Summary
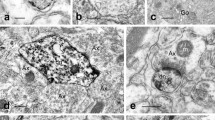
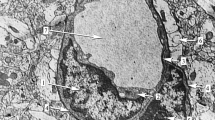
The ultrastructure of the capillaries in the area postrema of cats is described. — The capillaries are found to be lying in large channels which are surrounded by a basement membrane and by the processes of glial cells. The endothelium is very thin. It is characterized by the presence of numerous pores and some larger fenestrations. In some regions the basement membrane is enlarged and has a lamellar or reticular fine structure. In the pericapillary space outside the endothelium thin cells are concentrically arranged around the capillary (“hypendothelial cells”). There are some points of contact between the plasma membranes of these cells and those of the endothelial cells. In the tissue of the area postrema there are small neurones and some nerve fibres which are mostly unmyelinated. Complicated extensions of the perivascular spaces are found to be projecting into the nervous tissue.
Zusammenfassung
Die Ultrastruktur der Kapillaren in der Area postrema der Katze wird beschrieben.
Die Kapillaren liegen locker in weiten Kanälen, die von einer Basalmembran und Gliazellfortsätzen ausgekleidet sind. Das Endothel ist sehr dünn und weist zahlreiche Poren und einige größere Fensterungen auf. Die Basalmembran zeigt an manchen Stellen Erweiterungen mit einer lamellären oder reticulären Innenstruktur. Außerhalb der Endotheltapete liegen im perikapillären Spalt konzentrisch angeordnete Zellen („Hypendothelzellen“), die durch Kontaktflächen mit den Endothelzellen in Verbindung stehen. Im zentralnervösen Gewebe finden sich kleine Neurone und größtenteils marklose Nervenfasern. Der perivaskuläre Raum dringt mit komplizierten Fortsätzen in das nervöse Gewebe vor.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Borison, H. L., and S. C. Wang: Physiology and pharmacology of vomiting. Pharmacol. Rev. 5, 193–230 (1953).
Breemen, V. L. van, and C. D. Clemente: Silver deposition in the central nervous system and the hematoencephalic barrier studied with the electron microscope. J. biochem. biophys. Cytol. 1, 161–166 (1955).
Brizzee, K. R., and H. L. Borison: Studies on the localization and morphology of the chemoreceptor trigger (CT) zone in the area postrema of the cat. Anat. Rec. 112, 315 (1952).
—, and L. M. Neal: A re-evaluation of the cellular morphology of the area postrema in view of recent evidence for a chemoreceptor function. J. comp. Neurol. 100, 41–61 (1954).
Cammermeyer, J.: Is the human area postrema a neurovegetative nucleus ? Acta anat. (Basel) 2, 294–320 (1946).
—: The histochemistry of the mammalian area postrema. J. comp. Neurol. 90, 121–149 (1949).
Clemente, C. D., and V. L. van Breemen: Nerve fibers in the area postrema of cat, rabbit, guinea pig and rat. Anat. Rec. 123, 65–80 (1955).
Dempsey, E. W., and G. B. Wislocki: An electron microscopic study of the blood-brain barrier in the rat, employing silver nitrate as a vital stain. J. biochem. biophys. Cytol. 1, 245–256 (1955).
De Robertis, E., and H. M. Gerschenfeld: Submicroscopic morphology and function of glial cells. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 3, 1–65 (1961).
Duvernoy, H., et J. G. Koritke: Contribution à l'étude de l'angio-architectonic des organes circumventriculaires. Arch. Biol. (Liège) 75, 693–748 (1964).
Farquhar, M. G., and J. F. Hartmann: Electron microscopy of cerebral capillaries. Anat. Rec. 124, 288 (1956).
Hartmann, J. F.: Two views concerning criteria for identification of neuroglia cell types by electron microscopy. In: Biology of neuroglia (W. F. Windle, ed.). Springfield (Ill.): Ch. C. Thomas 1958.
King, L. S.: Cellular morphology in the area postrema. J. comp. Neurol. 66, 1–21 (1937).
Koritke, J. G., u. H. Duvernoy: Die Gefäßversorgung der Area postrema. Anat. Anz. 111, 61–72 (1962).
Lierse, W.: Die Kapillarabstände in verschiedenen Hirnregionen der Katze. Z. Zellforsch. 54, 199–206 (1961).
—: Elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen zur Cytologie und Angiologie des Epiphysenstiels von Anolis carolinensis. Z. Zellforsch. 65, 397–408 (1965).
Maynard, E. A., R. L. Schultz, and D. C. Pease: Electronmicroscopy of the vascular bed of rat cerebral cortex. Amer. J. Anat. 100, 409–433 (1957).
Morato, M. J. X.: Sur la structure et la signification fonctionelle de l'area postrema. Arch. port. Sci. Biol. 11, 50–70 (1955a).
—: Recherches histologiques sur l'area postrema. C. R. Ass. Anat. (Paris) 42, 1046–1054 (1955b).
—, et J. F. David, Ferreira: Recherches sur l'ultrastructure de l'area postrema. C. R. Ass. Anat. (Paris) 44, 541–548 (1957).
Morest, D. K.: A study of the structure of the area postrema with Golgi methods. Amer. J. Anat. 107, 291–303 (1960).
Mugnaini, E., and F. Walberg: Ultrastructure of neuroglia. Ergebn. Anat. Entwickl.-Gesch. 37, 194–236 (1964).
Pease, D. C., and R. L. Schultz: Electron microscopy of rat cranial meninges. Amer. J. Anat. 102, 301–321 (1958).
—: Circulation to the brain and spinal cord. In: Blood vessels and lymphatics (D. J. Abramson, ed.), p. 233–239. New York: Academic Press 1962.
Petry, G., u. W. Kühnel: Beitrag zur Kenntnis des Baues von Basalmembranen. Z. Zellforsch. 64, 533–540 (1964).
Shimizu, N., and J. Ishii: Fine structure of the area postrema of the rabbit brain. Z. Zellforsch. 64, 462–473 (1964).
Teixeira-Pinto, A. A.: Sur l'irrigation sanguine de l'area postrema du chat. C. R. Soc. Biol. (Paris) 151, 1482–1483 (1957).
—: Les vaisseaux de l'area postrema chez le chat. Réconstruction plastique. Arch. port. Sci. Biol. 3, 41–44 (1960).
Wilson, J. T.: On the anatomy of the calamus region in the human bulb; with an account of hitherto undescribed nucleus postremus. J. Anat. (Lond.) 40, 210–241, 357–386 (1906).
Wislocki, G. B., and L. S. King: The permeability of the hypophysis and hypothalamus to vital dyes, with a study of the hypophyseal vascular supply. Amer. J. Anat. 58, 421–472 (1936).
—, and T. J. Putnam: Note on the anatomy of the area postrema. Anat. Rec. 19, 281–287 (1920).
—: Further observations on the anatomy and physiology of the area postrema. Anat. Rec. 27, 151–156 (1924).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Mit Unterstützung durch die Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rivera-Pomar, J.M. Die Ultrastruktur der Kapillaren in der Area postrema der Katze. Zeitschrift für Zellforschung 75, 542–554 (1966). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00341512
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00341512