Abstract
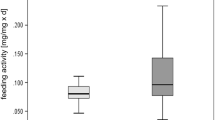
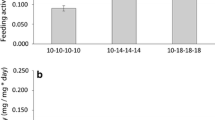
The specialised fauna of freshwater springs will have to cope with a possible temperature rise owing to Global Change. It is affected additionally by contamination of the water with xenobiotics from human activities in the surrounding landscape. We assessed the combined effects of temperature increase and exposure to toxins in laboratory experiments by using copper sulphate as a model substance and Gammarus fossarum Koch, 1835, as the model organism. This amphipod is a common representative of the European spring fauna and copper ions are widespread contaminants, mainly from agricultural practice. The experiments were conducted in boxes placed in flow channels and the water temperatures were varied. The gammarids were fed with conditioned beech leaf discs. The feeding activity of the amphipods was quantified on the level of the organism; and the respiratory electron transport system (ETS) assay was conducted in order to determine changes on the cellular level in the test organisms. The results show that the feeding activity increased slightly with higher water temperature. The sub-lethal copper dose had no significant effect other than a trend towards lower feeding activity. The ETS activity was significantly higher at the higher water temperatures, and the copper ions significantly lowered the ETS activity of the organisms. The combination of the two methods was useful when testing for combined effects of environmental changes and pollutants on a species. From the results one can reasonably infer a higher risk of adverse effects with increase in water temperature and exposure to a particular heavy metal.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alonso A, De Lange HJ, Peeters ETHM (2009) Development of a feeding behavioural bioassay using the freshwater amphipod Gammarus pulex and the multispecies freshwater biomonitor. Chemosphere 75:341–346
Alonso A, De Lange HJ, Peeters ETHM (2010) Contrasting sensitivities to toxicants of the freshwater amphipods Gammarus pulex and G. fossarum. Ecotoxicol 19:133–140
Bamsted U (1980) ETS activity as an estimator of respiratory rate of zooplankton populations. The significance of variations in environmental factors. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 42:267–283
Bat L, Akbulut M, Culha M, Gündogdu A, Satilmis HH (2000) Effect of temperature on the toxicity of zinc, copper and lead to the freshwater amphipod Gammarus pulex pulex (L., 1758). Turk J Zool 24:409–415
Bloor M (2009) Aquatic pollution. Case study of landfill leachate toxicity and remediation. VDM Verlag, Germany
Bloor MC (2010) Animal standardisation for mixed species ecotoxicological studies: establishing a laboratory breeding programme for Gammarus pulex and Asellus aquaticus. Zoologica baetica 21:179–190
Bloor MC, Banks CJ (2006) An evaluation of mixed species in situ and ex situ feeding assays: the altered response of Asellus aquaticus and Gammarus pulex. Environ Int 32:22–27
Brooks SJ, Mills CL (2003) The effect of copper on osmoregulation in the freshwater amphipod Gammarus pulex. Comp Biochem Physiol Part A 135:527–537
Bundschuh M, Hahn T, Gessner MO, Schulz R (2009) Antibiotics as a chemical stressor affecting an aquatic decomposer-detritivore system. Environ Toxicol Chem 28:197–203
Clesceri LS, Eaton AD, Greenberg AE (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 20th edn. American Public Health Organization, Washington
Cold A, Forbes VE (2004) Consequences of a short pulse of pesticide exposure for survival and reproduction of Gammarus pulex. Aquat Toxicol 67:287–299
Coulaud R, Geffard O, Xuereb B, Lacaze E, Quéau H, Garric J, Charles S, Chaumot A (2011) In situ feeding assay with Gammarus fosssarum (Crustacea): modelling the influence of confounding factors to improve water quality biomonitoring. Water Res 45:6417–6429
Danks HV, Williams DD (1991) Arthropods of springs, with particular reference to Canada: synthesis and needs for research. Mem Ent Soc Can 155:203–217
De Coen WM, Janssen CR (2003) The missing biomarker link: relationships between effects on the cellular energy allocation biomarker of the toxicant-stressed Daphnia magna and corresponding population characteristics. Environ Toxicol Chem 22:1632–1641
De Martins MG, Barcarolli IF, De Menezes EJ, Giacimin MM, Wood CM, Bianchini A (2011) Acute toxicity, accumulation and tissue distribution of copper in the blue crab Callinectes sapidus acclimated to different salinities: in vivo and in vitro studies. Aquat Toxicol 101:88–99
De Oliveira-Filho EC, Lopes RM, Paumgartten FJR (2004) Comparative study on the susceptibility of freshwater species to copper-based pesticides. Chemosphere 56:369–374
Debelius B, Forja JM, DelValls A, Lubian L (2009) Toxicity and bioaccumulation of copper and lead in five marine microalgae. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 72:1503–1513
Dedourge-Geffard O, Palais F, Biagianti-Risbourg S, Geffard O, Geffard A (2009) Effects of metals on feeding rate and digestive enzymes in Gammarus fossarum: an in situ experiment. Chemosphere 77:1569–1576
Effler SW, Litten S, Field SD, Tong-Ngork T, Hale F, Meyer M, Quirk M (1980) Whole lake responses to low level copper sulphate treatment. Water Res 14:1489–1499
Felten V, Charmantier G, Mons R, Geffard A, Rousselle P, Coquery M, Garric J, Geffard O (2008) Physiological and behavioural responses of Gammarus pulex (Crustacea: Amphipoda) exposed to cadmium. Aquat Toxicol 86:413–425
Fent K (2007) Ökotoxikologie, 3rd edn. Thieme Verl, Stuttgart/New York
Ferrington LC (1995) Biodiversity of aquatic insects and other invertebrates in springs: introduction. J Kans Entomol Soc. 68:1–3
Fischer J, Fischer F, Schnabel S, Bohle HW (1998) Spring fauna of the Hessian Mittelgebirge: population structure, adaptative strategies, and relations to habitats of the macroinvertebrates, as exemplified by springs in the Rhenisch metamorphic shieldand in the East-Hessian sandstone plate. In: Botosaneanu L (ed) Studies in crenobiology. The biology of springs and springbrooks. Backhuys Publishers, Leiden, pp 182–199
Foucreau N, Cottin D, Piscart C, Hervant F (2014) Physiological and metabolic responses to rising temperature in Gammarus pulex (Crustacea) populations living under continental or Mediterranean climates. Comp Biochem Physiol Part A 168:69–75
Geffard A, Sartelet H, Garric J, Biagianti-Risbourg S, Delahaut L, Geffard O (2010) Subcellular compartmentalization of cadmium, nickel, and lead in Gammarus fossarum: comparison of methods. Chemosphere 78:822–829
Guida M, Inglese M, Meric S (2008) A multi-battery toxicity investigation on fungicides. Desalination 226:262–270
Güven K, Özbay C, Ünlü E, Satar A (1999) Acute lethal toxicity and accumulation of copper in Gammarus pulex (L.) (Amphipoda). Turk J Biol 23:513–521
Haeckel JW, Meijering MPD, Rusetzki H (1973) Gammarus fossarum Koch als Fallaubzersetzer in Waldbächen. Freshw Biol 3:241–249
Heino J, Virkkala R, Toivonen H (2009) Climate change and freshwater biodiversity: detected patterns, future trends and adaptations in northern regions. Biol Rev 84:39–54
Holmstrup M, Bindesbøl A-M, Oostingh GJ, Duschl A, Scheil V, Köhler H-R, Loureiro S, Soares AMVM, Ferreira ALG, Kienle C, Gerhardt A, Laskowski R, Kramarz PE, Bayley M, Svendsen C, Spurgeon DJ (2010) Interactions between effects of environmental chemicals and natural stressors: a review. Sci Total Environ 408:3746–3762
IPCC (2007) Climate change, 2007. Synthesis report. In: Pachauri RK, Reisinger A (eds) Contribution of working groups 1, 2 and 3 to the fourth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. IPCC, Geneva
Janetzky W (1994) Distribution of the genus Gammarus (Amphipoda: Gammaridae) in the River Hunte and its tributaries (Lower Saxony, northern Germany). Hydrobiologia 294:23–34
Jonsson M, Malmquist B (2000) Ecosystem process rate increases with animal species richness: evidence from leaf-eating, aquatic insects. Oikos 89:519–523
Kenner RA, Ahmed SI (1975) Measurements of electron transport activities in marine phytoplancton. Mar Biol 33:119–127
Komarek M, Cadkova E, Chrastny V, Bordas F, Bollinger JC (2010) Contamination of vineyard soils with fungicides: a review of environmental and toxicological aspects. Environ Int 36:138–151
Ladewig V, Jungmann D, Köhler H-R, Schirling M, Triebskorn R, Nagel R (2006) Population structure and dynamics of Gammarus fossarum (Amphipoda) upstream and downstream from effluents of sewage treatment plants. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 50:370–383
Lebrun JD, Perret M, Geffard A, Gourlay-Francé C (2012) Modelling copper bioaccumulation in Gammarus pulex and alterations of digestive metabolism. Ecotoxicology 21:20022–22030
Lemus MJ, Chung KS (1999) Effect of temperature on copper toxicity, accumulation and purification in tropical fish Juveniles Petenia Kraussii (Pisces: Cichlidae). Caribb J Sci 35:64–69
Lindegaard C, Brodersen KB, Wiberg-Larsen P, Skriver J (1998) Multivariate analyses of macrofaunal communities in Danish springs and springbrooks. In: Botosaneanu L (ed) Studies in Crenobiology. The Biology of Springs and Springbrooks 201-219. Backhuys Publishers, Leiden
Litchfield JT Jr, Wilcoxon F (1948) A simplified method of evaluating dose-effect experiments. Stamford Research Laboratories, American Cyanamid Company, Stamford
Lukancic S, Zibrat U, Mezek T, Jerebic A, Simcic T, Brancelj A (2009) Effects of exposing two non-target crustacean species, Asellus aquaticus L., and Gammarus fossarum Koch, to Atrazine and Imidacloprid. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 84:85–90
Lukancic S, Zibrat U, Mezek T, Jerebic A, Simcic T, Brancelj A (2010) A new method for early assessment of effects of exposing two non-target crustacean species, Asellus aquaticus and Gammarus fossarum, to pesticides, a laboratory study. Toxicol Ind Health 26:217–228
Malbouisson JFC, Young TWK, Bark AW (1995) Use of feeding rate and repairing of precopulatory Gammarus pulex to assess toxicity of Gamma-Hexachlorocyclohexane (Lindane). Chemosphere 30:1573–1583
Maltby L, Clayton SA, Wood RM, McLoughlin N (2002) Evaluation of the Gammarus pulex in situ feeding assay as a biomonitor of water quality: robustness, responsiveness, and relevance. Environ Toxicol Chem 21:361–368
Meyer F (2001) Wie die Natur Chemie betreibt. Universität Heidelberg Ruperto Carola 3, Heidelberg
Mezek T, Simcic T, Arts MT, Brancelj A (2010) Effect of fasting on hypogean (Niphargus stygius) and epigean (Gammarus fossarum) amphipods: a laboratory study. Aquat Ecol 44:397–408
Moog O (1995) Fauna Aquatica Austriaca. Wasserwirtschaftskataster. Bundesministerium für Land- und Forstwirtschaft, Wien
Naylor C, Maltby L, Calow P (1990) Scope for growth in Gammarus pulex, a freshwater benthic detritivore. Hydrobiologia 188(189):517–523
Newmann MC (2010) Fundamentals of ecotoxicology, 3rd edn. CRC Press Taylor and Francis Group, Boca Raton
Nilsson LM (1974) Energy Budget of a laboratory population of Gammarus pulex (Amphipoda). Oikos 25:35–42
Packard TT (1971) The measurement of respiratory electron transport system activity in marine phytoplankton. J Mar Res 29:235–244
Pestana JLT, Re A, Nogueira AJA, Soares AMVM (2007) Effects of cadmium and zinc on the feeding behaviour of two freshwater crustaceans: Atyaephyra desmarestii (Decapoda) and Echinogammarus meridionalis (Amphipoda). Chemosphere 68:1556–1562
Pöckl M, Humpesh UH (1990) Intra- and inter-specific variations in egg survival and brood development time for Austrian populations of Gammarus fossarum and G. roeseli (Crustacea: Amphipoda). Freshw Biol 23:441–455
Pöckl M, Webb BW, Sutcliffe DW (2003) Life history and reproductive capacity of Gammarus fossarum and G. roeseli (Crustacea: Amphipoda) under naturally fluctuating water temperatures: a simulation study. Freshw Biol 48:53–66
Reichmuth JM, Weis P, Weis JS (2010) Bioaccumulation and depuration of metals in blue crabs (Callinectes sapidus Rathbun) from contaminated and clean estuary. Environ Pollut 158:361–368
Rinderhagen M, Ritterhof J, Zauke G (2000) Crustaceans as bioindicators. In: Gerhardt A (ed) Biomonitoring of polluted water—reviews on actual topics, vol 9., Environmental Research ForumTrans Tech Publications - Scitech Publications, Uetikon-Zuerich, pp 161–194
Ruyters S, Salaets P, Oorts K, Smolders E (2013) Copper toxicity in soils under established vineyards in Europe: a survey. Sci Total Environ 443:470–477
Schönborn W, Risse-Buhl U (2013) Lehrbuch der Limnologie. 2. Vollständig überarbeitet Auflage. Schweizerbart, Stuttgart, p 471
Simcic T (2005) Respiratory electron transport system (ETS) activity and respiration rate in cold-stenothermal and eurythermal chironomid larvae from high-mountain lakes. Archiv für Hydrobiologie 162:399–415
Simcic T, Brancelj A (1997) Electron transport system (ETS) activity and respiration rate in five Daphnia species at different temperatures. Hydrobiologia 360:117–125
Simcic T, Brancelj A (2004) Respiratory electron transport system (ETS) activity as an estimator of the thermal tolerance of two Daphnia hybrids. J Plankton Res 26:525–534
Simcic T, Brancelj A (2006) Effects of pH on electron transport system (ETS) activityand oxygen consumption in Gammarus fossarum, Asellus aquaticus and Niphargus sphagnicolus. Freshw Biol 51:686–694
Simcic T, Lukancic S, Brancelj A (2005) Comparative study of electron transport system activity and oxygen consumption of amphipods from caves and surface habitats. Freshw Biol 50:494–501
Sridhar KR, Krauss G, Bärlocher F, Raviraja NS, Wennrich R, Baumbach R, Krauss G-J (2001) Decomposition of alder leaves in two heavy metal-polluted streams in central Germany. Aquat Microb Ecol 26:73–80
Sutcliffe DW, Carrick TR, Willoughby LG (1981) Effects of diet, body size, age and temperature on growth rates in the amphipod Gammarus pulex. Freshw Biol 11:183–214
Tattersfield LJ (1993) Effects of copper on the energy budget of a stream detritivore: validation and ecological relevance. Dissertation. University of Sheffield
Taylor HH, Anstiss JM (1999) Copper and haemocyanin dynamics in aquatic invertebrates. Mar Freshw Res 50(8):907–931
Taylor EJ, Jones DPW, Maund SJ, Pascoe D (1993) A new method for measuring the feeding activity of Gammarus Pulex (L.). Chemosphere 26:1375–1381
Taylor EJ, Underhill KM, Blockwell SJ, Pascoe D (1998) Haem biosynthesis in the freshwater macroinvertebrate Gammarus pulex (L.): effects of copper and Lindane. Water Res 32:2202–2204
Toth GL (1999) Aktivität des Elektronentransportsystems. In: von Tümpling W, Friedrich G (eds) Biologische Gewässeruntersuchung. Methoden der Biologischen Wasseruntersuchung 2. Gustav Fischer Verl., Jena, Stuttgart, Lübeck, Ulm, pp 465–473
Vittoz P, Cherix D, Gonseth Y, Lubini V, Maggini R, Zbinden N, Zumbach S (2013) Climate change impacts on biodiversity in Switzerland: a review. J Nat Conserv 21:154–162
Von Fumetti S, Nagel P (2012) Discharge variability and its effect on faunistic assemblages in springs. Freshw Sci 31:647–656
Wagner R (1990) Influence of temperature, photoperiod and nutrition on growth and consumption of Chaetopteryx Villosa (Trichoptera). Holarct. Ecol 13(3):247–254
Webb DW, Wetzel MJ, Reed PC, Philippe LR, Young TC (1998) The macroinvertebrate biodiversity, water quality, and hydrogeology of ten karst springs in the Salem Plateau of Illinois. In: Botosaneanu L (ed) Studies in crenobiology: the biology of springs and springbrooks. Backhuys Publishers, Leiden, pp 39–48
Woodward G, Friberg N, Hildrew AG (2009) The need for scientific rigour in biomonitoring and conservation of fresh waters Freshwater ecosystems: biodiversity, management and conservation. Nova, Hauppage
Woodward G, Perkins DM, Brown LE (2010) Climate change and freshwater ecosystems; impacts across multiple levels of organization. Philos Trans R Soc B 365:2093–2106
Zollhöfer JM (1997) Quellen - die unbekannten Biotope im Schweizer Jura und Mittelland. Erfassen -Bewerten - Schützen. Bristol Stiftung, Zürich
Acknowledgments
The Janggen-Pöhn-Stiftung supported the PhD project by partially financing the main author. T. Simcic kindly introduced us to the ETS method. C. Clarke proof-read the manuscript. Thanks are owing to five anonymous reviewers, who made valuable comments on the manuscript. Thanks are also owing to further numerous people, especially to the first author’s family for valuable technical support and discussions.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmidlin, L., von Fumetti, S. & Nagel, P. Effects of increased temperatures on Gammarus fossarum under the influence of copper sulphate. Ecotoxicology 24, 433–444 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-014-1392-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-014-1392-6