Summary
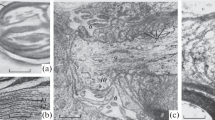
The nodes of Ranvier and their surrounding structures have been studied by means of serial and single ultrathin sections of the frog's optic tract and diencephalon.
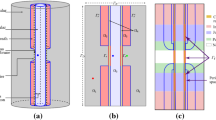
The following aspects of the ultrastructure of the myelin sheath at the nodes are described: (a) the site and manner of termination of the compact myelin and glia-satellite cytoplasm; (b) the reflection of the glia-satellite cytoplasm at the node; (c) the formation of compact myelin during development; (d) the involvement of the glia-satellite cell in the metabolism and impulse conduction of the fiber.
The nodes are surrounded by a considerable extension of the extracellular space — the perinodal extracellular space or perinodal matrix. The ground substance of the perinodal matrix consists of ill defined granules arranged in patches or in fibrillar or vacuolar manner. Microvilli-like protuberances of the glia and nervous processes emerge into the perinodal matrix. The shape and the volume of the perinodal extracellular space is determined using a reconstruction method from a series of sections through the node in diencephalon.
In the diencephalon nerve endings show close contact with the node and its surroundings. These nerve endings contain synaptic vesicles, mitochondria and small opaque particles. Small opaque particles, up to the present not recognized as components of synapses, have been observed in a number of nerve endings in the diencephalon. The possibility is considered that such nervous configurations at the node could be involved in subliminal interactions between different neurons.
Based on the ultrastructural data the concept of nodal apparatus is introduced as a working hypothesis. The nodal apparatus consists of the node, terminal compartments of the glia-satellite cell, the perinodal matrix, and the surrounding glia and nervous structures, which may be involved in the nodal activities. The structural pattern of such a nodal apparatus may vary in different parts of the central nervous system indicating the possibility of variation in the functioning of the corresponding nodes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abood, L. G., and S. K. Abul-Haj: Histochemistry and characterization of hyaluronic acid in axons of peripheral nerve. J. Neurochem. 1, 119–125 (1956).
Allison, A. C., and W. H. Feindel: Nodes in the central nervous system. Nature (Lond.) 163, 449 (1949).
Bennett, H. S.: The concepts of membrane flow and membrane vesiculation as mechanisms for active transport and ion pumping. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 2, Suppl. 99 (1956).
Bodian, D.: A note on nodes of Ranvier in the central nervous system. J. comp. Neurol. 94, 475–484 (1951).
—: Introductory survey of neurons. Cold Spr. Harb. Symp. quant. Biol. 17, 1–13 (1952).
—, and N. Taylor: Synapse arising at central node of Ranvier, and note on fixation of the central nervous system. Science 139, 330–332 (1963).
Bullock, T. H.: Neuron doctrine and electrophysiology. Science 129, 997–1002 (1959).
Bunge, R. P., M. B. Bunge, and H. Ris: Electron microscopic study of demyelination in an experimentally induced lesion in adult cat spinal cord. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 7, 685–696 (1960).
De Rényi, G. S.: The structure of cells in tissues as revealed by microdissection. II. The physical properties of the living axis cylinder in the myelinated nerve fibres of the frog. J. comp. Neurol., 47, 405–425 (1928/29).
Engström, A., and H. Luthy: The distribution of mass and lipids in the single nerve fibre. Exp. Cell. Res. 1, 81–91 (1950).
Galambos, R.: A glia-neural theory of brain function. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) 47, 129–136 (1961).
Hess, A., and J. Z. Young: Correlation of internodal length and fibre diameter in the central nervous system. Nature (Lond.) 164, 490–491 (1949).
—: The nodes of Ranvier. Proc. roy. Soc. B 140, 301 (1952–1953).
Hild, W., and I. Tasaki: Morphological and physiological properties of neurons and glial cells in tissue culture. J. Neurophysiol. 25, 277–304 (1962).
Howland, B., J. Y. Lettvin, W. S. McCulloch, W. Pitts, and P. D. Wall: Reflex inhibition by dorsal root interaction. J. Neurophysiol. 18, 1–17 (1955).
Hydén, H., and A. Pigon: A cytophysiological study of the functional relationship between oligodendroglial cells and nerve cells of Deiters' nucleus. J. Neurochem. 6, 57–72 (1960/61).
Kay, D.: Techniques for electron microscopy. Oxford: Blackwell Sci. Publ. 1961.
Koch, A., J. B. Ranck Jr., and B. L. Newman: Ionic content of the neuroglia. Exp. Neurol. 6, 186–200 (1962).
Landon, D. N., and P. L. Williams: Ultrastructure of the node of Ranvier. Nature (Lond.) 199, 575–577 (1963).
Luft, J. H.: Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 9, 409–414 (1961).
Maturana, H. R.: The fine anatomy of the optic nerve of anurans — an electron microscope study. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 7, 107–120 (1960).
Metuzals, J.: Ultrastructure of myelinated nerve fibres and nodes of Ranvier in the central nervous system of the frog, A. L. Houwink and B. J. Spit, edit. The Proceedings of the European Regional Conference on Electron Microscopy, Delft. De Nederlandse Vereniging voor Electronenmicroscopie 1960, vol 1.
—: Ultrastructure of Ranvier's node in central fibres, analysed in serial sections, S. S. Breese Jr., edit. Fifth Internat. Congr. Electron Microscopy, Philadelphia. New York and London: Academic Press 1962.
—: Ultrastructure of Ranvier's node in central fibres, analysed in serial sections. In: Progress in brain research, vol. 6. Topics in basic neurology. Third Internat. Meeting of Neurobiologists, Kiel, Deutschland, September 1962, edit. by W. Bargmann and J. P. Schadé. Amsterdam-London-New York: Elsevier, Publ. Co. 1964.
Müller-Mohnssen, H.: Morphologische Veränderungen des überlebenden Ranvierschen Schnürrings unter Einwirkung anisosmotischer Außenlösungen. Z. Zellforsch. 49, 287–318 (1959).
—: Der Einfluß elektrophysiologisch wirksamer Substanzen auf das mikroskopische Bild des überlebenden Ranvierschen Schnürrings. Z. Zellforsch. 52, 9–24 (1960).
Palade, G. E.: A study of fixation for electron microscopy. J. exp. Med. 95, 285 (1952).
Peters, A.: The formation and structure of myelin sheaths in the central nervous system. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 8, 431–446 (1960).
Ramón Y Cajal, S.: Histologie du système nerveux de l'homme et des vertébrés. I. Madrid. Instituto Ramón y Cajal 1952.
Robertson, J. D.: Preliminary observations on the ultrastructure of nodes of Ranvier. Z. Zellforsch. 50, 553 (1959).
- A new unit membrane organelle of Schwann cells. In: Biophysics of physiological and pharmacological action, p. 63–96, Abraham M. Shanes, edit. Publication No 69 of the Amer. Ass. for the Advancement of Science, Washington 1961.
- The unit membrane of cells and mechanisms of myelin formation. Ultrastructure and metabolism of the nervous system, vol. XL, Research Publications A.R.N.M.D. 1962. Association for Research in Nervous and Mental Disease.
—, T. S. Bodenheimer, and D. E. Stage: The ultrastructure of Mauthner cell synapses and nodes in goldfish brains. J. Cell Biol. 19, 159–199 (1963).
Schultz, R. L., E. A. Maynard, and D. C. Pease: Electron microscopy of neurons and neuroglia of cerebral cortex and corpus callosum. Amer. J. Anat. 100, 369–408 (1957).
Sjöstrand, F. S.: Ultrastructure of retinal rod synapses of the guinea pig eye as revealed by three-dimensional reconstructions from serial sections. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 2, 122–170 (1958).
Smith, C. A., and E. W. Dempsey: Electron microscopy of the organ of Corti. Amer. J. Anat. 100, 337 (1957).
—, F. S. Sjöstrand: Structure of the nerve endings on the external hair cells of the guinea pig cochlea as studied by serial sections. J. Ultrastruct, Res. 5, 523–556 (1961).
Szentágothai, J.: Personal communication of unpublished data.
Tasaki, I.: Conduction of the nerve impulse. In: Handbook of physiology, Sect. 1, Neurophysiology, vol 1, p. 75–121, 1959.
Thomas, P. K., and J. Z. Young: Internode lengths in the nerves of fishes. J. Anat. (Lond.) 83, 336–350 (1949).
Uzman, B. G., and G. M. Villegas: A comparison of nodes of Ranvier in sciatic nerves with node-like structures in optic nerves of the mouse. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 7, 761–762 (1960).
Williams, P. L., and D. N. Landon: Paranodal apparatus of peripheral myelinated nerve fibres of mammals. Nature (Lond.) 198, 670–673 (1963).
Wolpert, L., C. M. Thompson, and C. H. O'neill: Studies on the isolated membrane and cytoplasm of Amoeba proteus in relation to ameboid movement. In: Primitive motile systems in cell biology, Robert D. Allen and Noburô Kamiya, edit., The Proceedings of a Symposium on the Mechanism of Cytoplasmic Streaming, Cell Movement and the Saltatory Motion of Subcellular Particles held at Princeton University, 1963. New York and London: Academic Press 1964.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This investigation was supported by a grant from the Medical Research Council, Canada (MA-1247).
The author is very much indebted to Mrs. H. Rushforth for excellent technical assistance, to Mr. H. R. A. Meiborg, Groningen, for very skilful printing of the photographs and to Mr. Hoekstra, Groningen, who made the drawing of Fig. 8.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Metuzals, J. Ultrastructure of the nodes of Ranvier and their surrounding structures in the central nervous system. Zeitschrift für Zellforschung 65, 719–759 (1965). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00342593
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00342593