Summary
1. Effects of raising extracellular hydrogen-ion-concentration [H+] e on the action potential (AP) of isolated nodes of Ranvier in calcium-containing (1.08 mMol/l) and in calciumpoor (0.05 mMol/l) solutions were studied between ph 7 and 4.8.
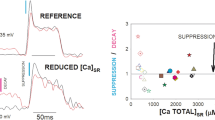
2. Threshold membrane potential (i.e. maximum subthreshold response) and membrane potential at the end of the slow first falling phase increase with increasing [H+] e , especially below ph 6.5. The amplitude of the AP is slightly raised.
3. Mild lowering of ph from 7 to 6.5 in Ca-containing solutions accelerates repolarization, mainly during the slow first phase. In Ca-poor solution, small drop in ph reverses the effects of Ca-lack.
4. Below ph 6.5 to 6.0, repolarization is delayed, mainly during the slow first phase and, to a smaller extent, during the negative after-potential. At low ph the AP becomes insensitive to lack of extracellular calcium.
5. Between ph 7 and 6.5 H+-ions are suggested mainly to act in an indirect way by raising Ca-activity in or at the membrane, thus accelerating the decrease of P Na or the increase in P K. From the effects at lower ph-values it is concluded that in this range H+-ions act directly on the membrane; they would delay and decrease the change of P K during the AP.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Arvanitaki, A., et N. Chalazonitis: Diffusibilité de l'anhydride carbonique dans l'axone géant, ses effets sur les vitesses de l'activité bioélectrique. C. R. Soc. Biol. (Paris) 148, 952–954 (1954).
Brink, F.: Discussion of action of calcium ions on excitability of frog A-fibers. 2nd Conf. Nerve Imp. pp. 38–43 (1951). New York: Josiah Macy jr. Foundation.
Britton, H. T. S.: Electrometric study of the precipitation of phosphates. J. chem. Soc. 1927, 614–630.
Caldwell, P. C.: Studies on the internal ph of large muscle and nerve fibres. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 142, 22–62 (1958).
Coraboeuf, E., u. R. Niedergerke: Kohlensäure- und ph-Wirkung an der markhaltigen Einzelfaser des Frosches. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol. 258, 103–107 (1953).
Dettbarn, W.-D., u. R. Stämpfeli: Untersuchungen über die ph-Wirkung auf das Membranpotential markhaltiger Nervenfasern. Helv. physiol. pharmacol. Acta 15, C16–17 (1957).
Frankenhaeuser, B.: The effect of calcium on the myelinated nerve fiber. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 137, 245–260 (1957).
Frankenhaeuser, B., and A. L. Hodgkin: The action of calcium on the electrical properties of squid axons. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 137, 218–244 (1957).
Kilb, H., u. R. Stämpfli: Eine Vorrichtung zur Membranpotentialmessung am einzelnen bespülten Ranvierschen Schnürring in Ruhe und Erregung. Helv. physiol. pharmacol. Acta 14, 251–254 (1956).
Lehmann, J. E.: The effect of changes in the potassium-calcium balance on the action of mammalian A-nerve fibers. Amer. J. Physiol. 118, 613–619 (1937).
Lüttgau, H.-Ch.: Das Na-Transportsystem während der Erregungsprozesse am Ranvier-Knoten isolierter markhaltiger Nervenfasern. Experientia (Basel) 12, 482–486 (1956).
Meves, H.: Die Wirkung der Wasserstoffionen und der Kohlensäure auf die Nervenleitungsgeschwindigkeit. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol. 261, 249–263 (1955).
Meves, H., u. E. Sauerland: Über den Einfluß von Kohlensäure und Wasserstoffionen auf das Verhalten markhaltiger Nervenfasern in der relativen Refraktärzeit. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol. 268, 366–375 (1959).
Meves, H., u. K.-G. Völkner: Die Wirkung von CO2 auf das Ruhemembranpotential und die elektrischen Konstanten der quergestreiften Muskelfaser. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol. 265, 457–476 (1958).
Monnier, A. M.: Die funktionelle Bedeutung der Dämpfung in der Nervenfaser. Ergebn. Physiol. 48, 230–285 (1955).
Niedergerke, R.: Reizschwelle und Leitungsgeschwindigkeit des Froschnerven unter Kohlensäureeinwirkung. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol. 254, 193–204 (1951).
Niedergerke, R., u. R. Stämpfli: Die Kohlensäurewirkung an der einzelnen markhaltigen Nervenfaser bei Rheobasenbestimmungen. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol. 258, 95–102 (1953).
Shanes, A. M., W. H. Freygang, E. Amatniek and H. Grundfest: Anesthetic and calcium action in the voltage clamped squid giant axon. J. gen. Physiol. 42, 793–802 (1959).
Spyropoulos, C. S.: Cytoplasmic ph of nerve fibers. J. Neurochem. 5, 185–194 (1960).
Stämpfli, R.: Nouvelle méthode pour enregistrer le potentiel d'action d'un seul étranglement de Ranvier et sa modification par un brusque changement de la concentration du mileu extérieur. J. Physiol. (Paris) 48, 710–714 (1956).
Ulbricht, W.: Über die Veränderungen des Aktionspotentials Ranvierscher Schnürringe in calciumreicher Ringerlösung. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol. 272, 68 (1960).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Mit 5 Textabbildungen
Mit Unterstützung durch die Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft. Die Ergebnisse wurden im Auszug auf dem Kongreß der Deutschen Physiologischen Gesellschaft, Zürich 1961, und auf dem Internationalen Kongreß für Biophysik, Stockholm 1961, vorgetragen.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heene, R. Das Aktionspotential des isolierten Ranvierschen Schnürrings bei Erhöhung der extracellulären Wasserstoffionen-Konzentration in calciumhaltigen und calciumarmen Lösungen. Pflügers Archiv 275, 1–11 (1962). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00362225
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00362225