Abstract
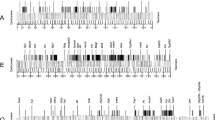
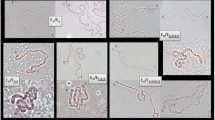
Thirty P1 clones from the X chromosome (Muller's A element) of Drosophila melanogaster were cross-hybridized in situ to Drosophila subobscura and Drosophila pseudoobscura polytene chromosomes. An additional recombinant phage λDsuby was also used as a marker. Twenty-three (77%) of the P1 clones gave positive hybridization on D. pseudoobscura chromosomes bat only 16 (53%) did so with those of D. subobscura. Eight P1 clones gave more than one hybridization signal on D. pseudoobscura and/or D. subobscura chromosomes. All P1 clones and λDsuby hybridized on Muller's A element (X chromosome) of D. subobscura. In contrast, only 18 P1 clones and λDsuby hybridized on Muller's D element (XR chromosomal arm) of D. pseudoobscura; 4 additional P1 clones hybridized on Muller's D element (XR chromosomal arm) of this species and the remaining P1 clone gave on hybridization signal on each arm of the X chromosome. This latter clone may contain one breakpoint of a pericentric inversion that may account for the interchange of genetic material between Muller's A and D elements in D. pseudoobscura. In contrast to the rare interchange of genetic material between chromosomal elements, profound differences in the order and spacing of markers were detected between D. melanogaster, D. pseudoobscura and D. subobscura. In fact, the number of chromosomal segments delimited by identical markers and conserved between pairwise comparisons is small. Therefore, extensive reorganization within Muller's A element has been produced during the divergence of the three species. Rough estimates of the number of cytologically detectable inversions contributing to differentiation of Muller's A element were obtained. The most reliable of these estimates is that obtained from the D. pseudoobscura and D. melanogaster comparison since a greater number of markers have been mapped in both species. Tentatively, one inversion breakpoint about every 200 kb has been produced and fixed during the divergence of D. pseudoobscura and D. melanogaster.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajioka JW, Smoller DA, Jones RW, Carulli JP, Vellk AEC, Garza D, Link AJ, Duncan IW, Hartl DL (1991) Drosophila genome project: one-hit coverage in yeast artificial chromosomes. Chromosoma 100:495–509
Ashburner M (1972) Puffing patterns in Drosophila melanogaster and related species. In: Beermann W (ed) Developmental studies on giant chromosomes. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 101–151
Ashburner M (1991) Drosophila genetic maps. Dros Inf Serv 69:1–399
Cai H, Kiefel P, Yee J, Duncan I (1994) A yeast artificial chromosome map of the Drosophila genome. Genetics 136:1385–1401
Clayton FE, Guest WC (1986) Overview of chromosomal evolution in the family Drosophilidae. In: Ashburner M, Carson HL, ThompsonJr JN (eds) The genetics and biology of Drosophila, vol 3e. Academic Press, New York, pp 1–38
Garza D, Ajioka JW, Burke DT, Hartl DL (1989) Mapping the Drosophila genome with yeast artificial chromosomes. Science 246:641–646
Hartl DL, Lozovskaya ER (1994) Genome evolution: between the nucleosome and the chromosome. In: Schierwater B, Streit B, Wagner GP, DeSalle R (eds) Molecular ecology and evolution: approaches and applications. Birkhäuser, Basel, pp 579–592
Hartl DL, Lozovskaya ER (1995) The Drosophila genome map: a practical guide. Landes, Austin, Texas (in press)
Hartl DL, Ajioka JW, Cai H, Lohe AR, Lozovskaya ER, Smoller DA, Duncan IW (1992) Towards a Drosophila genome map. Trends Genet 8:70–75
Hartl DL, Nurminsky DI, Jones RW, Lozovskaya ER (1994) Genome structure and evolution in Drosophila: applications of the framework P1 map. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:6824–6829
Kafatos FC, Louis C, Savakis C, Glover DM, Ashburner M, Link AJ, Sidén-Kiamos I, Saunders RDC (1991) Integrated maps of the Drosophila genome: progress and prospects. Trends Genet 7:155–161
Kunze-Mühl E, Müller E (1958) Weitere Untersuchungen über die chromosomale Struktur und die natürlichen Strukturtypen von Drosophila subobscura Coll. Chromosoma 9:559–570
Lefevre GJr (1976) A photographic representation and interpretation of the polytene chromosomes of D. melanogaster salivary glands. In: Ashburner M, Novitski E (eds) The genetics and biology of Drosophila, vol 1a. Academic Press, New York, pp 31–66
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J (1982) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Montgomery EB, Charlesworth B, Langley CH (1987) A test for the role of natural selection in the stabilization of transposable element copy number in a population of D. melanogaster. Genet Res 49:31–41
Muller HJ (1940) Bearings of the Drosophila work on systematics. In: Huxley J (ed) New systematics. Clarendon Press, Oxford, pp 185–268
Nadeau JH, Taylor BA (1984) Lengths of chromosomal segments conserved since divergence of man and mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:814–818
Nurminsky DI, Moriyama EN, Lozovskaya ER, Hartl DL (1995) Molecular phylogeny and genome evolution in the Drosophila virilis species group: duplication of the alcohol dehidrogenase gene. Mol Biol Evol (in press)
Patterson JT, Stone WS (1952) Evolution in the genus Drosophila. Macmillan, New York
Randazzo FM, Seeger MA, Huss CA, Sweeney MA, Cecil JK, Kaufman TC (1993) Structural changes in the antennapedia complex of D. pseudoobscura. Genetics 134:319–330
Segarra C, Aguadé M (1992) Molecular organization of the X chromosome in different species of the obscura group of Drosophila. Genetics 130:513–521
Smoller DA, Petrov D, Hartl DL (1991) Characterization of bacteriophage P1 library containing inserts of Drosophila DNA of 75–100 kilobase pairs. Chromosoma 100:487–494
Stocker AJ, Kastritsis CD (1972) Developmental studies in Drosophila. III. The puffing patterns of the salivary gland chromosomes of D. pseudoobscura. Chromosoma 37:139–176
Throckmorton LH (1975) The phylogeny, ecology and geography of Drosophila. In: King RC (ed) Handbook of genetics, vol 3. Plenum Press, New York, pp 421–469
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Segarra, C., Lozovskaya, E.R., Ribó, G. et al. P1 clones from Drosophila melanogaster as markers to study the chromosomal evolution of Muller's A element in two species of the obscura group of Drosophila . Chromosoma 104, 129–136 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00347695
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00347695