Summary
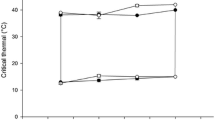
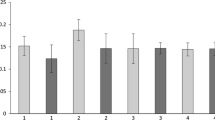
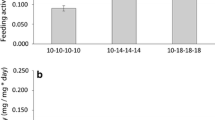
Comparative investigations on the physiological capacities of Gammarus locusta (L.), G. oceanicus Segerstråle, G. salinus Spooner, G. zaddachi Sexton and G. duebeni duebeni Liljeborg obtained from German coastal and estuarine areas were carried out under uniform experimental conditions. In order to assess the adaptation of these species to the abiotic conditions of their particular habitats, the following criteria were examined: (a) oxygen consumption as related to temperature, (b) time course of acclimation to a new steady state of metabolic rate following sudden temperature changes, (c) resistance to oxygen deficiency, and (d) resistance to aerial exposure. Considerable interspecific differences were found among the five amphipods studied. G. locusta reveals the highest O2 uptake rates and longest thermal acclimation periods as well as lowest resistance capacities to oxyten depletion and air exposure. The other species occupy an intermediate position as indicated in the above-cited order, but contrast with G. duebeni which exhibits comparatively high resistance capacities. The significance of the findings obtained is discussed in relation to the environmental requirements of the five crustaceans considered.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beadle, L.C., Cragg, J.B.: Studies on adaptation to salinity in Gammarus spp. I. Regulation of blood and tissues and the problem of adaptation to fresh water. J. exp. Biol. 17, 153–163 (1940)
Bulnheim, H.-P.: Vergleichende Untersuchungen zur Atmungsphysiologie euryhaliner Gammariden unter besonderer Berücksichtigung der Salzgehaltsanpassung. Helgol. wiss. Meeresunters. 23, 485–534 (1972)
Cook, R.H., Boyd, C.M.: The avoidance by Gammarus oceanicus Segerstråle (Amphipoda, Crustacea) of anoxic regions. Can. J. Zool. 43, 971–975 (1965)
Dorgelo, J.: Comparative ecophysiology of gammarids (Crustacea: Amphipoda) from marine, brackish and fresh-water habitats exposed to the influence of salinity-temperature combinations. III. Oxygen uptake. Netherl. J. Ses Res. 7, 253–266 (1973)
Dorgelo, J.: Comparative ecophysiology of gammarids (Crustacea: Amphipoda) from marine, brackish and fresh-water habitats, exposed to the influence of salinity-temperature combinations. I. Effect on survival. Hydrobiol. Bull. 8, 90–108 (1974)
Dorgelo, J.: Comparative ecophysiology of gammarids (Crustacea: Amphipoda) from marine, brackish- and fresh-water habitats exposed to the influence of salinity-temperature combinations. IV. Blood sodium regulation. Netherl. J. Sea Res. 11, 184–199 (1977a)
Dorgelo, J.: Comparative ecophysiology of two intertidal gammarids and the problem of zonation. Crustaceana Suppl. 4, 64–80 (1977b)
Fenchel, T., Frier, J.-O., Kolding, S.: The evolution of competing species. In: Marine organisms Genetics, ecology, and evolution. (B. Battaglia and J.A. Beardmore, eds.), pp. 289–301. New York-London: Plenum Press 1978
Forsman, B.: Studies on Gammarus duebeni Lillj., with notes on some rockpool organisms in Sweden. Zool. Bidr. Uppsala 29, 215–237 (1951)
Franke, U.: Experimentelle Untersuchungen zur Respiration von Gammarus fossarum Koch 1835 (Crustacea-Amphipoda) in Abhängigkeit von Temperatur, Sauerstoffkonzentration und Wasserbewegung. Arch. Hydrobiol. (Suppl.) 48, 369–411 (1977)
Halcrow, K., Boyd, C.M.: The oxygen consumption and swimming activity of the amphipod Gammarus oceanicus at different temperatures. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 23, 233–242 (1967)
Hartog, C. den: The amphipods of the deltaic region of the rivers Rhine, Meuse and Scheldt in relation to the hydrography of the area. Part III. The Gammaridae. Netherl. J. Sea Res. 2, 407–457 (1964)
Hoppenheit, M.: Strahlenbiologische Untersuchungen an Gammariden (Crustacea, Amphipoda). Helgol. wiss. Meeresunters. 19, 163–204 (1969)
Jażdżewski, K.: Biology of Crustacea Malacostraca in the Bay of Puck Polish Baltic Sea. Zool. Pol. 20, 423–480 (1970)
Kaufmann, H.: Ein einfaches Verfahren zur Auswertung von Überlebenskurven bei tödlich verlaufenden Erkrankungen. Strahlentherapie 130, 509–527 (1966)
Kinne, O.: Die Gammarus-Arten der Kieler Bucht. Zool. Jb. (Abt. Syst. Ökol. Geogr. Tiere) 82, 405–425 (1954a)
Kinne, O.: Interspezifische Sterilpaarung als konkurrenzökologischer Faktor bei Gammariden (Crustacea, Peracarida). Naturwiss. 41, 434–435 (1954b)
Kinne, O.: Ecological data on the amphipod Gammarus duebeni. A monograph. Veröff. Inst. Meeresforsch. Bremerh. 6, 177–202 (1959)
Lagerspetz, K.: Humidity reactions of three aquatic amphipods Gammarus duebeni, G. oceanicus and Pontoporeia affinis in the air. J. exp. Biol. 40, 105–110 (1963)
Lockwood, A.P.M., Inman, C.B.E.: The blood volume of some amphipod crustaceans in relation to the salinity of the environment they inhabit. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 44A, 935–941 (1973)
Movaghar, C.-A.: Verbreitung und Ökologie der Amphipoden im Elbe-Aestuar. Arch. Hydrobiol. (Suppl.) 29, 97–179 (1964)
Newell, R.C.: Factors affecting the respiration of intertidal invertebrates. Amer. Zool. 13, 513–528 (1973)
Newell, R.C.: Biology of intertidal animals. pp. 781. Faversham, U.K.: Marine Ecological Surveys. Third ed. 1979
Roux, C.: Les variations de la courbe métabolisme/température des Gammarus pulex (L.) et Gammarus fossarum Koch (Amphipodes) sous l'influence de divers facteurs écologiques. Crustaceana 29, 33–48 (1975)
Rygg, B.: Factors controlling the habitat selection of Gammarus duebeni Lillj. (Crustacea, Amphipoda) in the Baltic. Ann. Zool. Fenn. 9, 172–183 (1972)
Sachs, L.: Angewandte Statistik. 5. Aufl. pp 552. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1978
Schriever, G.: Die sessile, hemisessile und vagile Hartbodenfauna der Schlei im ökologischen Vergleich. Kieler Meeresforsch. 30, 80–90 (1974)
Segerstråle, S.G.: The amphipods on the coasts of Finland—some facts and problems. Comment. biol. 10, 1–28 (1950)
Segerstråle, S.G.: Synopsis of data on the crustaceans Gammarus locusta, Gammarus oceanicus, Pontoporeia affinis, and Corophium volutator (Amphipoda Gammaridea). Comment. biol. 20, 1–23 (1959)
Schulze, G., Arndt, E.A.: Zur Verbreitung der Gammariden (Amphipoda, Crustacea) in der Darßer Boddenkette. Wiss. Z. Univ. Rostock 20, 33–47 (1971)
Sutcliffe, D.W.: Sodium regulation and adaptation to fresh water in gammarid crustaceans. J. exp. Biol. 48, 359–380 (1968)
Sutcliffe, D.W.: Regulation of water and some ions in gammarids (Amphipoda). III. Three euryhaline species. J. exp. Biol. 55, 357–369 (1971)
Sutcliffe, D.W., Shaw, J.: The sodium balance mechanism in the fresh-water amphipod, Gammarus lacustris Sars. J. exp. Biol. 46, 519–528 (1967)
Taylor, E.W., Buttler, P.J., Al-Wassia, A.: Some responses of the shore crab, Carcinus maenas (L.) to progressive hypoxia at different acclimation temperatures and salinities. J. comp. Physiol. 122, 391–402 (1977)
Werntz, H.O.: Osmotic regulation in marine and fresh-water gammarids (Amphipoda). Biol. Bull. 124, 225–239 (1963)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bulnheim, H.P. Comparative studies on the physiological ecology of five euryhaline Gammarus species. Oecologia 44, 80–86 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00346402
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00346402