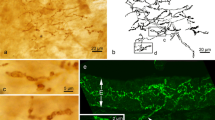
Summary
The apical region of the taste bud, delimited by the stratum disjunctum of the papillary epithelium, is divided into a distal taste pore, a channel, and a proximal chamber. In addition to “fuzzy coated” microvilli, the chamber contains an amorphous dense material histochemically defined as a neutral mucopolysaccharide.
Abounding in the apical cytoplasm of the taste cell is a randomly oriented filamentous component 60–70 Å in diameter extending into each microvillus. Likewise in this area membrane-bounded electron-dense bodies are found whose content is considered to be synthesized by the rough endoplasmic reticulum and subsequently concentrated and packaged by the Golgi complex. These bodies are thought to contain the neutral mucopolysaccharide, which finally reaches the chamber. Other components of the taste cell cytoplasm include vesicles, mitochondria, ribosomes, and nucleus. Two centrioles, each possessing a pair of rootlets, have been observed in the apical cytoplasm. Adjacent taste cells are attached apically by a zonula occludens followed by a zonula adhaerens. The synaptic clefts between taste cells and nerve fibers are acetylcholinesterase positive but are negative for butylcholinesterase and adenosine triophosphatase. A lineage of taste cells is postulated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, E.: Oocyte differentiation and vitellogenesis in the roach Periplaneta americana. J. cell Biol. 20, 131–155 (1964).
—: Events associated with differentiating oocytes in two species of amphineurans (Mollusca), Mopalia muscosa and Chaetopleura apiculata. J. Cell Biol. 27, 5A-6A (1965) (cmAbstract).
Ashford, T. P., and K. R. Porter: Cytoplasmic components in hepatic cell lysosomes. J. Cell Biol. 12, 198–202 (1962).
Baradi, A. F.: Gustatory and olfactory epithelia. Int. Rev. Cytol. 2, 289–330 (1953).
—: Histochemical localization of cholinesterase in gustatory and olfactory epithelia. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 7, 2–7 (1959).
—: Intergemmal spaces in taste buds. Z. Zellforsch. 65, 313–318 (1965).
—, and G. H. Bourne: Localization of gustatory and olfactory enzymes in the rabbit. Nature (Lond.) 168, 977–979 (1951).
Barka, T., and P. J. Anderson: Histochemistry, p. 63–64, 77–79, 81–86. New York: Harper & Row 1963.
Beidler, L. M.: Theory of taste stimulation. J. gen. Physiol. 38, 133–139 (1954).
—: Taste receptor stimulation. Progr. Biophys. 12, 107–151 (1961a).
—: Biophysical approaches to taste. Amer. Sci. 49, 421–431 (1961b).
—: Dynamics of taste cells. In: Y. Zotterman (ed.), Olfaction and taste, p. 133–148. New York: MacMillan (Pergamon) 1963.
—, and R. S. Smallman: Renewal of cells within taste buds. J. Cell Biol. 27, 263–272 (1965).
Bennett, S. H.: Morphological aspects of extracellular polysaccharides. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 11, 14–23 (1963).
Bourne, G. H.: Alkaline phosphatase in taste buds and nasal mucosa. Nature (Lond.) 161, 445–446 (1948).
Brandes, D.: Observation on the apparent mode of formation of pure lysosomes. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 12, 63–80 (1965).
—, F. Bertini, and E. T. Smith: Role of lysosomes in cellular lytic processes. II. Cell death during holocrine secretion in sebaceous glands. Exp. molec. Path. 4, 245–265 (1965).
Brandes, D., D. E. Buetou, F. Bertini, and D. B. Malkoff: Role of lysosomes in cellular lytio processes. I. Effect of carbon starvation in Euglena gracilis. Exp. molec. Path. 3, 583–609 (1964).
—, D. P. Groth, and F. Gyorkey: Occurrence of lysosomes in the prostatic epithelium of castrate rats. Exp. Cell Res. 28, 61–68 (1962).
Brandt, P. W.: A consideration of the extraneous coats of the plasma membrane. Circulation 26, 1075–1091 (1962).
Caro, L., and G. E. Palade: Protein synthesis, storage and discharge in the pancreatic exocrine cell, an autoradiographic study. J. Cell Biol. 20, 473–495 (1964).
Danielli, J. F.: Cytochemistry, p. 68–76. New York: John Wiley & Sons 1953.
De Duve, C.: The lysosomes. Science 208, 64–72 (1963).
De Lorenzo, A. J.: Ultrastructure and histophysiology of membranes. In: Y. Zotterman (ed.), Olfaction and taste, p. 5–17. New York: MacMillan (Pergamon) 1963.
Duncan, C. J.: Excitatory mechanisms in chemo- and mechanoreceptors. Biol. 5, 114–126 (1963).
—: Cation-permeability control and depolarization in excitable cells. J. theor. Biol. 8, 403–418 (1965).
Ebner, W. v.: Koelliker's Handbuch der Gewebelehre des Menschen, Bd. 3, S. 18–26. Leipzig: Engelmann 1899.
Ellis, R. A.: Cholinesterase in the mammalian tongue. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 7, 156–163 (1959).
Engström, H., and C. Rytzner: The fine structure of taste buds and taste fibers. Ann. Otol. (St. Louis) 65, 361–375 (1956a).
—: The structure of taste buds. Acta oto-laryng. (Stockh.) 46, 361–367 (1956b).
Evans, D. R.: Chemical structure and stimulation by carbohydrates. In: Y. Zotterman (ed.), Olfaction and taste, p. 165–175. New York: MacMillan (Pergamon) 1963.
Farbman, A. I.: Fine structure of the taste buds. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 12, 328–350 (1965).
Fawcett, D. W.: Surface specializations of absorbing cells. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 13, 75–91 (1965).
Gay, H.: Chromosome-Nuclear membrane-cytoplasmic interrelations in drosophila. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol., Suppl. 2, 407–414 (1956).
Graziadei, P.: Electron microscopy of some primary receptors in the sucker of Octopus vulgaris. Z. Zellforsch. 65, 510–522 (1964).
Hadek, R., and H. Swift: Intercisternal inclusion in the rabbit blastocyst. J. Cell Biol. 13, 445–451 (1962).
Heidenhain, M.: Über die Sinnesfelder und die Geschmacksknospen der Papilla foliata des Kaninchens. Arch. mikr. Anat. 85, 365–479 (1914).
Hodosh, M., and W. Montagna: Cholinesterases in the tongue of the potto (Perodieticus patto). Anat. Rec. 146, 7–15 (1963).
Ito, S.: The surface of enteric microvilli. Anat. Rec. 148, 294 (1964) (cmAbstract).
—: The enteric surface coat on cat intestinal microvilli. J. Cell Biol. 27, 475–491 (1965).
—, and R. Winchester: The fine structure of the gastric mucosa in the bat. J. Cell Biol. 16, 541–577 (1963).
Karnovsky, M. J.: The localization of cholinesterase activity in rat cardiac muscle by electron microscopy. J. Cell Biol. 23, 217–232 (1964).
Kimura, K., and L. M. Beidler: Microelectrode study of taste receptors of rat and hamster. J. cell. comp. Physiol. 58, 131–139 (1961).
Landgren, S., G. Liljestrand, and Y. Zotterman: Chemical transmission in taste fiber endings. Acta physiol. Scand. 30, 105–114 (1954).
Leblond, C. P.: The time factor in histology. Amer. J. Anat. 116, 1–27 (1965).
Leydig, F.: Über die Haut einiger Süßwasserfische. Z. wiss. Zool. 3, 1–11 (1851).
Lovén, C.: Beiträge zur Kenntnis vom Bau der Geschmackswärzchen der Zunge. Arch. mikr. Anat. 4, 96 (1868).
Luft, J. H.: Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 9, 409–414 (1961).
Matoltsy, A. G., and P. F. Parakkal: Membrane-coating granules of keratinizing epithelia. J. Cell Biol. 24, 297–307 (1965).
McNabb, J. D., and E. Sandborn: Filaments in the microvillus border of intestinal cell. J. Cell Biol. 22, 701–704 (1964).
Mollenhauer, H. H.: Transition forms of Golgi apparatus secretion vesicles. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 12, 439–446 (1965).
Moule, Y.: Endoplasmic reticulum and microsomes of rat liver. In: Michael Locke (ed.), Cellular membranes in development, p. 97–133. 22nd Symposium of the Society for the Study of Development and Growth. New York: Academic Press 1964.
Napolitano, L.: Cytolysosomes in metabolically active cells. J. Cell Biol. 18, 478–481 (1963).
Nemetschek-Gansler, H., u. H. Ferner: Über die Ultrastruktur der Geschmacksknospen. Z. Zellforsch. 63, 155–178 (1964).
Neutra, M., and C. P. Leblond: Synthesis of complex carbohydrates in Golgi region as shown by uptake of tritiated galactose. J. Cell Biol. 27, 72 A (1965).
Novikoff, A. B.: Lysosomes and related particles. In: J. Brächet and A. E. Mirsky (eds.), The Cell, vol. 2, p. 423–488. New York: Academic Press 1961.
—, and E. Essner: Cytolysosomes and mitochondrial degeneration. J. Cell Biol. 15, 140–146 (1962).
Palade, G. E.: A study of fixation for electron microscopy. J. exp. Med. 95, 285–298 (1952).
Rakhawy, M. T. E.: Succinic dehydrogenase in the mammalian tongue with special reference to gustatory epithelia. Acta anat. (Basel) 48, 122–136 (1962a).
—: The histochemistry of the lymphatic tissue of the human tongue and its probable function in taste. Acta anat. (Basel) 51, 259–270 (1962b).
—: Alkaline phosphatases in the epithelium of the human tongue and a possible mechanism of taste. Acta anat. (Basel) 55, 323–342 (1963).
—, and G. H. Bourne: Cholinesterase in the human tongue in histochemistry of cholinesterase. Symposium Basel, vol. 2, p. 243–255. Basel and New York: S. Karger 1960.
Revel, J. P.: A stain for the ultrastructural localization of acid mucopolysaccharides. J. Micr. 3, 535–544 (1964).
Reynolds, E. S.: The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J. Cell Biol. 17, 208–212 (1963).
Sabatini, D., K. Bensch, and R. Barrnett: Cytochemistry and electron microscopy. J. Cell Biol. 17, 19–58 (1963).
Scalzi, H. A.: The cytoarchitecture and cytochemistry of gustatory receptors in the rabbit foliate papillae. Anat. Rec. 154, 486 (1966) (Abstract).
Schwalbe, G.: Das Epithel der Vallatae. Vorläufige Mitteilung. Arch. mikr. Anat. 3, 504–509 (1867).
Slifer, E. H.: The fine structure of insect sense organs. Int. Rev. Cytol. 11, 125–159 (1961).
Steinhardt Jr., R. G., A. D. Calvin, and E. A. Dodd: Taste structure correlation with d-mannose and b-d-mannose. Science 135, 367–368 (1962).
Szollosi, D.: Extrusion of nucleoli from pronuclei of the rat. J. Cell Biol. 25, 545–562 (1965).
Trujillo-Cenoz, O.: Electron microscope study of the rabbit gustatory bud. Z. Zellforsch. 26, 272–280 (1957).
Wachstein, M., and E. Meisel: The histochemical distribution of 5-nucleotidase and unspecific alkaline phosphatase in the tactile of various species and in two human seminomas. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2, 137–148 (1954).
—: Histochemistry of hepatic phosphatase at a physiologic pH with special reference to the demonstration of bile canaliculi. Amer. J. clin. Path. 27, 13–23 (1957).
Watson, M. L.: The use of carbon films to support tissue sections for electron microscopy. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 1, 183–184 (1955).
—: Staining of tissue sections for electron microscopy with heavy metals. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 4, 475–478 (1958).
Yamada, E.: The fine structure of the gall bladder epithelium of the mouse. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 1, 445–458 (1955).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported in part by In House Independent Research Grant No. 6.11.30.01, 3A013001A91C; by National Defense Education Act Group IV Fellowship, awarded to the author; and in part by Grant No. GM-0877, awarded to Dr. Everett Anderson, University of Massachusetts, by the National Institutes of Health. I am grateful to Drs. Everett AnderSon, James N. Dumont, Gunter F. Bahr, and Joe L. GRiffin for their expert guidance and support in the preparation of this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Scalzi, H.A. The cytoarchitecture of gustatory receptors from the rabbit foliate papillae. Zeitschrift für Zellforschung 80, 413–435 (1967). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00339331
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00339331