhizon (I). Plant Cell Reports 1 (1981) 59
Fujita, Y.: Production of useful pigment by plant cell cultures. The Heredity 1 (separate volume) (1988) 117
Yamada, Y., et al.: Selection of cell lines with high productivity of Shikonin derivatives by protoplast culture of Lithospermum Erythrorhizon cells. Agric. Biol. Chem. 49 (1985) 1755
Fujita, Y., et al.: Production of Shikonin derivatives by cell suspension cultures of Lithospermum Erythrorhizon (II). Plant Cell Reports 1 (1981) 61
Maeda, Y., et al.: Callus formation from protoplasts of cultured Lithospermum Erythrorhizon cells. Plant Cell Reports 2 (1983) 179
Fujita, Y., et al.: Production of Shikonin derivatives by cell suspension cultures of Lithospermum erythrorhizon (III). Plant Cell Reports 2 (1983) 192
Kubota, T., Hinoh, H.: The constitution of saponins isolated from Bupleurum Falcatum L: Tetrahedron Letters 3 (1968) 303
Shimaoka, A.; Seo, S.; Minato, H.: Saponins isolated from Bupleurum falcatum L., Components of Saikosaponin b. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin I (1975) 2043
Abe, H.; Sakaguchi, M.; Konishi, H.; Tani, T.; Arichi, S.: The effects of Saikosaponins on biological membranes. Planta Medica 34 (1978) 160
Takagi, K.; Sibata, M.: Pharmacological studies on Bupleurum falcatum L. (I). Yagugaku Zasshi 89 (1969) 712
Kubota, T.; Hinoh, H.: The constitution of saponins isolated from Bupleurum falcatum L, Tetrahedron Letters 3 (1968) 303
Yamamoto, M.; Kumagai, A.; Yamamura, Y.: Structure and acitons of Saikosaponins isolated from Bupleurum falcatum L. (I). Arzneimittelforschung 25 (1975) 1021
Yamamoto, M.; Kumagai, A.; Yamamura, Y.: Structure and actions of Saikosaponins isolated from Bupleurum falcatum L. (II). Arzneimittelforschung 25, (1975) 1240
Arichi, S.; Konishi, H.; Abe, H.: Studies on mechanism of action of Saikosaponin effects of saikosaponin to hepatic injury induced by D-galactosamine. Acta Hepat. Jap. 19 (1978) 430
Uomori, A., et al.: Studies on constituents tissue cultures of Bupleurum falcatum L. Syôyakugaku Zasshi 28 (1974) 152
Linsmaier, E. M.; Skoog, F.: Organic growth factor requirements of Tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant. 18 (1965) 100
Murashige, T.; Skoog, F.: A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with Tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant. 15 (1962) 473
Gamborg, O. L., et al.: Nutrient requirements of suspension cultures of Soybean root cells. Exp. Cell. Res. 50 (1968) 151
White, P. R.: The Cultivation of Animal and Plant Cells, 2nd ed. 1963
Nitsch, J. P.; Nitsch, C.: Haploid plants from Pollen Grains. Science 163 (1969) 85
Harada, M.: 13. Bupleuri Radix (Bupleurum Root): Quantitative Analysis of Components in Crude Drugs (Shôyaku) used frequently, p. 161 1989
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Katakura, M., Kimura, T. & Endo, I. Production of saikosaponins by tissue culture of Bupleurum falcatum L.. Bioprocess Engineering 7, 97–100 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00369420
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00369420