Summary
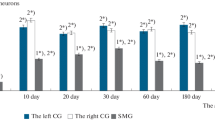
The concentration and distribution of glycogen in relation to postnatal differentiation of the mouse Leydig cell are studied by biochemical and ultrastructural methods. Glycogen decreases to less than one third in the first twelve days after birth. This decrease is accompanied by modifications of its distribution in the cytoplasm. In the newborn it is abundant and arranged in clusters of beta particles; in the mature Leydig cell, glycogen is found scattered in extremely low concentration interspersed among elements of the endoplasmic reticulum.
The role of glycogen during Leydig cell differentiation can be interpreted as a source of energy and/or as a source of building material in the biogenesis of membranous components.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armstrong, D. T.: Hormones and reproduction-gonadotropins, ovarian metabolism and steroid biosynthesis. Recent. Progr. Hormone Res. 24, 225–319 (1968).
Burgos, M. H., Fawcett, D. W.: Studies on the fine structure of the mammalian testis. I. Differentiation of the spermatids in the cat. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 9, 653–670 (1961).
Christensen, A. K.: The fine structure of testicular interstitial cells in guinea pigs. J. Cell. Biol. 26, 911–935 (1965).
—, Fawcett, D. W.: The normal fine structure of opossum testicular interstitial cells. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 9, 653–670 (1961).
Christensen, A. K., Fawcett, D. W.: The fine structure of testicular interstitial cells in mice. Amer. J. Anat. 118, 551–572 (1966).
Crabo, A. K.: The fine structure of the interstitial cells of the rabbit testes. Z. Zellforsch. 61, 587–604 (1963).
Dallner, G., Siekevitz, P., Palade, G. E.: Biogenesis of endoplasmic reticulum membranes. I. Structural and chemical differentiation in developing rat hepatocyte. J. Cell Biol. 30 73–96 (1966).
Drochmans, P.: Morphologie du glycogène. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 6, 141–163 (1962).
Duck-Chong, C., Pollak, J. K., North, R. J.: The relation between the intracellular ribonucleic acid distribution and amino acid incorporation in the liver of the developing chick embryo. J. Cell Biol. 20, 25–35 (1964).
Fahrenbach, W. H.: The sarcoplasmic reticulum of striated muscle of a cyclopoid copepod. J. Cell Biol. 17, 629–640 (1963).
Fawcett, D. W., Burgos, M. H.: Studies on the fine structure of the mammalian testis. II. The human interstitial tissue. Amer. J. Anat. 107, 245–269 (1960).
—, Revel, J. P.: The sarcoplasmic of a fast acting fish muscle. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 10, Suppl. 89–108 (1961).
—, Selby, C. C.: Observations to the fine structure of the turtle atrium. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 4, 63–72 (1958).
Grasso, J. A., Swift, H., Ackerman, G. A.: Observations on the development of erythrocytes in mammalian fetal liver. J. Cell Biol. 14, 235–254 (1962).
Karnovsky, M. J.: A formaldehyde-glutaraldehyde fixative of high osmolality for use in electron microscopy. J. Cell Biol. 27, 137 A (1965).
Krisman, C. R.: A method for colorimetric estimation of glycogen with iodine. Analyt. Biochem. 4, 17–21 (1962).
Leeson, C. R..: Observations on the fine structure of rat interstitial tissue. Acta anat. (Basel) 52, 34–48 (1963).
Mollenhauer, D. M.: Plastic embedding mixtures for use in electron microscopy. Stain Technol. 39, 111–114 (1964).
Munger, B. L., Roth, S. I.: The cytology of the normal parathyroid glands of man and Virginia deer. J. Cell Biol. 16, 379–400 (1963).
Nicander, L.: Histochemical study on glycogen in the testes of domestic and laboratory animals with special reference to variations during the spermatogenetic cycle. Acta morph. neerl. scand. 1, 233–247 (1957).
Niemi, M., Ikonen, M., Harvonen, A.: Histochemistry and fine structure of the interstitial tissue in the human foetal testis. Endocrinology of testis. CIBA Symposium 16, 31–55 (1967).
Omstad, O.: Studies on postnatal testicular changes, semen quality and anomalies of reproductive organs in the mink. Acta endocr. (Kbh.) Suppl. 117 (1967).
Palade, G. E.: A small particulate component of the cytoplasm. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 1, 59–68 (1955).
Peters, V. B., Dembitzer, H. M., Kelley, G. H., Baruch, E.: Proc. 5th Intern. Congr. E. M. Philadelphia 1962, vol. 2 TT 7. New York: Academic Press 1962.
Revel, J. P.: The sarcoplasmic reticulum of the bat cricothyroid muscle. J. Cell. Biol. 12, 571–589 (1960).
Reynolds, E. S.: The use of lead citrate at high pH. as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J. Cell Biol. 17, 208–212 (1963).
Rosenbluth, J.: Contrast between osmium-fixed and permanganate fixed Toad spinal ganglia. J. Cell Biol. 16, 143–157 (1963).
Russo, J.: Estudio ultraestructural de la diferenciación de la célula de Leydig. IX Congr. Latinoamericano de Ciencias Fisiológicas 7–12 Julio 1969, Belo Horizonte, Brazil.
Yamamoto, T.: Some observations on the fine structure of the sympathetic ganglia of bullfrog. J. Cell Biol. 16, 159–170 (1963).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported by Grant M 63,121 from the Population Council, U.S.A.
Fellow Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Cientificas y Técnicas, Argentina.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Russo, J. Glycogen content during the postnatal differentiation of the Leydig cell in the mouse testis. Z. Zellforsch. 104, 14–18 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00340046
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00340046