Summary
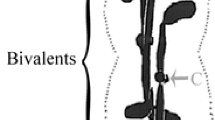
The spindle apparatus of the I. meiotic division in spermatocytes of Pales ferruginea was examined by means of ultra-thin sectioning of preselected single cells. Besides chromosomes 3 major components can be observed within the spindle region: 1. microtubules, 2. ribosomal particles, 3. intertubular spindle matrix of amorphous or filamentous appearance. As revealed from longitudinal and cross sections the microtubules are distributed more or less homogeneously within the spindle. There is no evidence for bundles of microtubules which may correspond to the chromosomal fibers of polarization microscopy. Determination of microtubular density in several division stages shows that the number of microtubules increasing during prometaphase up to metaphase, and does not decrease till late anaphase. Moving anaphase chromosomes show a characteristic change of form. Orientation of microtubules and their connexion with chromosomes and spindle matrix are discussed in detail.
Zusammenfassung
Der Spindelapparat der I. meiotischen Teilung in Spermatocyten von Pales ferruginea wurde nach gezielter Präparation einzelner Zellen mit der Ultradünnschnitttechnik untersucht. Neben den Chromosomen sind 3 Strukturkomponenten in der Spindelregion zu beobachten: 1. Mikrotubuli, 2. ribosomale Partikel, 3. amorph oder fädig erscheinende intertubuläre Spindelmatrix. Längs- und Querschnitte zeigen eine mehr oder weniger homogene Verteilung der Mikrotubuli in der Spindel. Es gibt keine Hinweise für Mikrotubulibündel, die den polarisationsmikroskopisch darstellbaren Chromosomenfasern entsprechen könnten. Bestimmungen der Mikrotubulidichte in einigen Teilungsphasen zeigen, daß die Anzahl der Tubuli während der Prometaphase bis zur Metaphase hin zunimmt und erst in der späten Anaphase abnimmt. Wandernde Anaphasechromosomen zeigen einen charakteristischen Formwandel. Die Orientierung der Mikrotubuli und ihre Beziehung zu Chromosomen und Spindelmatrix werden ausführlich diskutiert.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Bajer, A.: Behaviour and fine structure of spindle fibers during mitosis in endosperm. Chromosoma (Berl.) 25, 249–281 (1968).
Barer, R., Joseph, S.: Phase-contrast and interference microscopy in the study of cell structure. Symp. Soc. exp. Biol. 10, 160–184 (1957).
Bauer, H., Dietz, R., Röbbelen, C.: Die Spermatocytenteilungen der Tipuliden. III. Das Bewegungsverhalten der Chromosomen in Translokationsheterozygoten von Tipula oleracea. Chromosoma (Berl.) 12, 116–189 (1961).
Behnke, O., Forer, A.: Some aspects of microtubules in spermatocyte meiosis in a crane fly (Nephrotoma suturalis Loew): Intranuclear and intrachromosomal microtubules. C. R. Lab. Carlsberg 35, 437–455 (1966).
Belar, K.: Beiträge zur Kausalanalyse der Mitose. II. Wilhelm Roux' Arch. Entwickl.-Mech. Org. 118, 359–484 (1929a).
—: Beiträge zur Kausalanalyse der Mitose III. Z. Zellforsch. 10, 73–134 (1929b).
Bernal, J. D.: Structural units in cellular physiology. Publ. Amer. Ass. Adv. Sci. 14, 199–205 (1940).
Davies, H. G.: The ultra-violet absorption of living chick fibroblasts during mitosis. Exp. Cell Res. 3, 453–461 (1952).
Dietz, R.: Polarisationsmikroskopische Befunde zur chromosomeninduzierten Spindelbildung bei der Tipulide Pales crocata (Nematocera). Zool. Anz., Suppl. 26, 131–138 (1963).
—: Bau und Funktion des Spindelapparates. Naturwissenschaften 56, 237–248 (1969).
Forer, A.: Evidence for two spindle fiber components: A study of chromosome movement in living crane fly (Nephrotoma suturalis) spermatocytes, using polarization microscopy and an ultra-violet microbeam. Ph. D. Thesis, Dartmouth College, U.S. (1964).
—: Chromosome movements during cell-division. In: Handbook of molecular cytology, p. 553–601 (A. Lima-de-Faria, ed.). Amsterdam-London: North-Holland Publishing Company 1969
Freundlich, H.: Neuere Fortschritte der Kolloidchemie und ihre biologische Bedeutung. Protoplasma 2, 278–299 (1927).
— Enslin, O., Söllner, K.: Über die Bildung von Taktoiden in Gemischen zweier Sole und ihre biologische Bedeutung. Protoplasma 17, 489–498 (1933).
Fuge, H.: A crystalloid component in the meiotic spindle. Exp. Cell Res. 60, 309–313 (1970).
Hauser, M.: Elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen an dem Suktor Paracineta limbata Maupas. Z. Zellforsch. 106, 584–614 (1970).
Hepler, P. K., McIntosh, J. R., Cleland, S.: Intermicrotubule bridges in mitotic spindle apparatus. J. Cell Biol. 45, 438–444 (1970).
Inoué, S.: Polarization optical studies of the mitotic spindle. I. The demonstration of spindle fibers in living cells. Chromosoma (Berl.) 5, 487–500 (1953).
— Sato, H.: Cell motility by labile association of molecules. The nature of mitotic spindle fibers and their role in chromosome movement. J. gen. Physiol. 50, 259–292 (1967).
Jacobson, W., Webb, M.: The two types of nucleoproteins during mitosis. Exp. Cell Res. 3, 163–183 (1952).
Lane, N. C., Treherne, J. E.: Lanthanum staining of microtubules in axons from cockroach ganglia. J. Cell Sci. 7, 217–231 (1970).
Manton, I., Kowallik, K., von Stosch, H. A.: Observations on the fine structure and development of the spindle at mitosis and meiosis in a marine centric diatom (Lithodesmium undulatum). IV. The second meiotic division and conclusions. J. Cell Sci. 7, 407–443 (1970).
McIntosh, J. R., Hepler, P. K., van Wie, D.G.: Model for mitosis. Nature (Lond.) 224, 659–663 (1969).
Müller, W.: Interferenzmikroskopische Untersuchungen der Trockenmassenkonzentration in isolierten Mitoseapparaten und lebenden Spermatocyten von Pales ferruginea(Nematocera). Chromosoma (Berl.) 30, 305–316 (1970).
Östergren, G.: Luzula and the mechanism of chromosome movements. Hereditas 35, 445–468 (1949).
— Molé-Bajer, J., Bajer, A.: An interpretation of transport phenomena at mitosis. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 90, 381–408 (1960).
Petzelt, Ch.: RNS- und Proteinsynthese im Ablauf der Spermatocytenteilungen von Pales ferruginea (Nematocera). Chromosoma (Berl.) 29, 237–245 (1970).
Reynolds, E. S.: The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J. Cell Biol. 17, 208–213 (1963).
Rustad, R. C.: An interference microscopical and cytochemical analysis of local mass changes in the mitotic apparatus during mitosis. Exp. Cell Res. 16, 575–583 (1959).
Schmidt, W. J.: Doppelbrechung der Kernspindel und Zugfasertheorie der Chromosomenbewegung. Chromosoma (Berl.) 1, 253–264 (1939).
Schrader, F.: Mitosis, 2nd ed. New York: Columbia University Press 1953.
Stephens, R. E.: Reassociation of microtubule protein. J. molec. Biol. 33, 517–519 (1968).
Wilson, H. J.: Arms and bridges on microtubules in the mitotic apparatus. J. Cell Biol. 40, 854–859 (1969).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Herrn Dr. R. Dietz danke ich für freundlicherweise zur Durchsicht überlassene nichtpublizierte polarisationsmikroskopische Aufnahmen von der I. meiotischen Teilung der Spermatocyten von Pales crocata.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fuge, H. Spindelbau, Mikrotubuliverteilung und Chromosomenstruktur während der I. meiotischen Teilung der Spermatocyten von Pales ferruginea . Z. Zellforsch. 120, 579–599 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00340590
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00340590