Summary
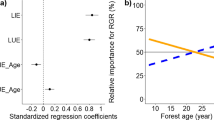
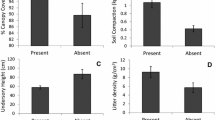
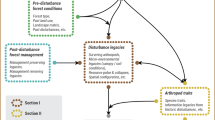
A laboratory study of Adelges cooleyi sistentes emerging from diapause shows that the sistentes redistribute themselves over the needles in the form of aggregations. At low densities needle bases are preferred to the tips, this preference becoming less marked as sistentes density increases. Within each needle aggregation a certain amount of ‘spacing out’ occurs which minimises the number of sistentes settling in close proximity. Over a given period of time adult sistentes produce more eggs at the base of the needles than at the tips. The settling behaviour ensures that at low densities the most favourable parts of the needle at the base are utilised first while the ‘spacing out’ factor provides sufficient space for the development of the egg masses and minimises the possibility of over-exploitation of one part of the needle in relation to the remainder.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carter, C. I.: Conifer woolly aphids (Adelgidae) in Britain. Bull. For. Comm. Lond. 42, 51 pp. (1971)
Dixon, A. F. G., Logan, M.: Population density and spacing in the sycamore aphid, Drepanosiphum platanoides (Schrank) and its relevance to the regulation of population growth. J. Anim. Ecol. 41, 751–760 (1972).
Dixon, A. F. G., MacKay, S.: Aggregation in the sycamore aphid Drepanosiphum platanoides (Schrank) (Hemiptera, Aphididae) and its relevance to the regulation of population growth. J. Anim. Ecol. 39, 439–454 (1970).
Ibbotson, A., Kennedy, J. S.: Aggregation of Aphis fabae Scop. 1. Aggregation on plants. Ann. appl. Biol. 38, 65–78 (1951).
Kennedy, J. S., Crawley, L.: Spaced out gregariousness in sycamore aphids Drepanosiphum platanoides (Schrank) (Hemiptera, Callaphididae). J. Anim. Ecol. 36, 147–170 (1967).
Kislow, C. J., Edwards, L. J.: Repellent odour in aphids. Nature (Lond.) 235, 108–109 (1972).
Parry, W. H.: Observations on the flight periods of aphids in a Sitka spruce plantation in north-eastern Scotland. Bull. ent. Res. 62, 391–399 (1973).
Southwood, T. R. E.: Ecological methods with particular reference to the study of insect populations, 391 pp. London: Methuen 1966.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Parry, W.H. Interaction between individuals during the colonisation of Douglas fir needles by sistentes of Adelges cooleyi . Oecologia 13, 227–238 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00360513
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00360513