Abstract
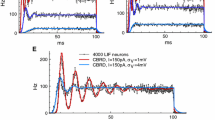
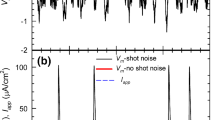
In spite of the fact that the participation of well defined ionic particles in generating convulsive unit discharges is established, there is a gap between the data on ionic movements and on first-order statistics of firing patterns. Our aim was to tight this gap by studying the effectiveness of functionally separated electrical conductances of membrane during the generation of consecutive interspike interval histograms (IIHs) of unitary discharges. On account of the non-stationarity of the process curve fitting analysis which based on the simple modifications of the integrate-and-fire model has been implemented in the sequential interspike interval histogram procedure (SIIH). The experimental data were recorded from cat cortex treated with 3-Aminopyridine (3-Ap) by glass microelectrodes during nembutal anesthezia. Assuming the normal distribution of input parameters it is concluded, that the efficiency of the fluctuations of the active spike-generating conductance g g and the passive diffusional conductance g l may increase during the generation of the unimodal IIHs and the first mode of the bimodal IIHs. The simple conductance coupling g l =a·g g +b may participate in g l activation, moreover, the reciprocally coupled mechanism g g =c/g l may be driven by g l activation (a, b, c are the coupling constants). A temporal separation of processes governed by g g or g l respectively was observed. The timeindependent occurrences of the reciprocally coupled conductance processes may be involved in the unit activities represented by the prolonged IIHs and second modes of the bimodal IIHs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, T.E., Rutledge, L.T.: Inhibition in penicillininduced epileptic foci. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophys. 46, 498–509 (1979)
Ayala, G.F., Spencer, W.A., Gumnit, R.J.: Penicillin as an epileptogenic agent: effect on an isolated synapse. Science 171, 915–917 (1971)
Carnevale, N.T., Wachtel, H.: Two reciprocating current components underlying slow oscillations in Aplysia bursting neurons. Brain Res. Rev. 2, 45–68 (1980)
Davenport, J., Schwindt, P.C., Crill, W.E.: Epileptogenic doses of penicillin do not reduce a monosynaptic GABA-mediated postsynaptic inhibition in the intact anaesthetized cat. Exp. Neurol. 65, 552–572 (1979)
Davenport, J., Schwindt, P.C., Crill, W.E.: Presynaptic and long-lasting postsynaptic inhibition during penicillininduced spinal seizures. Neurology 28, 592–597 (1978)
Dingleidine, R., Gjerstad, L.: Penicillin blocks hippocampal IPSPs, unmasking prolonged EPSPs. Brain Res. 168, 205–209 (1979)
Eckert, R., Lux, H.D.: A voltage-sensitive persistent calcium conductance in neuronal somata of Helix. J. Physiol. (London) 254, 129–151 (1976)
Futamachi, R.J., Prince, D.A.: Effects of penicillin on an excitatory synapse. Brain Res. 100, 589–597 (1975)
Heinemann, U., Lux, H.D., Gutnick, M.J.: Extracellular free calcium and potassium during paroxysmal activity in the cerebral cortex of the cat. Exp. Brain Res. 27, 237–243 (1977)
Heyer, C.B., Lux, H.D.: Control of the delayed outward potassium currents in bursting pace-maker neurones of the snail, Helix pomatia. J. Physiol. (London) 262, 349–382 (1976)
Jankowska, E., Lundberg, A., Rudomin, P., Sykova, E.: Effects of 4-aminopyridine on transmission in excitatory and inhibitory synapses in the spinal cord. Brain Res. 136, 387–392 (1977)
Kenyon, J.L., Gibbons, W.R.: 4-aminopyridine and the early outward current of sheep cardiac purkinje fibres. J. Gen. Physiol. 73, 139–157 (1979)
Knight, B.W.: Dynamics of encoding in a population of neurons. J. Gen. Physiol. 59, 734–766 (1972)
Kostyuk, P.G., Kulikov, M.A., Pyatigorsky, B.Ya., Vasilenko, D.A.: Analysis of background impulse activity of pyramidal tract neurons in cat. Nejrofiziologija 4, 3–11 (1972) (in russian)
Levine, M.W., Shefner, J.M.: A model for the variability of interspike intervals during sustained firing of a retinal neuron. Biophys. J. 19, 241–252 (1977)
Levithan, H., Segundo, J.P., Moore, G.P., Perkel, D.H.: Statistical analysis of membrane potential fluctuations. Biophys. J. 8, 1256–1274 (1968)
Lew, L.V., Ferreira, H.G.: Calcium transport and the properties of a calcium-activated potassium channel in red cell membranes. In: Current Topics in Membranes and Transport. Vol. 10, pp 217–277. Bronner, F., Kleinzeller, A. (eds.). New York: Academic Press 1978
Llinás, R., Walton, K., Bohr, V.: Synaptic transmission in squid giant synapse after potassium conductance blockadge with external 3- and 4-aminopyridine. Biophys. J. 16, 83–86 (1976)
Lundh, H., Thesleff, S.: The mode of action of 4-aminopyridine and quanidin on transmitter release from motor nerve terminals. Europ. J. Pharmacol. 42, 411–422 (1977)
Lux, H.D.: The kinetics of extracellular potassium: relation to epileptogenesis. Epilepsia 15, 375–393 (1974)
Matsumoto, H., Ayala, G.F., Gumnit, R.J.: Neuronal behavior and triggering mechanism in cortical epileptic focus. J. Neurophysiol. 32, 688–703 (1969)
Meyer, H., Prince, D.A.: Convulsant action of penicillin: effects on inhibitory mechanisms. Brain Res. 53, 477–482 (1973)
Moody, W.J., Jr., Futamachi, K.J., Prince, D.A.: Extracellular potassium activity during epileptogenesis. Exp. Neurol. 42, 248–263 (1974)
Nicholson, C., Steinberg, R., Stöckle, H., Ten Bruggencate, G.: Calcium decrease associated with aminopyridine-induced potassium increase in cat cerebellum. Neurosci. Lett. 3, 315–319 (1976a)
Nicholson, C., Ten Bruggencate, G., Senekowitch, R.: Large potassium signals and slow potentials evoked during aminopyridine or barium superfusion in cat cerebellum. Brain Res. 113, 606–610 (1976b)
Partridge, L.D., Thompson, S.H., Smith, S.J., Connor, J.A.: Currentvoltage relationships of repetitively firing neurons. Brain Res. 164, 69–79 (1979)
Parzen, E.: On estimation of a probability density function and mode. Ann. Math. Stat. 33, 1065–1076 (1962)
Pernier, J., Gerin, P.: Temporal patterns analysis of spontaneous unit activity in the neocortex. Biol. Cybern. 18, 123–136 (1975)
Pongrácz, F., Pongrácz, G., Szente, M.: Microcomputer method for the analysis of spontaneous bursting activity of units in epileptic cat cortex. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 49, 195–199 (1980)
Pongrácz, F., Szente, M.: Simulation of the ionic mechanisms of molluscan neurons under pentylenetetrazol-induced effects. Acta Phys. Sci. Hung. 53, 327–336 (1979)
Pongrácz, F., Szente, M.: Microcomputer-aided point-process analysis of epileptic unit activity. In: Lectures of Int. Symp. on Math. and Comp. Methods in Physiol., Budapest, 1980 (in press)
Sanderson, A.C., Kobler, B.: Sequential interval histogram analysis of non-stationary neuronal spike trains. Biol. Cybern. 22, 61–71 (1976)
Schwartzkroin, P.A., Slawsky, M.: Probable calcium spikes in hippocampal neurons. Brain Res. 135, 157–161 (1977)
Schwindt, P., Crill, W.: Role of a persistent inward current in motoneuron bursting during spinal seizures. J. Neurophysiol. 43, 1296–1318 (1980)
Spencer, A.W., Kandel, E.R.: Synaptic inhibition of seizures. In: Basic mechanisms of the epilepsies. pp. 575–603. Jasper, H.H., Ward, Jr.A.A., Pope, A. (eds.). Boston: Little Brown 1969
Sypert, G.W., Ward, A.A., Jr.: Changes in extracellular potassium activity during neocortical propagated seizures. Exp. Neurol. 45, 19–41 (1974)
Szente, M., Pongrácz, F.: Aminopyridine-induced seizure activity. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophys. 46, 605–608 (1979a)
Szente, M., Pongrácz, F.: Aminopyridine-induced scizure activity in the primary and mirror foci of the cat's cerebral cortex. In: Abstracts of 11th Epilepsy Int. Symp., p. 21, Firenze, 1979b
Traub, R.D., Llinás, R.: Hippocampal pyramidal cells: significance of dendritic ionic conductances for neuronal function and epileptogenesis. J. Neurophysiol. 42, 476–496 (1979)
Van Duijn, H., Schwartzkroin, P.A., Prince, D.A.: Action of penicillin on inhibitory processes in the cat's cortex. Brain Res. 53, 470–476 (1973)
Verveen, A.A., De Felice, L.J.: Membrane noise. In: Progress in Biophysics and Molecular Biology. Vol. 28, pp. 189–265. Butler, J.A.V., Noble, D. (eds.). Oxford: Pergamon Press 1974
Verveen, A.A., Derksen, H.E.: Fluctuation phenomena in nerve membrane. Proc. IEEE 56, 906–916 (1968)
Whisler, J.W., Johnston, D.: Epileptogenesis: a model for the involvement of slow membrane events and extracellular potassium. J. Theor. Biol. 75, 271–288 (1978)
Williamson, T.L., Crill, W.E.: The effects of pentylenetetrazol on molluscan neurons. I. Intracellular recording and stimulation. Brain Res. 116, 217–229 (1976a)
Williamson, T.L., Crill, W.E.: The effects of pentylenetetrazol on molluscan neurons. II. Voltage-clamp studies. Brain Res. 116, 231–249 (1976b)
Wong, R.K.S., Prince, D.A.: Participation of calcium spikes during intrinsic burst firing in hippocampal neurons. Brain Res. 159, 385–390 (1978)
Wong, R.K.S., Prince, D.A., Basbaum, A.I.: Intradendritic recordings from hippocampal neurons. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) 76, 986–990 (1979)
Yagi, K., Yukiko, S.: Recurrent inhibition and facilitation: demonstration in the tubero-infundibular system and effects of strychnine and picrotoxin. Brain Res. 84, 155–159 (1975)
Yeh, J.Z., Oxford, G.S., Wu, C.H., Narahashi, T.: Interactions of aminopyridines with potassium channels of squid axon membranes. Biophys. J. 16, 77–81 (1976)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pongrácz, F., Szente, M. On modelling the variability of interspike intervals during epileptic unit activity. Biol. Cybern. 41, 165–177 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00340318
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00340318